Modern Strategies for Wrist Pain Relief
Exploring the Root Causes of Wrist Pain
Understanding the Mechanics of Wrist Pain
Wrist pain can stem from a multitude of issues, ranging from simple overuse injuries to more complex conditions. The wrist's intricate network of bones, ligaments, tendons, and muscles makes it particularly vulnerable to stress and strain. Proper posture and grip techniques are often overlooked but play a pivotal role in preventing discomfort. When these mechanics fail, pain can manifest in various ways, from sharp stabs to dull aches, each hinting at different underlying issues.
Diagnosing wrist pain requires careful attention to its location and character. Pain near the joint often points to bone or cartilage problems, while radiating discomfort suggests tendon or muscle involvement. A thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional remains essential for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment planning.
Identifying Common Causes of Wrist Pain
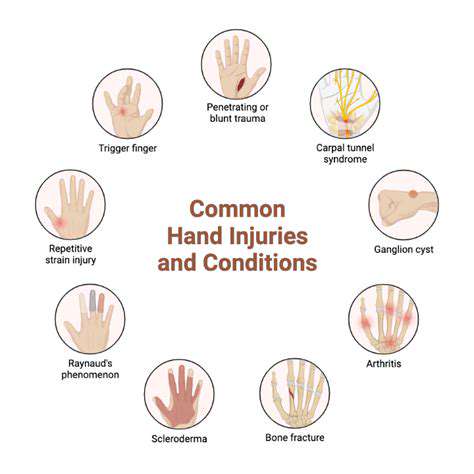
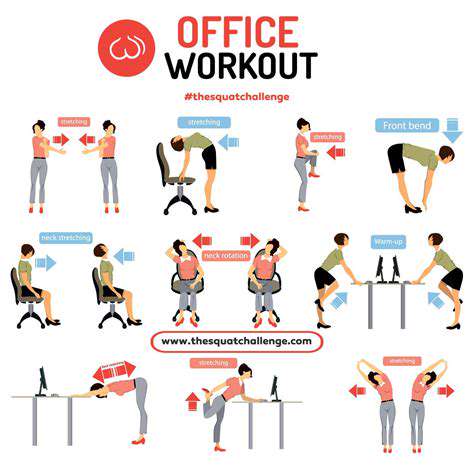
Repetitive strain injuries like carpal tunnel syndrome frequently plague those performing constant wrist movements. Office workers, musicians, and athletes often fall victim to these conditions. Poor ergonomics during computer use can transform simple tasks into painful ordeals over time. Beyond overuse, acute injuries like fractures from falls or sprains from sudden twists demand immediate attention.
Arthritis presents another challenge, gradually eroding joint function through persistent inflammation. Nerve compression issues can complicate matters further, sometimes requiring specialized intervention. Recognizing these varied causes helps tailor appropriate treatment strategies.
Lifestyle Modifications for Wrist Pain Relief
Simple adjustments often yield significant relief. Rest remains the cornerstone of recovery, allowing inflamed tissues to heal. Strategic use of ice reduces swelling, while heat soothes chronic muscle tension. Supportive braces provide stability during healing, particularly for those unable to completely avoid wrist use in daily activities.
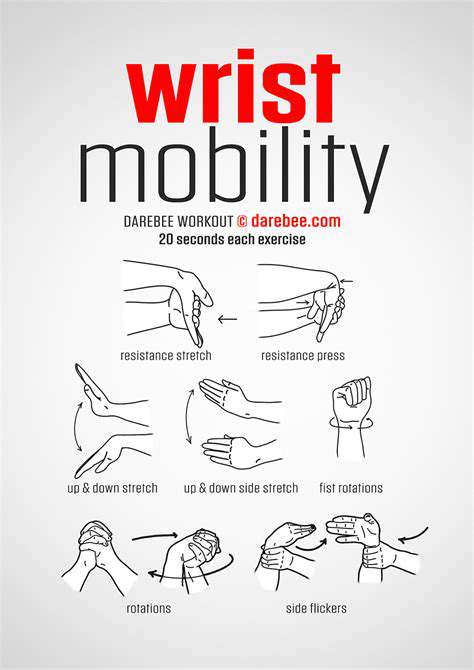
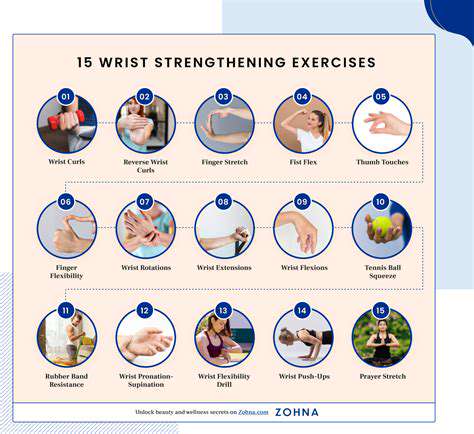
Weight management and targeted exercises offer long-term benefits. Gentle stretching maintains flexibility, while strengthening routines build joint resilience. Ergonomic assessments of workspaces can prevent recurring issues, making small changes that yield big results over time.
Advanced Treatment Options for Persistent Wrist Pain
When conservative measures fail, physical therapy often serves as the next step. Therapists design customized programs to restore function through progressive exercises. Corticosteroid injections provide temporary relief for stubborn inflammation, though their use requires careful consideration. In severe cases, surgical options may become necessary to repair structural damage or relieve nerve compression.
Occupational therapy bridges the gap between medical treatment and daily function. Specialists analyze work habits and recommend modifications to prevent reinjury. This holistic approach addresses both the physical and environmental factors contributing to persistent wrist issues.
