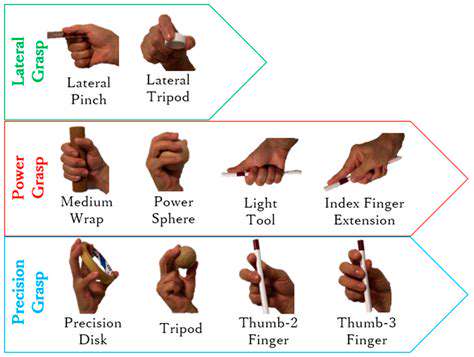
Pioneering Techniques in Finger Joint Rehabilitation
Utilizing Advanced Therapeutic Modalities
Minimally Invasive Techniques for Finger Joint Repair
Minimally invasive surgical techniques are revolutionizing the field of finger joint rehabilitation. These methods involve precise incisions, often considerably smaller than traditional approaches. This precision minimizes tissue trauma, leading to faster recovery times and reduced post-operative pain. The smaller incisions also result in less scarring, improving cosmetic outcomes. Minimally invasive procedures often utilize specialized instruments and advanced imaging technologies to ensure optimal visualization and control during the repair process. This approach allows for greater precision and accuracy, ultimately improving the long-term functional outcome for patients.
Specific examples of minimally invasive techniques include arthroscopic procedures. Arthroscopy allows surgeons to visualize and access the interior of the joint without extensive dissection. This approach offers significant advantages in terms of precision and reduced invasiveness, enabling repair of cartilage or ligament damage with minimal disruption to surrounding tissues. The smaller incisions also contribute to a quicker return to daily activities and improved patient satisfaction.
Utilizing Regenerative Medicine in Finger Joint Rehabilitation
Regenerative medicine holds immense promise for the treatment of finger joint injuries and degenerative conditions. This innovative approach focuses on stimulating the body's natural healing processes to repair damaged tissues. Researchers are exploring various methods, including stem cell therapies and growth factor injections, to promote the regeneration of cartilage, tendons, and ligaments. These advancements offer a potential solution for conditions like osteoarthritis and ligament tears, which often result in long-term disability if left untreated.
Stem cell therapy involves the transplantation of stem cells into the damaged area. These cells have the remarkable ability to differentiate into various cell types, potentially fostering the regeneration of damaged tissues. Growth factor injections, on the other hand, stimulate the body's own healing mechanisms by delivering proteins that accelerate tissue repair and regeneration. The ongoing research in this field is promising and may lead to significant advancements in the future management of finger joint injuries.
Another aspect of regenerative medicine is the development of bioengineered tissues. Scientists are working to create replacement tissues that can be implanted to restore lost or damaged structures. This approach may prove particularly valuable for severe cases where traditional methods are insufficient. While still in the research and development phase, bioengineered tissues hold the potential to revolutionize the field of finger joint rehabilitation.
The use of biomaterials in scaffolding structures for tissue regeneration is also gaining traction. These materials provide a framework for new tissue growth, potentially aiding in the repair of complex injuries. This innovative approach is demonstrating promise in laboratory settings and may soon translate into clinical applications.
The potential of these regenerative medicine approaches to promote natural healing and reduce the need for more invasive procedures is substantial. This holds the promise of improved functional outcomes and quality of life for patients.
The Role of Occupational Therapy and Ergonomic Considerations
Occupational Therapy's Multifaceted Approach
Occupational therapy plays a crucial role in pioneering techniques for enhancing daily living and work performance. Occupational therapists (OTs) employ a variety of assessment tools and interventions tailored to individual needs. This encompasses not only physical rehabilitation but also cognitive, psychosocial, and emotional well-being. By focusing on adapting tasks and environments, OTs empower individuals to regain independence and function effectively within their chosen roles, whether it be at work, home, or in the community. This personalized approach is vital to optimizing participation in meaningful activities.
A key aspect of occupational therapy's work is fostering client self-advocacy and promoting long-term well-being. Through education and skill-building, OTs equip individuals with the knowledge and resources necessary to make informed decisions about their health and well-being, leading to improved quality of life. Their expertise spans across diverse populations, offering specialized interventions for various conditions and challenges, ensuring that individuals can achieve optimal performance and participation.
Ergonomic Considerations in the Workplace
Ergonomic principles are paramount in creating a safe and productive work environment. Implementing ergonomic considerations not only minimizes the risk of workplace injuries but also enhances overall employee well-being. This involves analyzing tasks, tools, and the work environment to identify potential hazards and implement solutions that promote proper posture, body mechanics, and efficient movements. By proactively addressing ergonomic concerns, organizations can prevent musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs), reduce absenteeism, and boost employee morale.
Ergonomic assessments often involve evaluating workstation setups, including chair adjustments, monitor placement, keyboard and mouse positioning, and the proper use of specialized equipment. These assessments help determine if adjustments are needed to optimize comfort and reduce strain. The goal is to create an environment where employees can perform their tasks efficiently and comfortably throughout the workday, minimizing the risk of long-term health problems.
