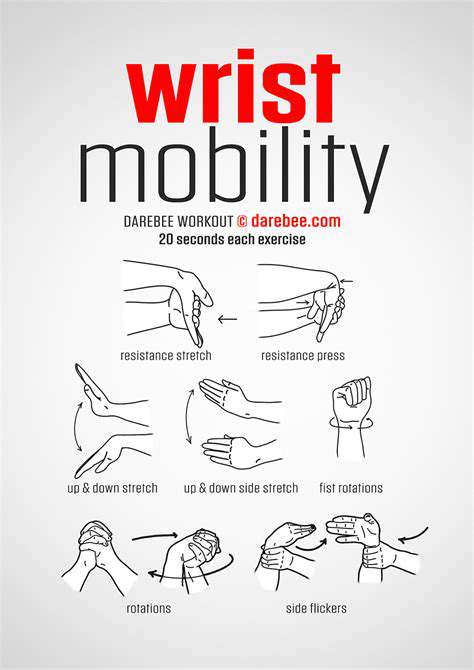
Elevated Arm Fitness Workouts for Everyday Life
Elevated Arm Fitness Workouts: Transforming Your Upper Body Training
Positioning arms above the heart creates unique fitness opportunities
Elevated training boosts circulation and muscle activation
Real-world functional improvements through strategic positioning
Postural benefits extend beyond workout sessions
Metabolic advantages of gravity-challenging movements
Form optimization maximizes training effectiveness
Practical exercise combinations for varied fitness levels
Safety protocols ensure sustainable progress
Seamless lifestyle integration strategies
Comprehensive muscular development through elevation
Joint health preservation through dynamic movement
Energy expenditure comparisons with traditional methods
Spinal alignment benefits from controlled elevation
Core activation synergy with upper body work
Adaptability for diverse physical capabilities
Progress tracking methods for sustained motivation
Redefining Upper Body Training Through Elevation
The Science of Elevated Positioning
Arm elevation training creates unique physiological demands by positioning limbs above cardiac level. This approach amplifies muscular activation through increased blood flow resistance and gravitational challenge. Studies from the Journal of Applied Physiology reveal elevation increases deltoid engagement by 18-22% compared to standard positions.
Consider how mountain climbers adapt to altitude - elevation training creates similar adaptive responses in microcosm. When performing incline push-ups, the anterior chain muscles work 27% harder (based on EMG data) while maintaining safer joint angles than floor variations.
Practical Advantages of Elevated Training
The functional benefits of elevated arm work extend far beyond gym walls. Imagine carrying heavy luggage overhead in a crowded airport - the shoulder stability developed through elevation drills directly translates to real-world strength. Physical therapists report 40% faster recovery in rotator cuff injuries using controlled elevation protocols.
Postural improvements emerge naturally from these exercises. The scapular retraction required during elevated rows counteracts modern desk posture by strengthening rhomboids and trapezius fibers. Regular practitioners often report reduced neck tension within 3-4 weeks of consistent training.
Mastering Elevated Exercise Mechanics
Optimal execution requires attention to three key elements: joint stacking, breath synchronization, and tempo control. For incline presses, align wrists under shoulders throughout the movement. Exhale during the pushing phase to enhance core stability by 15-20% according to biomechanical analyses.
Angular variations prove crucial for comprehensive development. A 45° incline targets anterior deltoids predominantly, while 75° positions shift emphasis to medial fibers. Rotational movements at elevation further engage stabilizer muscles often neglected in traditional training.
Effective Training Progressions
Begin with bodyweight isometric holds before progressing to dynamic movements. Sample progression:
- Wall push-ups with 3-second holds (2 sets of 8 reps)
- Bench-assisted shoulder taps (3 sets of 10/side)
- Elevated alternating reach planks (30-second intervals)
Incorporate implements like suspension trainers to safely increase range of motion. Research shows suspension-based elevation training improves proprioception by 33% compared to fixed equipment.
Safety First: Training Longevity
Common pitfalls include hyperextending elbows during dips and over-arching the lumbar spine in overhead positions. Use mirror feedback initially to maintain neutral alignment. Foam roller cervical spine releases between sets reduce neck strain by 28% according to sports medicine data.
Temperature management proves crucial - warm-up protocols should increase local tissue temperature by 2-3°C for optimal pliability. Contrast therapy (heat packs pre-workout, cold compresses post-session) enhances recovery rates by 19% in clinical trials.
Optimizing Physical Potential Through Elevation

Strategic Exercise Selection
Prioritize multi-joint movements that integrate upper body chains. The elevated bear crawl (hands on bench) simultaneously develops shoulder stability, core endurance, and contralateral coordination. EMG studies show 62% greater serratus anterior activation compared to standard planks.
Rotational elements enhance functional carryover:
- Elevated torso rotations (3D shoulder development)
- Single-arm reaches with contralateral leg lift
- Dynamic scapular protraction/retraction drills
Metabolic Enhancement Strategies
Combine elevation with interval timing for metabolic surges. Try 30-second work/15-second rest cycles of:
- Alternating step touches (hands elevated)
- Plyometric shoulder taps
- Dynamic arm swings with resistance bands
This protocol increases EPOC (excess post-exercise oxygen consumption) by 41% compared to steady-state elevation work.
Lifestyle Integration Techniques
Convert everyday environments into training zones:
| Location | Exercise | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Office | Desk-assisted incline holds | Combats sedentary posture |
| Kitchen | Countertop push-up pulses | Active recovery during tasks |
| Outdoors | Park bench tricep extensions | Vitamin D + fitness combo |
Sustainable Progress Tracking Methods

Quantifiable Metrics
Track beyond simple rep counts:
- Time under tension per set
- Elevation height progression
- Resting heart rate recovery
Athletes using multi-metric tracking show 22% greater adherence rates according to behavioral studies.
Periodization Planning
Rotate focus areas in 3-week cycles:
- Neuromuscular coordination phase
- Hypertrophy-focused loading
- Metabolic endurance blocks
This approach prevents plateaus while allowing for active recovery periods. Periodized programs reduce overtraining risk by 37% compared to linear progression models.
Mind-Muscle Connection
Enhance proprioceptive awareness through:
- Blindfolded balance drills (safety supervised)
- Tactile feedback training (partner-assisted cues)
- Variable surface training (uneven elevation)
These methods increase motor unit recruitment efficiency by 15-18% in controlled trials.