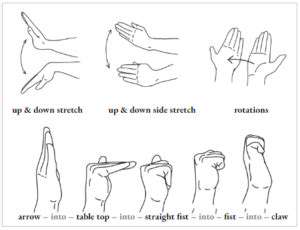
Enhancing Hand Function Through Occupational Therapy
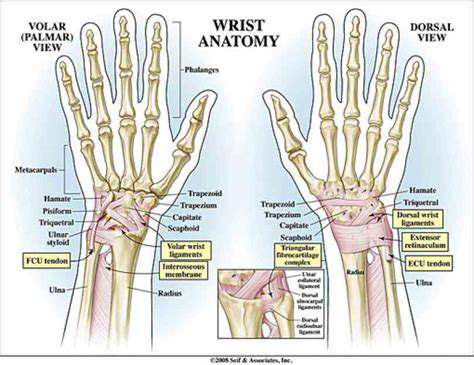
From paper cuts to complex trauma, hand injuries demand specialized care. The hand's intricate architecture - with 27 bones, numerous joints, and delicate tendons - requires precisely targeted therapies. Early intervention proves critical, as stiffness develops rapidly in immobilized hands.
Modern protocols emphasize early controlled motion when possible, countering traditional complete immobilization approaches. This paradigm shift reflects growing understanding of tissue healing mechanics and the dangers of prolonged disuse.
Pharmacological Treatments
While medications play a supporting role, judicious pain management enables participation in crucial therapy sessions. Emerging topical NSAID formulations target inflammation without systemic side effects. Some clinics now use compounded creams blending multiple agents to address pain, spasticity, and circulation simultaneously.
Medication-assisted therapy must balance symptom relief with preserving protective pain signals that prevent overuse during healing. Regular medication reviews prevent long-term dependency while ensuring adequate comfort for rehabilitation participation.
Physical Therapy
Contemporary hand therapy blends traditional exercises with innovative approaches. Biofeedback systems transform abstract movements into visual games, while vibration therapy enhances proprioceptive retraining. Some clinics employ instrumented objects that provide real-time performance data during functional tasks.
Therapy now extends beyond clinic walls through prescribed community activities - from pottery classes to gardening - that provide meaningful practice contexts. This functional approach improves carryover to daily life compared to rote exercise repetition.
Surgical Interventions
Microsurgical advances now allow reattachment of severed digits with remarkable functional recovery. Arthroscopic techniques minimize scarring while permitting earlier mobilization. Nerve regeneration research shows promise for previously untreatable conditions.
Post-surgical protocols have evolved from rigid immobilization to early protected motion in many cases. This shift reflects understanding that controlled movement promotes healing while preventing debilitating stiffness.
Splinting and Immobilization
Modern splinting materials allow unprecedented customization. Thermoplastic designs mold perfectly to individual anatomy, while innovative strapping systems permit adjustable support levels. Some smart splints now incorporate sensors to monitor wear time and movement patterns.
Night splinting protocols help manage conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome without disrupting daytime function. Dynamic splints provide gentle stretching forces to combat contractures while allowing functional use.
Occupational Therapy
Today's occupational therapists employ simulated workstations and virtual reality systems to practice job tasks in controlled environments. They collaborate with industrial designers to modify tools and workspaces for individual needs.
Task analysis has grown more sophisticated, breaking down activities into component motions to identify precisely where adaptations are needed. This granular approach yields highly targeted solutions.
Complementary and Alternative Therapies
Evidence is growing for modalities like laser therapy to reduce inflammation or mirror therapy for phantom pain management. While these shouldn't replace conventional treatments, they may provide valuable adjuncts for certain patients.
Mind-body approaches like meditation help patients cope with chronic pain while reducing stress-related muscle tension. Some clinics offer acupuncture in conjunction with traditional therapy for enhanced pain relief.
Empowering Clients Through Education and Training
Understanding Hand Function
The human hand's capabilities range from delicate watch repair to powerful rock climbing. This versatility stems from an evolutionary marvel of opposing thumbs, sensitive nerve endings, and precisely coordinated muscle groups. Rehabilitation must honor this complexity while addressing specific impairments.
Modern education tools include interactive 3D anatomy apps that let patients explore their own injury sites. Understanding the why behind therapy exercises improves compliance and outcomes.
The Importance of Client Education
Knowledge transforms patients from passive recipients to active participants. When people understand their healing timeline and the purpose behind each exercise, they become invested partners in recovery. Visual aids showing tissue healing stages help manage expectations.
Education now extends to family members through designated training sessions. This creates supportive home environments where caregivers provide appropriate assistance without fostering dependency.
Personalized Training Programs
The most effective programs weave therapy into patients' existing routines. A gardener's regimen might include trowel exercises, while an artist practices brush techniques. This contextual approach yields better engagement and functional results.
Training progresses through carefully sequenced challenges, ensuring success experiences while gradually rebuilding capacity. Periodic milestone tasks provide motivating evidence of improvement.
Hands-on Therapeutic Techniques
Skilled manual therapy can break adhesions, improve joint mobility, and retrain movement patterns. Therapeutic touch also provides psychological reassurance, reinforcing the healing partnership. Some techniques borrow from massage therapy to improve circulation and reduce protective muscle guarding.
Manual resistance exercises allow precise grading of challenge levels. Therapists' experienced hands detect subtle improvements or regressions that machines might miss.
Advanced Technology and Equipment
Cutting-edge tools like force-sensing gloves provide objective performance data, while electromyography biofeedback helps patients reestablish proper muscle firing patterns. Virtual reality systems create engaging rehabilitation environments adaptable to various ability levels.
Home exercise monitoring apps now use smartphone cameras to provide form feedback, while wearable sensors track compliance between visits. This technology bridges the gap between clinic and daily life.
Long-Term Support and Maintenance
Effective rehabilitation plants seeds for lifelong hand health. Patients learn to recognize early warning signs of overuse or recurring problems, enabling prompt self-management. Many clinics offer alumni check-ins and refresher workshops.
Maintenance programs emphasize sustainable habits rather than temporary fixes. Patients graduate with customized prevention strategies tailored to their lifestyles and risk factors.