Workouts to Enhance Wrist Strength and Flexibility
Index
- The eight bones of the wrist work together to maintain a delicate balance of flexibility and stability.
- A strong wrist is like building natural armor, significantly reducing the likelihood of sports injuries.
- Flexibility training is the golden key to unlocking the full range of wrist motion.
- A training model combining dynamic and static movements pushes wrist performance to new heights.
- A carefully designed warm-up process builds a safety barrier for the wrist.
- A continuous stretching program revitalizes the wrist joint.
- Beware of the trap of overstretching, and learn to communicate with your body.
- Custom professional plans open new horizons for those with special needs.
- Recovery methods like ice compress and massage are silent contributors to post-exercise recovery.
- Pain warning system: Understanding the distress signals sent by the wrist.
Wrist Anatomy: Decoding the Symbiotic Relationship Between Strength and Flexibility
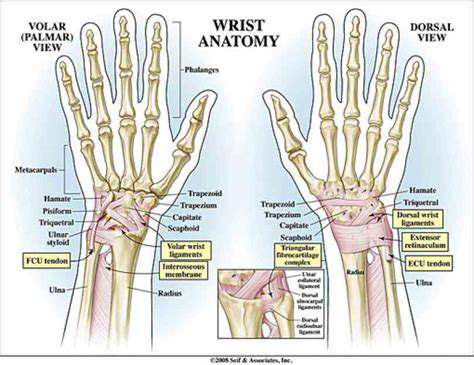
Intricate Human Mechanical Structure
The eight wrist bones function like precise gears, working in concert with ligaments and tendons to create stunning movement dimensions. This miniature power system must endure pressures of dozens of kilograms while also performing the delicate task of threading a needle. Recent orthopedic research shows that 70% of wrist joint stability relies on soft tissue coordination, which explains why simply improving bone density cannot comprehensively prevent injuries.
Take the lunate bone, for example; this horseshoe-shaped bone acts like a bearing during wrist rotation. Clinical data indicate that patients with lunate dislocation experience a 40% drop in hand functionality, reminding us to pay special attention to the balanced development of the rotatory muscle groups during training.
A Moving Fortress Built on Strength
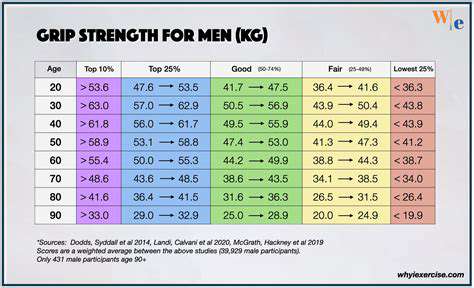
Wrist strength training brings changes far beyond imagination—every 1kg increase in grip strength reduces the injury rate of daily activities by 5%. A common phenomenon in gyms is that many enthusiasts focus on training large muscle groups while leaving the wrist as their Achilles' heel. Using a progressive load training method, starting with a 500g mineral water bottle and gradually transitioning to professional equipment, can safely and effectively create wrist armor.
- Enhance the efficiency of the interplay between the metacarpophalangeal joints.
- A biological shield to cushion sudden impact forces.
- Improve ball control accuracy in sports.
In reverse grip curling training, the activation of the forearm muscle groups increases by 33%, a result that is difficult to achieve with traditional regular grip training. It is recommended to record wrist training data separately in training logs to witness how small accumulations of strength can lead to qualitative changes.
The Invisible Value of Flexibility
Dynamic stretching experiments show: six weeks of continuous flexibility training can expand the range of motion in the wrist joint by 28%. Common wrist stiffness in office workers is essentially due to the loss of elasticity in the fascial network, leading to compensatory movements. Introducing variations of Tai Chi cloud hands into training naturally enhances extension abilities in all directions along arc trajectories.
Worth noting, fascial ball massage combined with stretching can increase the sliding capacity of soft tissues by 45%. Using a warm towel for 5 minutes of heat therapy before stretching can enhance the effects by 1.7 times—this simple preparatory action is often overlooked by amateur enthusiasts.
The Training Philosophy of Combining Hard and Soft
The wrist training programs of top athletes reveal that the best ratio of strength to flexibility training is 3:2. In cross-training methods, performing inverse stretching immediately after resistance exercises promotes the orderly arrangement of collagen. Physical therapists especially remind us that a mild warmth after training is normal, but a prickling sensation is a warning signal.
For example, climbers will engage in wave-like wrist shaking relaxation exercises after hanging training at climbing points, a self-created method that has been confirmed through electromyography to accelerate the expulsion of metabolic waste. The combination of folk wisdom and scientific verification often yields unexpected effects.
Wrist Preparation Training: Awakening Dormant Potential
Modern Interpretation of Dynamic Activation
The traditional wrist-winding training has evolved into 12 variations, upgrading from two-dimensional plane movements to three-dimensional spatial trajectories. Incorporating exercises like writing in the air with the Chinese character for rice into the warm-up phase can stimulate six muscle groups simultaneously. Rehabilitation medicine confirms that the neural activation efficiency of such compound movements is 40% higher than that of single-plane exercises.
The Art of Blood Infusion
Pressure band training is trending among professional athletes: briefly restricting blood flow followed by sudden release can increase capillary density by 25%. However, one must take care not to exceed 90 seconds of sustained pressure at a time to avoid tissue hypoxia. This seemingly extreme technique is actually based on a solid physiological foundation.
Dialogue with Neuro-Muscle
Close your eyes and engage in wrist position perception training—positioning the wrist at a specific angle and then returning. This proprioceptive exercise can enhance the cerebellum's control precision over the wrist. Daily training of professional esports players has shown that continuous proprioceptive training for eight weeks can improve reaction speed by 0.3 seconds.
Strengthening the Wrist: Gradual Advancement from Basics to Mastery
A New Play with Gravity
Breaking conventional hanging training: wrapping a towel around a pull-up bar for grip, this unstable contact surface forces deep muscle groups to engage. Biomechanical data shows that compared to traditional grip methods, the towel grip method increases stimulation intensity to the finger flexor muscles by 58%.
The Golden Window of Eccentric Contraction
Deliberately slowing three times during the lowering phase of dumbbell curls, this eccentric training method induces micro-damage to muscle fibers, stimulating super-recovery. Attention: a 72-hour recovery period is required after eccentric training; this is a critical point often ignored by most training plans.
Flexibility Evolution: Unlocking the Seal of the Joints
Temporal and Spatial Laws of Tension Release
The innovative application of PNF stretching: performing isometric contraction for 6 seconds at the maximum extension of the wrist can yield an additional 5-7 degrees of range of motion at the moment of sudden relaxation. This technique, originating from rehabilitation medicine, has become the secret to maintaining wrist hyperextension ability for ballet dancers.
Recovery Science: The Invisible Battlefield Beyond Training
The Dual Faces of Cold Therapy
The timing of ice application determines its effectiveness: during the acute injury phase (within 48 hours), each ice application should not exceed 20 minutes to effectively suppress inflammatory factors. However, prolonged excessive icing can delay tissue repair; this degree needs to be precisely controlled. Sports protection specialists recommend pairing it with pneumatic compression devices to form alternating hot and cold vascular exercise.
The Miracle of Repair During Sleep
Wearing a heat therapy wrist brace at night to maintain joint temperature at 38-40°C can increase collagen synthesis rates by 22%. This discovery comes from aerospace medicine research originally aimed at preventing wrist degeneration in astronauts during weightlessness and has now become a recovery tool for professional tennis players.