Techniques to Restore Hand Muscle Strength
Gradual and Progressive Exercises for Hand Strength
Warm-up Exercises
Before engaging in hand strengthening exercises, warming up the muscles is absolutely essential. Neglecting this step could lead to unnecessary strain or injury. Start with gentle motions like making soft fists, then slowly opening and closing your hands. Rotate your wrists clockwise and counterclockwise, and gently stretch each finger. These movements increase circulation, making the muscles more responsive to exercise. Performing these warm-ups consistently can dramatically reduce post-exercise soreness.
Adding light stretching targeting the hand and wrist tendons proves equally beneficial. Gently pull back on each finger for 15-30 seconds, being careful not to overextend. Pain signals your body's limits - never push through discomfort. Proper warm-ups create the foundation for safe, effective strength training.
Finger Extension Exercises
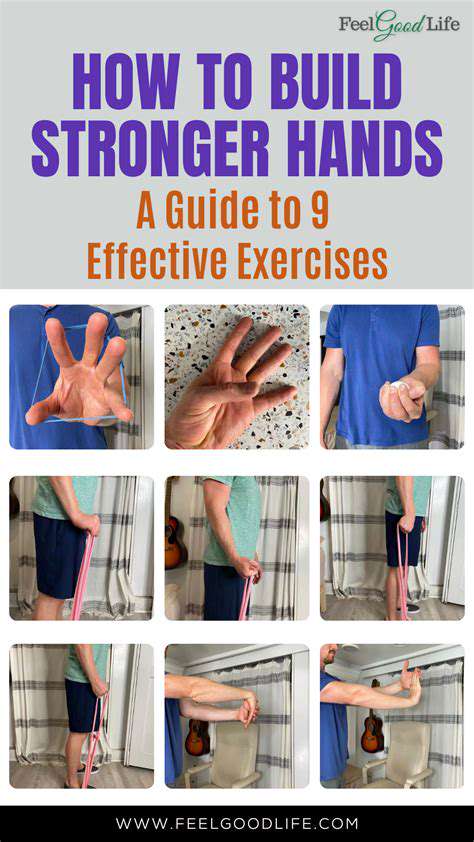
Building finger extensor strength requires targeted movements. Try holding a light resistance band between your fingers, then spreading them apart against the tension. Complete 10-15 repetitions, gradually increasing resistance as your strength improves. Alternatively, use your opposite hand to provide gentle resistance as you extend your fingers. This dual approach builds both strength and flexibility in the extensor muscles.
Finger Flexion Exercises
Developing finger flexion strength enhances overall hand functionality. Begin by making tight fists, holding for 3-5 seconds, then slowly releasing. Repeat this 10-15 times per session. For added resistance, use therapy putty or light hand weights while curling your fingers toward your palm. Varying your grip positions targets different muscle groups for comprehensive development. Consistent practice yields noticeable improvements in hand function and recovery.
Wrist Flexion and Extension Exercises
Wrist stability forms the foundation for hand strength. For flexion, position your forearm palm-down and gently bend your wrist downward, holding for 5 seconds. Reverse the motion for extension exercises, bending your wrist upward with palm facing up. Perform 10-15 repetitions of each movement. Adding light weights progressively challenges the muscles as your strength increases, but bodyweight alone provides excellent initial resistance.
Grip Strength Exercises
Developing grip strength impacts countless daily activities. Start by squeezing a soft stress ball for 30-second intervals, gradually progressing to firmer resistance as your strength improves. Resistance bands offer another effective option - grip and hold for increasing durations. The key lies in progressive challenge without overexertion. Regular practice significantly enhances your ability to perform tasks requiring strong, sustained grips.
Object Manipulation Exercises
Fine motor control develops through precise object handling. Practice transferring small items like buttons or coins between hands to improve dexterity. Using tweezers to pick up small objects challenges hand-eye coordination while strengthening delicate muscle groups. These exercises prove particularly valuable for regaining precision after injury, helping restore the intricate movements needed for daily tasks.
Progressive Overload and Rest
Effective strength development requires strategic progression. Gradually increase resistance, repetitions, or sets by about 10% weekly to continue challenging your muscles. Equally crucial is allowing 48 hours between intense sessions for proper recovery. Overtraining leads to diminished returns and potential injury. This balanced approach ensures steady progress while maintaining hand health.
Lifestyle Modifications to Support Hand Recovery

Prioritizing Physical Activity
Regular movement benefits overall health and specifically aids hand recovery. Strive for 150 weekly minutes of moderate activity like walking or swimming, which improves circulation to the extremities. Break this into manageable segments - even 10-minute walks accumulate benefits. Discover activities you genuinely enjoy, whether gardening, dancing, or recreational sports, as enjoyment boosts consistency.
Strength training twice weekly complements aerobic exercise beautifully. Full-body resistance work enhances bone density and metabolic function while supporting hand rehabilitation. Bodyweight exercises, resistance bands, or light weights all provide effective options. Focus on controlled movements and proper form to maximize benefits while minimizing injury risk.
Nourishing Your Body with a Balanced Diet
Optimal recovery requires proper nutritional support. Emphasize whole foods - colorful vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats provide essential nutrients for tissue repair. Omega-3 fatty acids from fish or flaxseeds particularly support joint health and reduce inflammation. Limit processed foods and excess sugars, which can impede recovery processes.
Regular, balanced meals maintain stable energy levels throughout the day. Including protein with each meal helps preserve muscle mass during recovery. Stay well-hydrated, as water comprises a significant portion of joint cartilage and supports nutrient transport to healing tissues.
Managing Stress and Prioritizing Mental Well-being
Chronic stress negatively impacts physical recovery through elevated cortisol levels. Develop personalized stress-reduction techniques like deep breathing exercises or progressive muscle relaxation. Just five minutes of mindful breathing daily can significantly lower stress hormones.
Prioritize seven to nine hours of quality sleep nightly, as most tissue repair occurs during deep sleep stages. Establishing a consistent sleep routine enhances both physical recovery and emotional resilience. For persistent stress or recovery challenges, consider consulting a therapist who can provide evidence-based coping strategies tailored to your situation.