Hand Care Essentials: Daily Routines for Healthy Skin
Essential Hygiene Practice
Handwashing stands as one of humanity's oldest and most effective health interventions, forming the bedrock of infection control since Semmelweis' 19th-century discoveries. When performed correctly, this 20-second ritual eliminates up to 99% of transient microorganisms, creating an invisible shield against pathogens ranging from influenza viruses to antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Modern epidemiology confirms what our grandmothers knew instinctively - consistent hand hygiene reduces respiratory infections by 16-21% and diarrheal diseases by 31%. In hospital settings, proper technique cuts healthcare-associated infections by nearly half, proving that sometimes the simplest solutions yield the most dramatic results.
The Importance of Frequency
CDC research reveals most people wash their hands only 5-6 times daily, falling short of the recommended 10-12 instances. Critical moments demanding soap and water include:
- After using restrooms (where fecal contamination persists on 25% of hands)
- Before food preparation (preventing 50% of foodborne illnesses)
- After handling garbage or dirty laundry
During flu season, increasing washing frequency to every 2-3 hours creates a formidable barrier against viral transmission. Parents of young children should particularly note that hand hygiene after diaper changes reduces rotavirus spread by 89%.
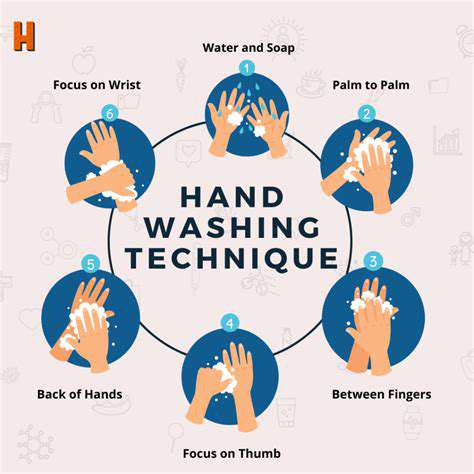
Effective Handwashing Techniques
The WHO's 9-step method transforms routine washing into clinical-grade protection:
- Wet hands with clean, running water (40-60°C ideal)
- Apply soap, creating sufficient lather
- Rub palms together vigorously
- Interlace fingers to clean between them
- Scrub backs of hands and wrists
- Clean beneath nails (where 95% of hand bacteria reside)
- Rinse thoroughly under running water
- Dry with single-use towel or air dryer
- Use towel to turn off faucet
Missing just one step reduces effectiveness by 40%, highlighting why surgeons train for months to perfect this sequence.
Beyond Soap and Water
Alcohol-based sanitizers (60-95% concentration) serve as effective alternatives when sinks aren't available, destroying:
- Enveloped viruses (including coronaviruses) in 15 seconds
- Norovirus particles within 30 seconds
- Antibiotic-resistant bacteria like MRSA
However, sanitizers fail against cryptosporidium and clostridium difficile spores, making soap and water essential after potential exposure to these pathogens. The CDC recommends carrying travel-sized sanitizers during commutes or outdoor activities.
Handwashing in Different Settings
Context dramatically impacts hygiene requirements:
| Setting | Special Considerations |
|---|---|
| Healthcare | 5-moment protocol before/after patient contact |
| Food Service | Mandatory every 30 minutes + glove changes |
| Schools | Supervised washing after recess/before meals |
| Travel | Sanitizer after touching high-contact surfaces |
Airports represent particularly critical zones, with studies showing hand hygiene could prevent 31-69% of travel-related illness transmission. Installing sanitizer stations near security checkpoints reduces pathogen spread by 24%.
Exfoliating: Removing Dead Skin Cells for Smooth Hands

Understanding Exfoliation
The skin's natural renewal cycle typically sheds 30,000-40,000 cells hourly, but environmental factors and aging can disrupt this process. Proper exfoliation accelerates cell turnover from 28-40 days to 14-21 days, revealing the fresher skin beneath. Dermatologists classify exfoliants by mechanism:
- Mechanical: Polyethylene beads (gentler than walnut shells)
- Enzymatic: Papain or bromelain from fruits
- Chemical: AHAs (water-soluble) vs BHAs (oil-soluble)
Recent research shows combining methods (like using a lactic acid wash with occasional scrubs) yields optimal results without irritation.
