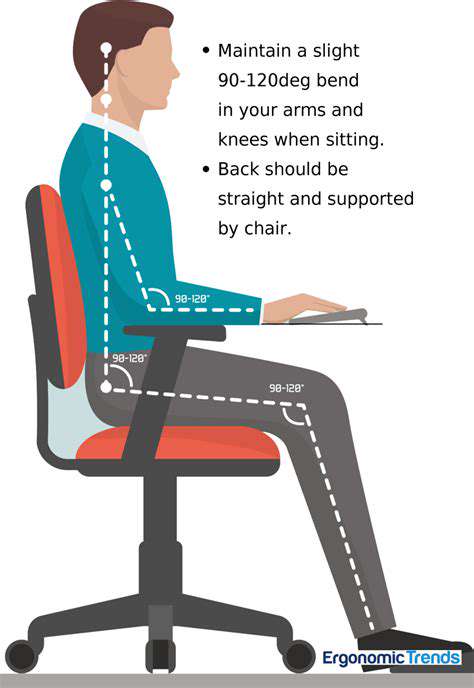
Innovative Methods for Reducing Hand Fatigue
Task Rotation Strategies
Job rotation isn't just about preventing monotony—it's a strategic tool for building institutional knowledge. When team members cycle through different roles, they develop connective tissue understanding of how departments interrelate. This cross-pollination often reveals process inefficiencies that specialists might overlook. A manufacturing case study showed rotating assembly line workers reduced error rates by 18% within three months.
The hidden benefit lies in creating a Swiss Army knife workforce. Employees with diversified skills become invaluable during staffing fluctuations or unexpected projects. Tech companies like GitHub attribute their rapid pivoting capability to mandatory quarterly role rotations. This approach also surfaces latent talents—many organizations discover star performers in unexpected areas through rotation programs.
Optimizing Workflows for Breaks and Rotation
Successful implementation requires more than policy changes—it demands workflow redesign. Forward-thinking companies are baking break triggers into project management tools, with apps like Focus@Will automatically scheduling micro-pauses based on cognitive load algorithms. For creative roles, some firms implement walking meetings that combine movement with collaborative thinking.
The magic happens when customization meets structure. A biotech startup reported 40% fewer overtime hours after introducing energy mapping—letting employees schedule intensive tasks around personal productivity peaks. Regular rotation retrospectives help teams refine the system, with many finding that 6-8 week rotations strike the ideal balance between depth and variety.
Promoting Employee Awareness and Education for Prevention Strategies
Understanding the Importance of Prevention
Prevention isn't about compliance—it's about cultivating organizational resilience. When employees develop safety vision—the ability to spot potential hazards before they manifest—companies see incident rates drop dramatically. This mindset shift transforms safety from a rulebook into a shared value that permeates daily decisions.
The most overlooked risks often stem from gradual changes. Ergonomic injuries frequently develop through millimeter adjustments to posture over months, while psychological safety erodes through unchecked microaggressions. Training should emphasize these subtle danger signs alongside obvious physical hazards.
Developing Targeted Training Programs
Generic safety lectures belong in the past. Cutting-edge programs use just-in-time learning—delivering bite-sized safety reminders via Slack bots when employees clock into specific work zones. Construction firms are having success with AR goggles that overlay hazard warnings directly onto job sites in real time.
The most effective trainings employ emotional inoculation. Simulations that induce controlled stress—like timed emergency drills—create stronger memory retention than passive videos. One oil rig company reduced response time by 47% after implementing VR simulations that included realistic distractions and consequences.
Implementing a Culture of Safety
True safety cultures measure what matters—not just accidents prevented, but near-misses reported. Companies leading in this space reward employees for identifying potential hazards, creating a good catch mentality. Some organizations have safety ambassadors from frontline staff who rotate monthly, bringing fresh perspectives.
The psychological component is critical. Teams that conduct pre-mortems—imagining how accidents could occur—identify 30% more prevention opportunities than those only analyzing past incidents. This forward-looking approach builds collective responsibility.
Utilizing Technology for Enhanced Education
AI is revolutionizing safety training through personalized learning paths. Adaptive platforms analyze individual knowledge gaps, serving customized content based on role, experience level, and past incident data. Some systems even adjust training frequency based on behavioral indicators like fatigue patterns from wearable devices.
Evaluating and Measuring Program Effectiveness
The most insightful metrics track leading indicators, not just lagging ones. Instead of waiting for accidents, measure participation in safety innovations, peer-to-peer coaching instances, and time spent discussing prevention in meetings. One automotive plant created a safety curiosity index tracking how often employees ask safety-related questions—a metric that predicted 89% of future incident reductions.
Continuous improvement comes from treating safety data as a living system. Machine learning models can now predict high-risk periods by correlating weather patterns, production schedules, and even local events that might impact employee focus. This predictive approach is transforming reactive safety programs into strategic advantage.