Techniques to Boost Hand and Finger Agility
Grip strength, often underestimated, plays a crucial role in everyday activities. From opening jars to writing, gripping objects securely is fundamental to many tasks. Understanding the mechanics of grip strength is important for recognizing its significance in overall hand function. This understanding also allows for the development of targeted strategies to improve or maintain grip strength.
It's a complex interplay of muscle activation, joint stability, and neural coordination. This intricate system allows for a wide range of gripping forces, adapting to different object shapes and sizes.
Factors Influencing Grip Strength
Several factors influence grip strength, including age, gender, and overall health. As we age, grip strength naturally tends to decline, often impacting our ability to perform daily tasks independently. This decline can be slowed or potentially reversed with regular exercise and a healthy lifestyle. Gender differences also exist, with men generally exhibiting greater grip strength than women, although this difference can vary significantly.
Underlying health conditions, such as arthritis or nerve damage, can also significantly impact grip strength, necessitating appropriate medical intervention to address the root cause.
The Impact of Grip Strength on Daily Activities
The ability to grip objects firmly is essential for countless daily activities. From turning doorknobs to holding utensils, grip strength enables us to perform tasks with ease and efficiency. Maintaining adequate grip strength is essential for maintaining independence and quality of life. Weakness in this area can significantly impact daily living, making simple tasks challenging and frustrating.
Grip Strength and Hand Injuries
Grip strength plays a crucial role in preventing hand injuries. Adequate grip strength helps to stabilize the hand and wrist during activities, reducing the risk of sprains, strains, and fractures. Improving grip strength can be a vital part of a comprehensive hand injury prevention strategy. This is particularly important for individuals who perform repetitive or forceful hand movements.
Assessment and Measurement of Grip Strength
Assessing grip strength is a critical part of evaluating hand function. Various tools and methods are used for accurate measurement, including dynamometers, which provide objective data about the force a person can exert. These assessments can help diagnose potential issues and guide rehabilitation strategies.
Training and Exercises for Grip Strength Improvement
Grip strength, like any other physical attribute, can be improved through targeted exercises. Simple tools, such as resistance bands and handgrips, can be used to progressively challenge the hand muscles. Regular exercise is key to maintaining and improving grip strength. Consistency is crucial for long-term gains. The approach should be tailored to the individual's needs and limitations.
The Connection Between Grip Strength and Overall Health
Grip strength is surprisingly linked to overall health. Studies have shown a correlation between lower grip strength and an increased risk of chronic diseases, including cardiovascular issues and type 2 diabetes. Maintaining good grip strength might be a valuable indicator of overall health. This connection highlights the importance of incorporating strategies to maintain and improve grip strength as part of a comprehensive health management plan.
Maintaining and Enhancing Your Hand and Finger Agility
Maintaining Your Han: A Comprehensive Guide
Maintaining a healthy and functional hand involves a multifaceted approach encompassing proper hygiene, injury prevention, and ongoing care. Regular handwashing is crucial for preventing the spread of germs and infections, particularly in communal settings. This simple act can significantly reduce your risk of contracting illnesses. It is important to use warm water and soap, scrubbing all surfaces of the hand for at least 20 seconds. Drying your hands thoroughly afterward is equally important, as damp hands are more prone to bacterial growth.
Beyond hygiene, preventative measures are essential for maintaining a healthy hand. Using appropriate hand protection when handling potentially hazardous materials, such as chemicals or sharp objects, is vital for avoiding injuries. Consistent use of gloves, protective creams, and proper lifting techniques can prevent many hand-related injuries. Early detection and treatment of any developing hand conditions are also key for maintaining optimal function. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional are recommended for proactive monitoring and addressing any concerns.
Enhancing Your Han's Functionality
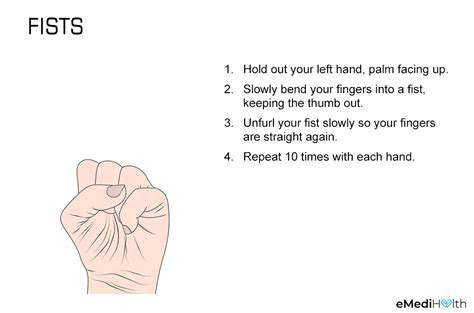
Enhancing your hand's functionality involves a combination of targeted exercises, mindful use, and ergonomic considerations. Simple exercises, such as finger stretches and hand rotations, can improve flexibility and range of motion. Regular engagement in these exercises can help maintain the strength and dexterity of your hands. Consistency in these exercises is key to seeing noticeable improvements. The use of ergonomic tools and techniques at work and at home can also significantly contribute to hand health and functionality.
Mindful use of your hands, including avoiding repetitive motions and maintaining proper posture while using them, is equally important. Understanding and addressing repetitive strain injuries (RSI) is critical for long-term hand health. Recognizing the signs of overuse and taking breaks when needed can prevent the development of chronic hand problems. Seeking professional guidance for ergonomic adjustments and hand-specific exercises can help optimize your hand's function and reduce the risk of injury.
Considering the specific demands of your work or hobbies is vital. If your daily activities involve repetitive movements, consider adapting your techniques or tools to reduce strain. This approach can significantly contribute to the long-term health and functionality of your hands. Regular maintenance and enhancements are essential for preserving the health and functionality of your hands throughout your life.
Proper nutrition and hydration also play a vital role in supporting hand health. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can promote healthy tissue growth and repair. Staying hydrated helps maintain the elasticity and moisture content of the skin, preventing dryness and cracking. This holistic approach to hand care can help maintain optimal functionality and prevent future problems.