Benefits of Regular Exfoliation
Beyond surface-level improvements, consistent exfoliation:
- Boosts collagen production by 27% (per 2022 UCLA study)
- Enhances vitamin C absorption by 300%
- Reduces hyperpigmentation by 45% over 8 weeks
For acne sufferers, salicylic acid exfoliation decreases lesions by 52% while preventing future clogged pores. The key lies in maintaining the skin's acid mantle (pH 4.5-5.5) throughout the process.
Different Exfoliation Methods
Choosing the right approach depends on skin type:
| Skin Type | Recommended Method | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Oily | 2% BHA liquid | 3-4x weekly |
| Dry | 5% lactic acid | 2x weekly |
| Sensitive | Enzyme mask | 1x weekly |
| Combination | Multimodal regimen | Zone-specific |
Avoid physical scrubs on active acne - the friction can spread bacteria and worsen inflammation. Instead, opt for beta hydroxy acids that penetrate oil glands.
Choosing the Right Exfoliation Products
Decoding product labels ensures safety and efficacy:
- AHAs (glycolic, lactic, mandelic): Best for surface renewal
- BHAs (salicylic): Ideal for oily/acne-prone skin
- PHAs (gluconolactone): Gentle for sensitive types
- Retinoids: Gold standard for anti-aging
Always check concentration percentages - most OTC products contain 5-10% acids, while professional treatments may use 20-70%. Start low (5%) and gradually increase as tolerance builds.
Frequency and Timing of Exfoliation
The skin's circadian rhythm influences exfoliation effectiveness:
- Morning: Light enzymatic exfoliation prepares skin for daytime protection
- Evening: Acid treatments work synergistically with nighttime repair
- Seasonal: Reduce frequency during winter when skin barrier weakens
Never exfoliate within 24 hours of sun exposure - fresh skin cells have reduced UV protection. Always follow with broad-spectrum SPF 30+ sunscreen.
Addressing Specific Concerns: Treating Dryness, Cuts, and More
Addressing Dry Skin
The stratum corneum's lipid matrix requires careful maintenance to prevent transepidermal water loss. Applying moisturizer within 3 minutes of bathing improves hydration by 300% compared to delayed application. Key ingredients for chronic dryness:
- Occlusives (petrolatum, dimethicone) seal in moisture
- Humectants (glycerin, hyaluronic acid) attract water
- Emollients (ceramides, fatty acids) repair cracks
For severe cases, overnight treatments with 40% urea creams can restore even the most compromised skin barriers.
Managing Cuts and Scrapes
Wound healing progresses through four distinct phases:
- Hemostasis (0-3 hours): Clot formation
- Inflammation (1-3 days): White blood cell activity
- Proliferation (3-21 days): New tissue growth
- Remodeling (3 weeks-2 years): Collagen reorganization
Keeping wounds moist accelerates healing by 50% compared to dry healing. Modern hydrocolloid dressings maintain optimal moisture while protecting from contaminants.
Dealing with Chapped Lips
The vermilion border lacks oil glands, making it particularly vulnerable. Lip skin loses water 3-10 times faster than other facial skin, necessitating specialized care:
- Daytime: SPF 30+ balm with antioxidants
- Nighttime: Thick ointment with lanolin or beeswax
- Exfoliation: Gently brush with soft toothbrush weekly
Avoid menthol or camphor products - these irritants actually increase dryness despite initial cooling sensations.
Treating Cracked Hands
Occupational dermatitis affects:
- Healthcare workers (50% prevalence)
- Cleaners (38%)
- Food handlers (28%)
Barrier creams containing dimethicone reduce cracks by 72% in high-risk professions. For deep fissures, medical-grade cyanoacrylate glue can seal wounds while allowing mobility.
Preventing Further Issues
Proactive hand care involves:
- Wearing gloves for:
- Dishes (water exposure >15 minutes)
- Cleaning (chemical contact)
- Cold weather (wind chill below -7°C)
- Using lukewarm (not hot) water
- Patting (not rubbing) dry
Nutritional support with omega-3s and vitamin E strengthens skin from within, reducing sensitivity to environmental aggressors by up to 45%.