Best Practices for Maintaining Hand Flexibility
Finger Extension and Flexion Exercises
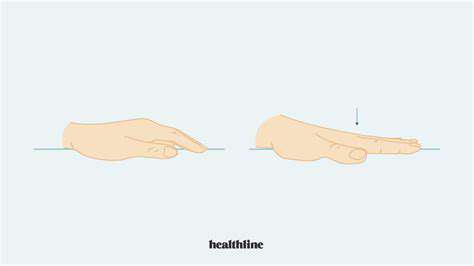
Balanced hand strength requires equal attention to extension (opening) and flexion (closing) movements. These complementary exercises prevent muscle imbalances that can lead to injury.
Use rubber bands around fingers for resistance when opening hands. For flexion, squeeze a soft ball or therapeutic putty. Gradually increase resistance as strength improves.
Hand and Finger Circles
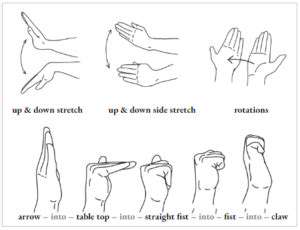
Circular motions lubricate joints and improve mobility. Make small, controlled circles with each finger joint, then progress to full hand rotations. This gentle movement enhances synovial fluid distribution, reducing stiffness.
Thumb Exercises for Enhanced Control
The opposable thumb's unique mobility requires special attention. Thumb circles, opposition touches (to each fingertip), and abduction/adduction movements maintain this crucial digit's full functionality.
Try the thumb walk exercise: place hand flat and slowly walk thumb across palm to little finger. This improves both mobility and fine motor control.
Using Resistance Bands for Added Challenge
Progressive resistance training builds hand strength safely. Bands allow adjustable tension for customized workouts. Start with light resistance, focusing on proper form before increasing difficulty.
Anchor bands to a fixed object for pulling exercises, or loop around fingers for extension training. Always maintain controlled movements to prevent strain.
The Role of Diet and Hydration in Hand Health

The Importance of Macronutrients
A balanced macronutrient profile supports tissue repair and energy production. Lean proteins rebuild muscle, complex carbohydrates fuel activity, and healthy fats reduce inflammation - all crucial for hand function. Omega-3 fatty acids particularly benefit joint health.
Prioritize whole food sources like fish, nuts, and whole grains over processed alternatives. These provide superior nutrient density without additives that may exacerbate inflammation.
Hydration's Impact on Cellular Function
Water comprises over 70% of muscle tissue and 80% of joint cartilage. Even mild dehydration impairs tendon elasticity and synovial fluid viscosity, directly affecting hand mobility. Carry a water bottle and sip consistently throughout the day.
Monitor hydration through urine color - pale yellow indicates proper hydration, while darker shades signal need for increased intake.
The Relationship Between Diet and Immunity
Nutrient-dense foods fortify the immune system against inflammatory conditions that can affect joints. Colorful fruits and vegetables provide antioxidants that combat oxidative stress in delicate hand tissues.
Vitamin C-rich foods support collagen production, essential for tendon and ligament integrity. Citrus fruits, bell peppers, and berries make excellent dietary choices.
Micronutrient Significance for Overall Health
Key micronutrients directly impact hand function. Magnesium relaxes muscles, zinc aids tissue repair, and vitamin D enhances calcium absorption for bone strength. A deficiency in any can manifest as hand stiffness or weakness.
Dark leafy greens, seeds, and fatty fish provide these essential micronutrients. Consider periodic blood testing to identify potential deficiencies.
The Role of Diet in Weight Management
Excess weight strains joints throughout the body, including hands. A balanced diet maintains healthy weight, reducing osteoarthritis risk. Portion control combined with nutrient density proves more effective than restrictive dieting.
Importance of Dietary Variety
Rotate protein sources, vegetable types, and whole grains to ensure comprehensive nutrient intake. Seasonal eating naturally provides diverse phytonutrients that support overall health, including hand function.
Dietary Considerations for Specific Needs
Individual requirements vary significantly. Office workers might prioritize anti-inflammatory foods, while manual laborers need extra protein for tissue repair. Consulting a nutrition professional ensures personalized recommendations for optimal hand health.