How to Use Ergonomic Tools to Protect Your Hands
Introduction to Ergonomic Hand Protection

Ergonomics in Hand Care
Ergonomic hand protection goes beyond simply wearing gloves. It involves a comprehensive approach to minimizing risks and maximizing comfort and efficiency during tasks that demand hand use. Understanding the specific demands of the job is crucial for selecting the right tools and techniques. This includes factors like repetitive motions, force application, and environmental conditions.
Careful consideration of hand posture and wrist position is paramount to preventing strain and injury. Proper posture can significantly reduce the risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome and other repetitive strain injuries. Ergonomic hand care isn't just about safety; it also improves overall performance and reduces discomfort.
Types of Ergonomic Hand Protection
A variety of tools and equipment can aid in protecting and supporting the hands. These include specialized gloves designed for specific tasks, such as those made from materials that provide enhanced grip or protection against chemicals. The selection of the appropriate hand protection depends heavily on the nature of the work being performed.
Other ergonomic tools include ergonomic hand tools, which are designed with a comfortable grip and reduced force requirements. These tools can be instrumental in minimizing the strain on the hands and wrists.
Benefits of Ergonomic Hand Protection
Implementing ergonomic hand protection strategies yields numerous benefits. Reduced risk of injury is arguably the most significant advantage, protecting workers from conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome, tendonitis, and other repetitive strain injuries. These injuries can lead to significant pain, lost productivity, and even long-term disability.
Beyond the physical benefits, ergonomic hand protection can also contribute to a more comfortable and efficient work environment. Improved employee well-being is a direct result of these strategies, contributing to a more positive and productive work atmosphere.
Choosing the Right Ergonomic Hand Protection
The process of selecting the best ergonomic hand protection requires careful consideration of several factors. The type of work being performed is a primary consideration, as different tasks demand different levels of protection and support. Environmental factors, such as temperature and humidity, also play a crucial role.
Proper fit is critical for effective protection and comfort. Gloves that are too tight or too loose can hinder performance and increase the risk of injury. Consulting with occupational health and safety professionals can provide valuable insights and guidance in selecting the appropriate solutions.
Implementing Ergonomic Practices for Maximum Hand Protection
Understanding Hand Anatomy and Function
Understanding the intricate structure of the hand, including the delicate bones, tendons, ligaments, and muscles, is crucial for implementing ergonomic practices. This knowledge allows us to appreciate the complex interplay of forces and movements involved in various tasks. Recognizing the specific roles of different hand components, such as the fingers, palm, and wrist, helps in identifying potential strain points and designing tasks that minimize the risk of injury.
Proper hand function relies on a coordinated effort between these components. Understanding how these parts work together allows for the development of ergonomic solutions that support natural hand movements and reduce repetitive stress.
Proper Tool Selection and Design
Choosing the right tools for the job is paramount in hand protection. Tools should be ergonomically designed to fit the hand comfortably and reduce stress on joints and muscles. Consider the size, shape, weight, and texture of the tool when selecting it. Features like non-slip grips and cushioned handles can significantly impact user comfort and reduce the risk of slips and injuries.
Tools with adjustable features allow for customized fit, minimizing strain on the hand during prolonged use. This not only enhances comfort but also promotes efficiency and productivity by allowing for a more controlled and precise grip.
Posture and Body Mechanics
Maintaining good posture and using appropriate body mechanics during tasks involving hand usage is essential for preventing hand injuries. A straight back, aligned shoulders, and a neutral wrist position can significantly reduce strain on the hand and forearm. Proper body alignment distributes weight evenly, reducing the risk of muscle fatigue and injury.
Workstation Design and Layout
A well-designed workstation plays a vital role in promoting hand health. Ensuring adequate workspace layout and sufficient space for comfortable hand movements is crucial. Positioning tools and materials within easy reach prevents unnecessary reaching and twisting, minimizing stress on the hand and wrist.
Adjusting the height of the workstation, chair, and equipment to accommodate the user's height is essential for promoting proper posture and reducing strain. Adequate lighting and a comfortable temperature also contribute to a supportive work environment.
Frequency and Duration of Tasks
Recognizing the importance of task frequency and duration is key to preventing hand injuries. Prolonged exposure to repetitive motions or forceful exertions can lead to cumulative trauma. Strategies for task rotation, taking regular breaks, and varying activities can help alleviate strain and prevent overuse injuries. Introducing periods of rest and recovery allows the hand to recover and reduce the risk of fatigue-related injuries.
Hand Exercises and Stretches
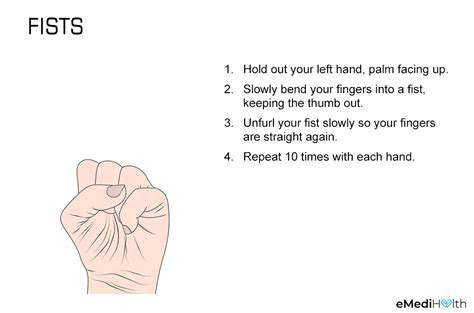
Regular hand exercises and stretches can help maintain flexibility, strength, and range of motion in the hand and wrist. Simple exercises such as finger stretches, wrist rotations, and hand gripping exercises can improve hand health and prevent stiffness. These exercises should be performed regularly, both during work breaks and at home, to maintain optimal hand function.
Training and Education
Providing comprehensive training and education to employees on ergonomic principles and hand protection practices is crucial for creating a proactive safety culture. Training sessions should cover proper tool usage, posture techniques, and the importance of recognizing early signs of hand discomfort. Encouraging open communication about hand pain or discomfort is essential for early intervention and preventing serious injuries.
Regular reminders and visual aids can reinforce these practices, ensuring that employees are consistently applying ergonomic principles throughout their workday. This proactive approach significantly reduces the risk of hand injuries and promotes a healthier work environment.