Routines to Sustain Finger Dexterity
Crafting and Fine Motor Skills: A Powerful Combination
Importance of Fine Motor Skills Development
Fine motor skills involve the delicate movements of small muscles in the hands and fingers, which are vital for countless everyday actions. Whether it's fastening buttons or jotting down thoughts, these abilities form the foundation of self-sufficiency and engagement in daily life. Early development of these skills can set the stage for future achievements in education and careers, while also nurturing a child's sense of pride and self-assurance.
Beyond practical applications, these skills play a pivotal role in cognitive growth. The complex motions needed for fine motor tasks activate brain functions and sharpen hand-eye coordination - both critical elements for effective learning and creative problem-solving.
Crafting Activities and Hand-Eye Coordination
Creative pursuits like sketching, watercolor painting, clay modeling, and sculpture work offer exceptional avenues for refining fine motor capabilities. These endeavors demand exact hand positioning and train young minds to pay attention to minute details, simultaneously developing spatial awareness and hand-eye synchronization.
When children handle art tools and materials during creative projects, they naturally build strength in their hand muscles, gaining better command over their movements. This enhanced control allows for more sophisticated and deliberate actions, taking coordination skills to higher levels.
The Role of Finger Dexterity in Daily Life
Finger agility significantly influences routine activities, affecting how effortlessly children can complete everyday tasks. Actions like using cutlery or fastening shoes may appear simple, but they actually require remarkable precision and timing. Well-developed finger dexterity transforms these chores from frustrating challenges into manageable, even enjoyable, activities.
This improved nimbleness also translates to better classroom performance. Writing assignments, art projects, and handling small objects become less taxing and more accurate, boosting children's enthusiasm for learning and their belief in their own abilities.
Crafting as a Sensory and Cognitive Stimulator
Artistic activities provide rich sensory experiences for young learners. The varied textures of different mediums, the visual stimulation of colors and patterns, and the sounds created while working all combine to create a multi-dimensional learning environment. This sensory immersion helps maintain focus and encourages deeper involvement with the creative process.
Crafting also serves as excellent cognitive exercise. As children experiment with materials, design projects, and make artistic decisions, they're constantly solving problems. This mental workout strengthens analytical abilities while nurturing original thinking and imaginative capacity.
Routines for Sustaining Finger Dexterity
Maintaining regular creative sessions can dramatically improve and preserve finger agility. Consistent practice strengthens hand muscles and refines movement precision. Over time, this disciplined approach solidifies learned skills and allows for continuous advancement.
Setting aside specific times each week for creative projects establishes helpful patterns and emphasizes the value of motor skill development. This structured approach often yields visible progress in coordination, spatial understanding, and overall manual dexterity.
The Connection Between Crafting and Emotional Well-being
Creative activities can positively influence children's emotional health. Completing an art project generates feelings of achievement that elevate self-worth and confidence. This sense of accomplishment plays a crucial role in developing positive self-perception and encouraging ongoing participation in creative endeavors.
The focused attention required during crafting can also serve as effective stress management. This meditative quality helps children develop healthy coping strategies. The artistic process itself can be healing, supporting emotional balance and providing avenues for personal expression.
Technology Integration: Digital Tools for Dexterity Enhancement
Leveraging Augmented Reality for Enhanced Dexterity Training
Augmented reality applications present innovative methods for improving manual skills. By superimposing digital elements onto physical environments, AR creates interactive training scenarios for precision-based activities. Medical education provides excellent examples, where virtual surgical simulations allow trainees to hone their techniques risk-free before working with actual patients. These digital rehearsals offer instant performance analysis and unlimited repetition opportunities.
AR technology also proves valuable for visualizing complex assembly processes or manufacturing procedures. Detailed digital overlays can emphasize crucial movements and spatial configurations, helping users perfect their techniques with remarkable efficiency.
Interactive Software for Motor Skill Refinement
Specialized computer programs deliver focused exercises for developing manual precision. These applications typically combine visual guides, sound cues, and hands-on challenges to lead users through graduated skill-building activities. The software automatically adjusts difficulty levels based on user performance, ensuring appropriate challenge levels while maintaining motivation through achievable goals.
Performance metrics collected by these programs enable instructors to pinpoint specific areas needing improvement. This data-driven approach allows for customized training adjustments, optimizing skill acquisition.
Robotics and Dexterity: A Collaborative Approach
Incorporating robotic systems into skill training offers unique developmental opportunities. Robotic arms can provide calibrated resistance, letting users practice specific motions while receiving real-time feedback on accuracy and timing. This method proves particularly effective for repetitive tasks common in manufacturing or medical fields.
The interactive quality of robot-assisted training creates more dynamic learning experiences. Direct interaction with robotic systems provides immediate performance assessment, allowing users to refine their techniques through continuous adjustment. This cyclical process promotes deeper movement comprehension and more instinctive task execution.
Gamification: Engaging and Motivating Dexterity Practice
Applying game design elements to skill training can dramatically increase participant involvement and drive. By incorporating scoring systems, achievement rewards, and competitive rankings, users feel motivated to actively improve their abilities. This approach not only makes training more enjoyable but also fosters healthy competition and goal orientation.
Gamified platforms can deliver personalized learning experiences by adapting challenges to individual progress rates and preferences. This customized method ensures users face appropriate challenges while experiencing regular success milestones throughout their training.
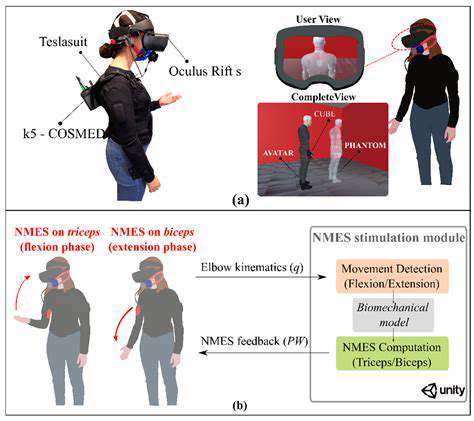
Virtual Reality Environments for Immersive Dexterity Training
VR technology creates deeply engaging practice environments for manual skill development. These simulated spaces allow users to rehearse tool handling, equipment operation, or medical procedures without real-world consequences. Such risk-free practice opportunities enable extensive repetition and experimentation.
The interactive nature of VR simulations provides valuable performance insights while enhancing understanding of spatial relationships and movement sequences. Additionally, VR scenarios can be precisely configured to match various difficulty levels and specific training requirements.