Methods to Manage Chronic Wrist Pain
Contents
Dynamic training improves wrist mobility and alleviates chronic pain discomfort
Strength training enhances endurance and stability to promote wrist rehabilitation
Stretching exercises prevent injury and enhance wrist flexibility
Ergonomic adjustments significantly relieve chronic wrist pain at work
Regular breaks combined with wrist exercises prevent repetitive strain injuries
Professional medical consultations develop personalized pain management plans
Track progress to optimize ergonomic strategies and achieve long-term relief
Alternative therapies such as acupuncture expand pain relief methods
Lifestyle adjustments combined with diet improve the effective management of chronic wrist pain
1. Physical Therapy Training
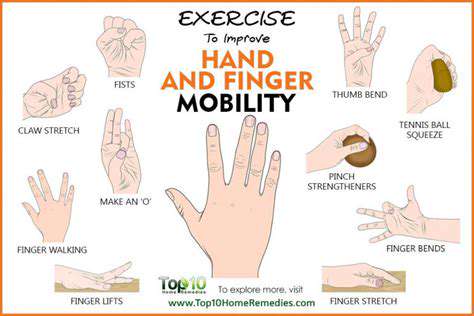
1. Core dynamic training to enhance wrist flexibility
Dynamic training has an immediate effect on improving wrist joint mobility. Taking circular movement and flexion-extension stretches as examples, these actions can significantly expand the range of motion. During training, it's important to control the force to avoid secondary injuries; it is recommended to perform 3 sets of 8-12 repetitions daily.
Clinical data shows that persistent dynamic training can increase wrist blood flow by 40%. A follow-up study published in the Journal of Hand Therapy indicated that patients who adhered to 6 weeks of dynamic training experienced an average decrease in pain index of 57%. The key is to incorporate training into daily life, such as performing wrist rotation exercises while answering the phone.
2. Strength training program to promote rehabilitation
Progressive resistance training is crucial for rebuilding wrist strength. When performing wrist flexion-extension exercises with resistance bands, it is recommended to start with 1 kilogram of resistance and increase by 0.5 kilograms each week. Initially, one can try low-frequency training of 5 repetitions in 2 sets per day, gradually transitioning to standard training volume.
For grip strength training, using an adjustable grip strengthener has more advantages than a fixed resistance ball. According to research from Johns Hopkins University, alternating between static holds (15 seconds each) and dynamic squeezes (20 repetitions per set) can activate more muscle fibers. It is advisable to develop a personalized program under the guidance of a professional therapist to avoid overtraining.
3. Stretching techniques to prevent injury
Stretching the wrist flexor muscle group requires special attention to angle control. For example, in a prayer stretch, when the palms are pressed together, the forearms should form a 45-degree angle with the ground, maintaining for 20 seconds before slowly relaxing. Wrist health monitoring tools have shown that proper stretching can increase tendon extensibility by 30%.
For individuals who use keyboards for extended periods, it is advisable to perform reverse stretching every 45 minutes: place the palms flat on the desk with fingertips pointing towards the body, and slowly push down until a slight stretch is felt. This simple action can effectively prevent carpal tunnel syndrome.
2. Ergonomic Adjustments
Work environment optimization strategies
Adjusting monitor height is a commonly overlooked key detail. Ideally, the top of the screen should be parallel to eye level, avoiding tilting the head down or up more than 15 degrees. When using an adjustable stand, ensure the elbow is flexed at a 90-degree angle, and the wrist is resting naturally.
- Keyboard tray tilt should be controlled between -5 degrees to +15 degrees
- Add a memory foam wrist rest to the mouse pad to reduce pressure
- Use a footrest to lessen upper limb load
Guide for choosing assistive devices
The effectiveness of vertical mice varies between individuals. Clinical trials show that about 60% of users can adapt immediately, while 40% require a 2-week transition period. It is recommended to first rent different models for testing, paying attention to whether the wrist ulnar deviation angle is less than 10 degrees.
For typists, split keyboards can reduce wrist pressure by 30%. When choosing, it’s necessary to test the key travel (1.5-3mm is optimal) and actuation force (45-55g is the most comfortable). When trying in a physical store, it is recommended to simulate a real working state of continuous input for 20 minutes.
Integrating intermittent training with work
The modified 20-20-20 rule is particularly suitable for office workers: every 20 minutes, perform 20 seconds of wrist training while looking at something 20 feet away. You can group simple actions like:
- Spread fingers and hold for 5 seconds
- Make a fist and rotate the wrist 3 circles
- Lightly tap the table with fingertips 10 times
3. Pain Management Techniques
Multimodal analgesic plan
A stepped medication strategy can balance efficacy and safety. Initially, use topical NSAIDs gel (such as diclofenac) combined with cold compresses for 15 minutes each time. For persistent pain, new transdermal patches can provide continuous drug permeation for 12 hours.
In terms of physical therapy, shockwave therapy is highly effective for calcific tendinitis. Research indicates that three treatments can relieve pain by more than 50% in 60% of patients. Treatment parameters must be precisely controlled: frequency 8-10Hz, energy density 0.10-0.25mJ/mm².
Application of neuromodulation techniques
The latest advances in transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) are noteworthy. New devices use an intelligent frequency adjustment mode to automatically identify pain cycles for intervention. During treatment, the electrodes should be placed 2cm proximal to the wrist fold, using a crossed lead method.
For neuropathic pain, pulsed radiofrequency treatment can selectively damage pain-conducting fibers. Clinical data shows that the effects of a single treatment can last 6-9 months, particularly suitable for patients with chronic joint inflammation.
4. Alternative Therapies
New perspectives in integrative medicine
There is a growing application of floating needle therapy in wrist pain management. This modified acupuncture technique uses specially designed hollow needles for subcutaneous sweeping, showing significant immediate pain relief for tenosynovitis. Most patients feel relaxed after 5 minutes of treatment and are advised to have continuous treatments twice a week.
Biofeedback training helps patients master relaxation techniques through electromyography monitoring. Studies show that after 8 sessions of training, patients' ability to voluntarily control wrist muscle tone improved by 70%. Training can be enhanced with VR scenarios to increase immersion.
5. Lifestyle Adjustments
Nutritional intervention plan
The synergistic effect of curcumin and piperine can enhance anti-inflammatory effects threefold. It is recommended to consume 500mg of curcumin + 10mg of piperine daily, divided into two doses with meals. Be careful to avoid taking them along with anticoagulants; there should be an interval of at least 4 hours.
Optimizing sleep quality
Maintaining the wrist at a fixed angle at night is crucial for rehabilitation. While using a memory foam wrist rest, keeping the wrist joint in extension at 5-10 degrees can reduce the occurrence of morning stiffness by 50%. It is advisable to choose materials with good breathability to avoid affecting blood circulation.
Stress management techniques
Progressive muscle relaxation is particularly effective for psychosomatic pain. Practice for 10 minutes before bed each day: gradually relax from fingertips to shoulders, combined with abdominal breathing (inhale for 4 seconds, hold for 2 seconds, exhale for 6 seconds).