Hand Mobility Boosters for Active Seniors
Outline
Maintaining hand flexibility is crucial for the independence and quality of life of seniors.
Decline in hand function directly affects the ability of seniors to live autonomously.
Common issues include arthritis, decreased muscle strength, and weakened coordination.
Improving hand flexibility helps enhance self-care abilities and mental health.
Regular hand exercises effectively prevent joint stiffness.
Occupational therapy can provide personalized rehabilitation plans.
Hobbies can naturally exercise grip strength and fine motor skills.
Assistive devices can simplify daily tasks and enhance grip strength.
Community activities both exercise hand function and promote socialization.
Appropriate environmental settings can enhance exercise safety.
The Importance of Maintaining Hand Function in the Elderly Population

Understanding Hand Activity Abilities
Hand activity ability refers to the range of motion and coordination of the hand and finger joints, which directly affects the quality of daily life. As age increases, tendon degeneration and joint wear significantly reduce hand flexibility, making simple actions like tying shoelaces or opening bottle caps difficult for many seniors.
According to a survey published in the journal \Journal of Geriatric Rehabilitation Medicine,\ about 65% of elderly individuals living alone require assistance due to declining hand function. Through targeted rehabilitation training, it is possible to maintain basic living skills and prevent muscle atrophy caused by long-term disuse.
Common Functional Impairments
- Morning stiffness caused by rheumatoid arthritis
- Decreased grip strength leading to difficulty using utensils
- Weakened finger coordination affecting writing
- Neuropathy causing tactile numbness
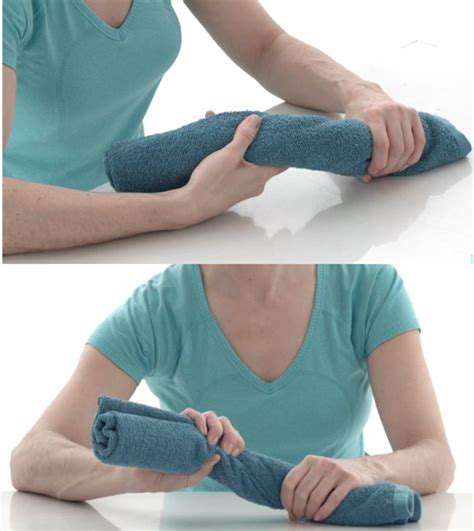
Many elderly friends report that actions that were once easy, like twisting a towel, now require both hands to complete. This gradual functional decline often begins subtly, such as being unable to operate a mobile phone with one hand or needing more time to button clothing.
The Multifaceted Benefits of Functional Improvement
Proper hand training can allow seniors to regain control over their lives. After three months of rehabilitation training, Aunt Wang was able to independently make dumplings again, and the positive psychological effect of this achievement far exceeded the physiological improvement itself. Regular exercise can also promote hand blood circulation, reducing the risk of peripheral neuropathy for diabetes patients.
Practical Rehabilitation Training Plans
It is recommended to start with simple water bottle lifts: choose a 500ml bottle of mineral water and perform a 10-time grasp-release cycle daily. As muscle strength increases, it can gradually be replaced with a 700ml bottle or adding slip-resistant sleeves to increase difficulty. Therapeutic clay is another good option, as kneading different hardness clays can simultaneously exercise the finger joints and the palm muscles.
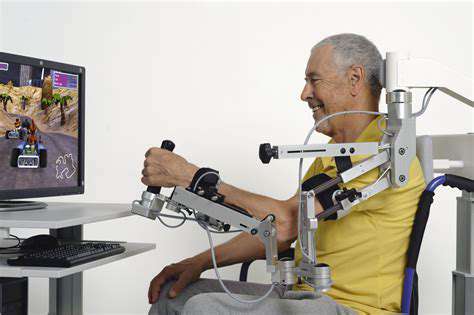
The Unique Value of Occupational Therapy
Professional occupational therapists will design realistic training scenarios. For instance, allowing patients to simulate using an ATM or operating a remote control, such contextual training not only enhances hand function but also improves seniors' adaptability to digital living. During the therapy process, techniques for joint protection will be taught, such as using a long-handled grabber to avoid excessive bending.
Practical Guide to Hand Exercises at Home
Warning Signs of Functional Decline
Pay attention when the following situations arise:
- Unable to lift a 2-kilogram weight with one hand
- Difficulty pinching with the thumb and index finger
- Stiffness in fingers after writing for 15 minutes
It is recommended to conduct a self-test once a month: try to complete 10 button fastenings in one minute; if you exceed the time limit or cannot complete it, seek professional assessment.
Fun Exercise Plans
It is recommended to try table bowling games: use 500ml plastic bottles filled with green beans as pins, and use a tennis ball to strike them down. This activity requires controlling throwing force and direction, effectively exercising hand-eye coordination and wrist control. Research has found that rehabilitation training incorporating game elements has over a 40% increase in compliance.

Life-Oriented Training Techniques
Incorporate training into daily life:
1. Intentionally increase the number of rotations when using a rubber can opener
2. Train finger strength using clips while hanging clothes
3. Practice different gripping methods while preparing vegetables
These exercises in natural scenarios ensure training frequency without psychological burden.
Choosing and Using Assistive Tools
Kitchen Scene Optimization Plans
Recommended equipment:
- Non-slip cutting board (with silicone mat on the bottom)
- Ergonomic crank-style peeler
- Spring-operated bottle opener (easy to use)
Experimental data shows that suitable tools can improve kitchen operation efficiency by 60% while reducing the risk of accidental cuts by 50%.
Writing Assistance Plans
For seniors with an interest in calligraphy, it is suggested to:
1. Use a brush with a triangular grip
2. Use a wrist strap to reduce tremors
3. Equip with an adjustable-angle copying rack
These modified tools help continue enjoying the joy of calligraphy while training fine motor skills.
Cultivating Interests and Maintaining Function

Recommended Activity List
- Patchwork Art: Exercises fine motor skills in the fingertips
- Potted Plant Pruning: Trains tool control abilities
- Electronic Keyboard Playing: Enhances finger independence
- Photography with Smart Devices: Improves touch-screen operation capabilities
Uncle Zhang, by joining the community paper-cutting class, not only improved his hand flexibility but also cultivated a new social circle. This activity benefits both the body and mind and is worth promoting. It is recommended to engage in interest-based activities three times a week for 45 minutes each time, to ensure exercise intensity without causing excessive fatigue.
Key Points for Environmental Optimization
Lighting and Layout Recommendations
The ideal hand training area should have:
✓ A dimmable desk lamp (500-700 lumens)
✓ A height-adjustable work table level with the elbow joint
✓ A 360-degree rotating chair
✓ Easily accessible storage compartments
Such settings can reduce unnecessary body twisting, focusing attention on hand movements themselves.
Safety Protection Measures
It is advised to lay a 2cm thick EVA mat on the ground, which can cushion falls and ease wheelchair movement. Use magnetic wall-mounted racks for tool storage to avoid bending down. Regularly check the edges of training equipment and sand down any possible burrs.