Non-Surgical Interventions for Wrist Pain Relief
Conservative Treatments for Wrist Pain
Conservative approaches successfully manage most wrist pain cases without surgery. Therapeutic exercises gradually rebuild strength while improving flexibility. Manual therapies like specialized massage techniques address soft tissue restrictions that contribute to discomfort. Properly fitted braces offer crucial support during healing phases, particularly for those with repetitive strain injuries.
Medication management requires balance - anti-inflammatories reduce swelling but carry potential side effects with prolonged use. Many patients find combining these methods creates synergistic benefits, accelerating recovery while minimizing reliance on any single approach.
Lifestyle Modifications and Ergonomic Adjustments
Simple habit changes often produce dramatic improvements. Maintaining healthy body weight reduces joint stress, while regular activity preserves mobility. Workstation ergonomics deserve particular attention - monitor height, keyboard position, and chair adjustments collectively influence wrist strain. Even household tools can be modified to reduce stress during daily tasks.
Activity modification proves equally important. Alternating tasks, taking frequent breaks, and varying hand positions prevent overuse. These practical adjustments often mean the difference between chronic pain and comfortable function.
Injections and Other Medical Interventions
Corticosteroid injections serve as powerful anti-inflammatory tools for acute flare-ups. Their targeted action provides localized relief when other methods fall short. Emerging treatments like PRP therapy harness the body's healing potential, though research continues to define their optimal use. These advanced options complement rather than replace foundational treatments.
Stress management techniques often surprise patients with their effectiveness. Since tension exacerbates pain perception, relaxation methods can indirectly improve physical symptoms while enhancing overall wellbeing.
Complementary Therapies for Wrist Pain
Alternative approaches like acupuncture offer additional relief avenues for some patients. The precise needle placement may stimulate natural pain relief mechanisms. Therapeutic massage improves circulation while reducing muscle tightness that contributes to wrist strain. Yoga's combination of stretching and mindful movement often helps restore comfortable range of motion.
These modalities work best when integrated into comprehensive treatment plans. Their holistic focus addresses both physical symptoms and the personal experience of pain, creating more complete healing opportunities.
Lifestyle Modifications for Long-Term Wrist Pain Management

Prioritizing Physical Activity
Regular movement forms the foundation of joint health. Consistent, moderate activity maintains circulation and flexibility better than intermittent intense workouts. The key lies in finding sustainable routines that fit individual lifestyles and limitations. Water exercises often provide excellent low-impact options for those with significant wrist concerns.
Activity modifications allow continued participation despite limitations. Gripping aids, adapted equipment, and alternative techniques keep people engaged in favorite pastimes. Small daily efforts compound into significant long-term benefits for joint preservation.
Maintaining a Balanced Diet
Nutrition plays a subtle but important role in joint health. Anti-inflammatory foods like fatty fish and leafy greens may help manage chronic discomfort. Adequate protein supports tissue repair, while proper hydration maintains joint lubrication. Some find reducing processed foods decreases overall inflammation levels.
Targeted supplementation sometimes helps, though professional guidance ensures safety and appropriateness. The dietary approach should complement other treatments rather than replace them.
Stress Management Techniques
The mind-body connection significantly influences pain perception. Mindfulness practices help break the cycle of tension that exacerbates physical discomfort. Simple breathing exercises can be performed anywhere, providing immediate relaxation during flare-ups.
Creative outlets offer therapeutic benefits beyond simple distraction. Engaging activities that don't strain the wrists provide meaningful alternatives during recovery periods.
Adequate Sleep and Hydration
Healing accelerates during quality sleep, making proper rest non-negotiable for recovery. Sleep position adjustments often benefit those with nighttime wrist discomfort. Hydration supports all bodily functions, including joint lubrication and nutrient delivery to injured tissues.
These fundamental aspects of health sometimes receive inadequate attention despite their proven benefits. Small improvements in sleep hygiene and water intake frequently yield noticeable improvements.
Social Connections and Support Systems
Chronic pain often leads to isolation, which ironically worsens symptoms. Maintaining social engagement provides emotional resilience that aids physical recovery. Support groups connect people facing similar challenges, fostering practical solution-sharing.
Adaptive social activities ensure continued participation despite physical limitations. The psychological benefits of connection often translate into tangible physical improvements.
When to Seek Professional Medical Attention

When to Worry About Pain
Persistent discomfort that disrupts sleep or daily function warrants professional evaluation. Sudden severe pain, especially following trauma, requires immediate assessment to rule out fractures. Progressive worsening despite home care suggests the need for more targeted intervention.
Associated symptoms like numbness or weakness indicate potential nerve involvement. Timely consultation prevents minor issues from becoming chronic problems.
Fever and Chills
Systemic symptoms accompanying wrist pain suggest possible infection. Joint infections demand prompt treatment to prevent permanent damage. Unexplained fever with localized tenderness should never be ignored.
Unexplained Weight Loss or Gain
Metabolic changes sometimes manifest in joint symptoms. Significant weight fluctuation without lifestyle changes may indicate underlying systemic issues. Endocrine disorders frequently present with both weight changes and musculoskeletal complaints.
Changes in Vision or Hearing
While seemingly unrelated, these symptoms sometimes accompany systemic conditions affecting joints. Autoimmune disorders can present with both joint pain and sensory changes. Comprehensive evaluation helps identify potential connections.
Persistent Fatigue and Weakness
When tiredness accompanies joint pain, broader health assessments become necessary. Chronic fatigue may indicate nutritional deficiencies or inflammatory conditions. Proper diagnosis guides appropriate treatment strategies beyond simple pain management.