Fresh Perspectives on Arm Injury Prevention
Selecting appropriate seating significantly impacts upper body comfort. Chairs with adjustable lumbar support and properly positioned armrests promote natural spinal alignment. Quality ergonomic seating represents a worthwhile investment in long-term musculoskeletal health, potentially preventing conditions like repetitive strain injuries.
Optimal chair adjustment ensures feet rest flat on the floor with knees forming right angles. Recline mechanisms allow periodic posture changes that reduce spinal compression. A properly fitted chair serves as the cornerstone of workplace comfort and injury prevention.
Keyboard and Mouse Placement: Positioning for Precision
Input device positioning profoundly affects wrist and forearm strain. Keyboards should maintain straight wrist alignment while allowing relaxed shoulder positioning. Maintaining this neutral posture helps prevent cumulative trauma disorders that develop over time.
Mice should remain within easy reach to minimize arm extension. Ergonomic mouse designs that accommodate natural hand positions can significantly reduce strain during prolonged use. Small adjustments to input device positioning often yield substantial comfort improvements.
Monitor Positioning: Eyes on the Prize, Arms Relaxed
Display placement directly influences overall posture and comfort. The monitor's top edge should align with eye level when sitting upright. Proper screen distance prevents neck strain while maintaining clear visibility without excessive leaning.
Dual monitor setups require careful arrangement to avoid constant head turning. Optimal screen positioning reduces strain on both visual and musculoskeletal systems. Adjustable monitor arms facilitate precise positioning for individual needs.
Wrist Supports: Gentle Guidance for a Healthy Wrist
Padded wrist rests help maintain neutral hand positions during typing sessions. These accessories particularly benefit users performing extended data entry or coding work. Properly positioned supports distribute pressure evenly across the wrist area.
Keyboard Alternatives: Exploring Different Options
Alternative input devices can alleviate strain for some users. Split keyboards allow more natural hand positioning, while vertical mice reduce pronation strain. Periodically switching input methods may help prevent overuse injuries. Touchscreen interfaces offer temporary alternatives to traditional input devices.
Regular Breaks and Movement: Preventing Cumulative Strain
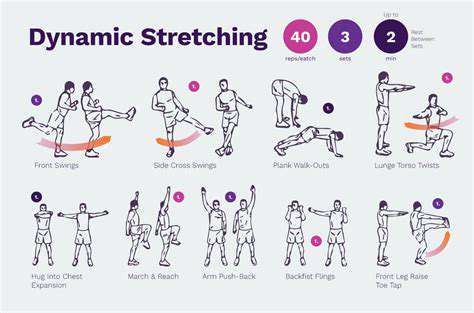
Frequent short breaks prove more effective than occasional long pauses. Stretching routines targeting arms, shoulders, and neck help maintain flexibility. Microbreaks every 30 minutes significantly reduce fatigue accumulation. Standing periodically improves circulation and changes musculoskeletal loading.
Workplace Assessments: A Proactive Approach to Prevention
Professional ergonomic evaluations identify potential problem areas before they cause injury. These assessments examine workstation layout, equipment choices, and work habits. Customized recommendations address individual physical characteristics and job requirements. Follow-up evaluations ensure continued effectiveness of ergonomic interventions.
Beyond the Workplace: Sports and Lifestyle Considerations
Enhancing Arm Health Through Sports
Athletic activities require careful attention to arm mechanics. Proper technique and conditioning help prevent sports-related injuries. Sport-specific protective gear and training regimens minimize repetitive stress on joints and soft tissues.
Different athletic disciplines impose unique demands on upper extremities. Racquet sports emphasize forearm strength, while swimming focuses on shoulder mobility. Sport-specific conditioning programs address the particular stresses of each activity.
Lifestyle Impacts on Arm Function
Daily activities significantly influence musculoskeletal health. Carrying heavy loads improperly can strain shoulders and elbows. Balanced nutrition supports tissue repair and maintenance following physical exertion.
Hydration maintains joint lubrication and muscle function. Conscious movement patterns during routine tasks prevent unnecessary strain. Regular physical activity promotes circulation and tissue resilience.
Ergonomics and Arm Health
Thoughtful equipment selection reduces strain during daily activities. Adjustable work surfaces accommodate different task requirements. Alternating between sitting and standing positions varies musculoskeletal loading. Task rotation prevents prolonged stress on specific muscle groups.
Nutrition for Arm Health
Dietary choices influence tissue integrity and recovery capacity. Protein supports muscle maintenance while omega-3 fatty acids help manage inflammation. Antioxidant-rich foods combat oxidative stress in active tissues. Proper electrolyte balance ensures optimal muscle function.
Rest and Recovery for Arm Well-being
Adequate sleep facilitates tissue repair and regeneration. Scheduled rest periods prevent overtraining in athletic contexts. Active recovery techniques maintain mobility without excessive strain. Listening to bodily signals helps prevent overuse injuries.
Professional Arm Care and Treatments
Persistent discomfort warrants professional evaluation. Physical therapists develop customized rehabilitation programs. Early intervention prevents minor issues from becoming chronic problems. Multidisciplinary approaches often yield the best outcomes for complex conditions.
Arm Health and Mental Well-being
Chronic pain can significantly impact quality of life. Stress management techniques help cope with injury recovery. Maintaining arm function supports independence and self-efficacy. Balanced activity participation promotes overall psychological health.
The Importance of Early Detection and Prompt Treatment
Early Detection: A Crucial First Step
Recognizing early warning signs enables timely intervention. Subtle changes in sensation or mobility often precede more serious issues. Prompt medical consultation improves treatment options and outcomes.
Early-stage conditions typically respond better to conservative treatments. Delaying evaluation risks progression to more complex problems. Regular self-examinations help detect changes requiring professional attention.
Understanding the Symptoms
Pain characteristics provide important diagnostic clues. Numbness or tingling may indicate nerve involvement. Swelling or discoloration suggests vascular or inflammatory processes. Documenting symptom patterns aids accurate diagnosis.
The Role of Professional Diagnosis
Comprehensive evaluations determine underlying causes precisely. Imaging studies visualize structural abnormalities when necessary. Specialized tests assess nerve conduction and muscle function. Accurate diagnosis guides appropriate treatment selection.
Prompt Treatment for Optimal Outcomes
Treatment plans should address both symptoms and root causes. Conservative measures often resolve acute issues effectively. Patient adherence significantly influences treatment success rates. Progress monitoring ensures appropriate adjustments when needed.
The Impact of Lifestyle Factors
Weight management reduces joint stress in upper extremities. Smoking cessation improves circulation to peripheral tissues. Regular physical activity maintains joint mobility and muscle strength. Proper lifting techniques prevent acute injuries.
The Importance of Follow-up Care
Continued monitoring detects recurrence or complications early. Treatment modifications address changing conditions or needs. Preventive strategies reduce future injury risks. Ongoing education empowers patients in self-management.
Long-Term Management Strategies
Maintenance exercises preserve gains from acute treatment. Activity modifications prevent symptom recurrence. Periodic professional evaluations ensure sustained progress. Comprehensive approaches address all aspects of arm health.