Integrating Occupational Therapy and Ergonomics for Enhanced Productivity
Combining the expertise of occupational therapists and ergonomic principles results in a powerful approach for enhancing productivity and well-being. Occupational therapists can assess individual needs, identify specific ergonomic challenges, and design personalized interventions that address both the physical and cognitive aspects of work performance. This collaborative approach ensures that interventions are not just about fixing a problem but about creating a supportive and efficient environment, where employees can thrive.
By understanding the specific demands of a task and the individual capabilities of the worker, occupational therapists can recommend ergonomic solutions that are tailored to each situation. This includes designing customized workstation setups, recommending assistive technologies, and providing training on proper body mechanics. This integration promotes a proactive approach to preventing injuries and maximizing employee potential, leading to improved overall performance and a healthier work environment.
This combined strategy can significantly reduce workplace injuries and improve employee satisfaction. Through proactive measures, organizations can foster a culture of health and well-being, leading to greater productivity and a more positive work experience.
By focusing on the individual needs of each worker, occupational therapists can help businesses create a workplace where employees can perform their duties efficiently and comfortably, minimizing risks and maximizing their potential.
The integration of these two disciplines creates a synergistic approach, empowering individuals to perform their jobs effectively while protecting their long-term health and well-being.
This multifaceted approach to improving work performance, ultimately, fosters a more productive and fulfilling workplace for everyone.
Surgical Advancements and Post-Operative Rehabilitation Protocols
Minimally Invasive Techniques
Recent advancements in surgical techniques, particularly in laparoscopic and robotic surgery, have revolutionized the field. These minimally invasive procedures offer several advantages over traditional open surgery, including smaller incisions, reduced blood loss, less postoperative pain, and a faster recovery time. Minimally invasive techniques, such as keyhole surgery, utilize specialized instruments and cameras to perform complex procedures with precision, leading to improved patient outcomes and a higher quality of life post-operation. This approach significantly reduces the risk of complications associated with large incisions, promoting faster healing and faster return to daily activities.
The precision and control afforded by robotic surgery further enhance the benefits of minimally invasive procedures. Surgeons can operate with enhanced dexterity and visualization, leading to greater accuracy and precision in complex surgeries. This technology allows for greater control, particularly in delicate procedures, minimizing tissue trauma and promoting a more rapid recovery for the patient.
Enhanced Imaging and Diagnostics
The development of advanced imaging technologies, such as high-resolution CT scans, MRI, and ultrasound, provides surgeons with detailed anatomical information before and during surgical procedures. This detailed visualization allows for precise surgical planning, enabling surgeons to identify potential complications and guide instruments with accuracy, thereby minimizing the risk of injury to surrounding tissues. Pre-operative imaging plays a crucial role in diagnosis and treatment planning, improving the overall safety and success of surgical interventions.
The use of intraoperative imaging, such as fluorescence imaging and intraoperative ultrasound, further refines the surgical process. These technologies allow surgeons to visualize tissues and anatomical structures in real time, enabling precise identification and manipulation of targeted areas during the operation. This real-time feedback enhances surgical precision, minimizing the risk of complications and optimizing surgical outcomes.
Advanced Surgical Materials
The development of advanced biomaterials has significantly improved surgical outcomes. These materials, engineered with specific properties like biocompatibility and biodegradability, are designed to promote tissue healing and integration. This results in stronger and more durable surgical repairs, with reduced risk of complications such as infection or rejection. Using advanced biomaterials allows for more intricate and precise surgical repairs, leading to better long-term results.
Personalized Treatment Strategies
A crucial aspect of modern surgical practice is the implementation of personalized treatment strategies. These strategies consider individual patient factors, such as genetic predispositions, lifestyle choices, and medical history, to tailor surgical interventions and post-operative care. This approach ensures that patients receive the most appropriate and effective treatment, leading to improved outcomes and a reduced risk of complications.
Post-Operative Pain Management
Advanced pain management techniques are integral to post-operative rehabilitation. These techniques encompass a range of strategies, including multimodal analgesia, regional anesthesia, and targeted pain medications. Effective pain management significantly improves patient comfort and allows for a more rapid recovery, enabling early mobilization and physical therapy. Minimizing pain post-surgery encourages patients to participate actively in their rehabilitation process.
Rehabilitation Protocols and Physical Therapy
Comprehensive rehabilitation protocols, often incorporating physical therapy and other therapies, are essential for optimal post-operative recovery. These protocols are tailored to the specific surgical procedure and the individual patient's needs, focusing on restoring strength, mobility, and function. Early mobilization and targeted exercises are critical in preventing complications, promoting healing, and enabling a smooth transition back to daily activities. A well-structured rehabilitation plan is an integral part of the overall surgical process, maximizing patient outcomes and ensuring a successful recovery journey.