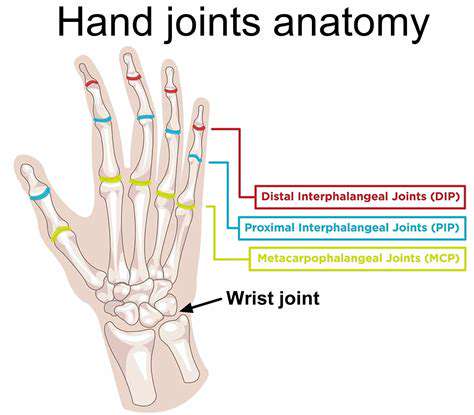
Protocols for Restoring Hand Joint Integrity
Non-Surgical Protocols for Restoring Hand Joint Integrity
Non-Surgical Approaches to Restorative Dentistry
Modern dentistry provides numerous conservative techniques for repairing compromised teeth while avoiding invasive surgical methods. These approaches have gained popularity due to their gentle nature, shorter recovery periods, and economic advantages. What makes them particularly valuable is their ability to resolve dental issues while preserving the patient's natural tooth structure and oral health. Successful implementation requires thorough examination and personalized treatment planning to match each patient's unique requirements.
Contemporary restorative materials like tooth-colored composites and ceramic inlays play a pivotal role in these treatments. These substances closely replicate natural dentition, delivering both visual appeal and practical functionality. The durability of these restorations heavily depends on evaluating the patient's dental care routine and daily habits during the treatment planning phase.
Managing Small-Scale Dental Damage
When dealing with minor decay or surface wear, direct fillings frequently serve as the optimal solution. These restorative techniques aim to rebuild both form and function of affected teeth. An experienced clinician will carefully prepare the tooth surface, eliminating all decayed material to establish a clean foundation. This meticulous preparation is fundamental for achieving proper adhesion and ensuring the restoration's longevity.
Composite bonding presents another minimally invasive option for correcting small fractures or surface irregularities. The technique involves sculpting a resin material directly onto the tooth surface, blending seamlessly with the natural anatomy. Typically completed in a single visit, this approach offers an efficient solution for minor cosmetic enhancements with immediate results.
Conservative Alternatives to Tooth Removal
For extensively damaged or missing teeth, full-coverage restorations and fixed bridges represent viable alternatives to extraction. Dental crowns serve as protective shells that encase compromised teeth, reinstating both durability and proper occlusion. Bridges fill gaps by anchoring artificial teeth to adjacent natural teeth. These solutions help maintain proper bite alignment and prevent subsequent dental complications.
Treatment planning requires careful evaluation as these procedures often involve multiple phases of preparation and fitting. However, they typically offer a more conservative pathway to restoring oral function and appearance compared to more radical surgical options.
While these treatments may involve some preparatory procedures, they generally avoid the need for extensive surgical intervention. Comprehensive evaluation and strategic planning remain critical for achieving optimal clinical outcomes.
Surgical Interventions for Severe Hand Joint Injuries
Surgical Management of Bone Fractures
Complex hand joint injuries often necessitate operative treatment when fractures are present. These fractures vary from simple linear breaks to complicated multi-fragment injuries that compromise hand function. Surgical correction focuses on anatomical realignment and stabilization, frequently utilizing specialized hardware like compression plates or intramedullary fixation. Surgical precision directly influences healing quality and eventual functional recovery.
Contemporary surgical trends favor minimally invasive approaches to decrease complication risks and accelerate rehabilitation. These methods utilize smaller access points, resulting in reduced postoperative discomfort, minimal scarring, and faster return to daily activities. Individualized treatment planning based on fracture characteristics and patient factors determines the most suitable surgical strategy.
Correcting Wrist Instability
Post-traumatic carpal instability can severely limit hand functionality, often requiring surgical stabilization. The procedure aims to restore proper carpal bone alignment through specialized reconstruction techniques. Surgeons may employ various fixation methods to repair damaged supporting structures. The primary objectives include preventing progressive deterioration and ensuring sustainable wrist function.
Comprehensive postoperative therapy significantly impacts recovery outcomes. Customized rehabilitation programs focusing on mobility restoration, strength building, and fine motor skills are essential for complete functional recovery. Treatment must be tailored to each patient's specific needs and recovery progress.
Reconstructing Soft Tissue Structures
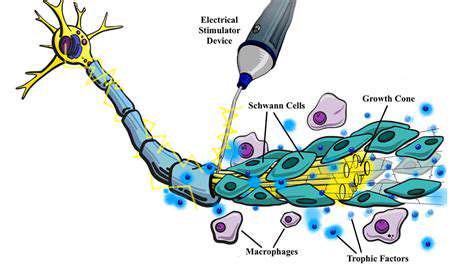
Significant hand trauma frequently involves injury to critical stabilizing soft tissues. Surgical restoration of these components is vital for proper joint mechanics and preventing chronic dysfunction. The surgical team evaluates the injury pattern to determine whether primary repair, grafting, or tendon transfer techniques would be most appropriate. The ultimate goal is to recreate normal hand biomechanics for optimal functional restoration.
Joint Stabilization Procedures
For joints with irreversible damage, arthrodesis may become the treatment of choice. This surgical technique creates a permanent bony union between joint surfaces to eliminate painful motion while maintaining stability. While sacrificing joint mobility, this procedure can provide reliable pain relief and functional improvement in carefully selected cases where other treatments have proven ineffective.