Finger Flexibility Drills for Enhanced Function
Introduction to Finger Flexibility Exercises
Understanding the Importance of Finger Flexibility
Finger flexibility plays a vital role in countless everyday actions, whether it's fastening buttons or mastering intricate musical passages. Keeping your fingers supple isn't just about convenience—it's about preventing pain and injury, particularly for those whose work or hobbies demand constant hand use. This aspect of hand health directly affects how effortlessly we can perform routine tasks and maintain our independence as we age.
The Mechanics Behind Finger Movement
Our fingers represent an engineering marvel—a network of bones, tendons, and ligaments working in perfect harmony. The smooth bending and straightening we take for granted depends entirely on this delicate balance. Recognizing how these components interact underscores why preserving mobility matters so much for preventing stiffness and maintaining function.
What Limits Finger Mobility?
Several factors can gradually reduce finger flexibility, from prolonged disuse to repetitive stress injuries, medical conditions, and natural aging processes. Trauma to tendons or ligaments often creates lasting movement restrictions, making complete finger extension or flexion challenging. Additionally, poor ergonomic habits and repeated motions can lead to muscular imbalances that further compromise flexibility.
Practical Exercises for Enhanced Flexibility
The good news? Numerous straightforward exercises can dramatically improve finger mobility. These techniques require minimal time and equipment, easily fitting into daily schedules. Gentle stretching and controlled motion exercises help maintain and rebuild finger flexibility. Dedicated, regular practice yields noticeable improvements in both finger dexterity and range of motion. Like any physical training, consistency proves more valuable than intensity.
Lifestyle's Role in Finger Health
Whole-body wellness significantly impacts finger flexibility. Balanced nutrition, proper hydration, and regular physical activity create the foundation for healthy, mobile fingers throughout life. Preventing repetitive strain through ergonomic adjustments and scheduled breaks protects long-term hand function. Activities that naturally engage hand movements—from gardening to crafts—provide enjoyable ways to maintain finger agility.
When to Seek Professional Help
Persistent finger stiffness or discomfort warrants medical consultation. Specialists can pinpoint underlying causes and create personalized treatment plans, which might include targeted exercises, therapy, or other interventions. Addressing flexibility issues early often prevents worsening conditions and facilitates complete functional recovery. Don't dismiss ongoing symptoms—timely professional guidance makes all the difference.
Simple Stretches for Improved Finger Mobility
Essential Warm-up Techniques
Never skip finger warm-ups before activities requiring fine motor control. Proper preparation reduces injury risk while enhancing performance. Begin with gentle individual finger bends, circular motions, and brief holds—these simple actions increase blood flow and prepare tissues for movement. The few minutes invested in warming up pay dividends in comfort and capability.
Another effective preparatory method involves gently stretching fingers in opposing directions. This technique particularly benefits tendons and ligaments, promoting freer movement. Making warm-ups a consistent habit represents one of the smartest investments in long-term hand health.
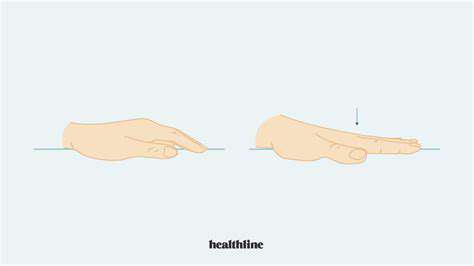
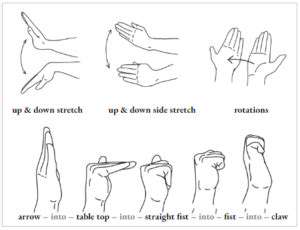
Extension Stretches for Full Mobility
Maintaining complete finger extension prevents stiffness and preserves range. Isolate each finger, straightening it fully while focusing on joint sensation. This proves especially valuable for typists, musicians, and anyone performing repetitive hand tasks.
For deeper stretching, apply gentle opposing pressure to each extended finger. This controlled resistance safely increases flexibility while improving precision—critical for activities requiring fine motor control.
Flexion Stretches for Balanced Mobility
Complement extension work with dedicated flexion stretches. Slowly bend each finger toward your palm, maintaining the position briefly while concentrating on joint sensations. This balanced approach ensures comprehensive mobility.
Group finger flexion provides additional benefits. Bend all fingers simultaneously, feeling the stretch through your hand and wrist. This coordinated movement enhances both flexibility and functional coordination.
Circular Motions for Joint Health
Rotational movements offer exceptional benefits for finger joints. Perform controlled circles with each finger—both clockwise and counterclockwise—to improve circulation and lubrication. Enhanced blood flow from these motions prevents stiffness and maintains joint health. Regular rotational exercises significantly contribute to lasting finger dexterity and comfort.
Expand the benefits by incorporating full hand rotations. Feel the movement through your wrist and fingers, creating comprehensive mobility benefits that support all hand functions.
Incorporating Finger Flexibility Drills into Your Routine
Effective Warm-up Strategies
Proper preparation transforms flexibility training from risky to rewarding. Design warm-ups that gradually increase circulation and joint mobility through progressive movements. Finger extensions, flexions, and wrist circles all serve as excellent starting points, preparing tissues for more intensive work.
Tailor warm-up duration (5-10 minutes typically) to your needs and any existing conditions. Never push through pain—adjust intensity or consult specialists if concerns arise about hand health.
Fundamental Stretching Techniques
Basic stretches form the foundation of finger flexibility. Individual finger extensions with brief holds, followed by gentle flexion stretches, create balanced mobility. The key lies in controlled, mindful execution—never forced movements.
Remember that flexibility develops gradually. Regular, moderate stretching outperforms occasional intense sessions. Patience and persistence yield the best long-term results.
Strength Training for Finger Support
Flexibility requires muscular support. Simple strength exercises like stress ball squeezes or resistance band work build the foundation for safe, sustainable mobility. These exercises simultaneously enhance fine motor control—valuable for both daily tasks and specialized activities.
Progress resistance gradually, allowing tissues to adapt without strain. Strength and flexibility represent complementary goals, each supporting the other.
Tool-Assisted Training Methods
Specialized equipment can enhance flexibility training. Finger exercisers provide targeted resistance, while weighted implements add progressive challenge to grip and pinch exercises. These tools help track progress through measurable resistance increases.
When selecting equipment, prioritize quality and appropriate resistance levels. Overly ambitious starting points often lead to frustration or injury.
The Principle of Progressive Challenge
Gradual difficulty increases drive continuous improvement. Whether extending hold durations, adding repetitions, or increasing resistance, small weekly progressions prevent plateaus while minimizing injury risk.
Document your progress—tracking metrics like hold times or resistance levels provides motivation and ensures appropriate progression pacing.
Recovery's Critical Role
Training represents only half the equation—proper recovery completes it. Schedule rest days between intensive sessions, and listen to your body's signals. Adequate sleep and nutrition support tissue repair and adaptation.
Remember that flexibility develops during recovery periods, not training sessions. Respect this biological reality for optimal, sustainable results.