Managing Chronic Wrist Pain: Expert Advice and Strategies
Rest and Physical Therapy
Giving your wrist adequate recovery time serves as the foundation for effective non-surgical treatment. Temporarily reducing activities that cause discomfort creates optimal conditions for natural healing. The body's innate repair mechanisms work most efficiently when not constantly challenged by repetitive stress. Patients often underestimate how minor daily movements can delay recovery when performed excessively.
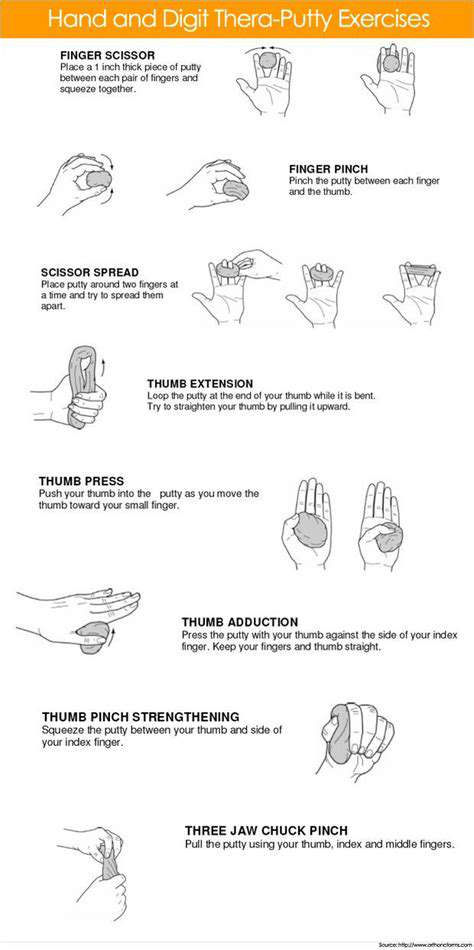
Targeted rehabilitation under professional guidance helps rebuild wrist functionality systematically. Certified therapists develop customized regimens incorporating progressive exercises that evolve with the patient's recovery. These programs typically combine mobility drills, controlled resistance training, and specialized techniques to address specific biomechanical imbalances contributing to wrist dysfunction.
Medications
Common anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen provide temporary relief for acute symptoms while the body heals. Patients should remain vigilant about medication duration and potential side effects, as prolonged use without medical supervision can create additional health complications. For persistent cases, physicians may recommend prescription-strength alternatives or specialized pharmaceutical interventions targeting specific pain pathways or inflammatory processes.
Lifestyle Modifications
Comprehensive lifestyle adjustments significantly influence treatment outcomes for chronic wrist conditions. Weight management reduces mechanical stress on joints, while balanced nutrition provides essential building blocks for tissue regeneration. Regular low-impact movement maintains joint lubrication and prevents stiffness, creating an internal environment conducive to healing.
Stress-reduction practices demonstrate measurable benefits for pain management by modulating the nervous system's response to discomfort. Eliminating tobacco use and moderating alcohol consumption removes additional inflammatory triggers that could otherwise hinder the recovery process.
Thermal Modalities
Strategic application of temperature therapies offers simple yet effective symptom management. Warm compresses enhance circulation to deliver nutrients and oxygen to affected tissues, while cold applications help control acute inflammation episodes. Many patients find alternating between heat and cold provides optimal symptomatic relief for different stages of recovery.
Supportive Devices
Properly fitted orthotic devices serve multiple therapeutic purposes - they immobilize injured structures during healing while promoting proper alignment. Ill-fitting supports can paradoxically worsen symptoms by creating pressure points or restricting circulation, making professional fitting essential. Temporary use of adaptive tools helps patients maintain independence while protecting vulnerable wrist structures.
Nutritional Support
Emerging research suggests certain nutraceuticals may support joint tissue integrity when used appropriately. While evidence remains mixed for some supplements, compounds like omega-3 fatty acids demonstrate consistent anti-inflammatory properties. Patients should approach supplementation cautiously, recognizing these represent adjunct therapies rather than standalone solutions. A qualified nutrition professional can help identify potential nutrient deficiencies contributing to musculoskeletal issues.
Preventing Future Wrist Pain: Proactive Strategies
Understanding the Root Causes
Persistent wrist discomfort often stems from identifiable mechanical stressors rather than random occurrences. Systematic analysis of daily routines frequently reveals preventable contributors like sustained awkward postures or repetitive microtraumas. Modern work environments particularly challenge wrist health through prolonged computer use and smartphone interactions, creating new patterns of cumulative stress injuries.
The concept of use cycles proves valuable in prevention - alternating between different types of hand activities allows specific tissues recovery periods. For instance, alternating typing tasks with non-repetitive manual activities distributes mechanical loads more evenly across various musculoskeletal structures.
Implementing Preventative Measures
Effective prevention requires moving beyond temporary fixes to establish sustainable movement habits. Ergonomic optimization involves more than equipment - it requires conscious attention to body mechanics during all activities. Simple adjustments like maintaining neutral wrist alignment during tasks and taking microbreaks every 20-30 minutes can dramatically reduce cumulative stress.
Progressive strengthening programs build wrist resilience by gradually increasing load tolerance in all movement planes. Isometric exercises initially develop stability, followed by controlled dynamic movements that mimic real-world demands. This systematic approach allows tissues to adapt safely without overload.
Pre-activity preparation proves equally important as post-activity recovery. Dynamic warm-ups increase tissue elasticity and neuromuscular coordination, while cool-down routines facilitate waste removal and tissue realignment. These practices become particularly crucial for athletes or workers performing wrist-intensive tasks.
Holistic health maintenance supports wrist integrity through multiple pathways. Adequate hydration maintains tendon gliding efficiency, while anti-inflammatory nutrition patterns help regulate tissue repair processes. Sleep quality significantly influences pain perception and recovery capacity, creating another important prevention variable.
Collaboration with movement specialists provides customized prevention strategies based on individual risk profiles. These professionals analyze movement patterns, identify compensatory behaviors, and design targeted interventions to address specific vulnerabilities before they manifest as pain.