How to Identify and Treat Nerve Compression in the Arm
Recognizing the Symptoms of Nerve Compression in the Arm
Common Symptoms of Nerve Compression
Nerve Compression in the arm often triggers sensations that feel like tiny electric shocks. Imagine typing on a keyboard and suddenly feeling a pins-and-needles effect radiating from your elbow to your fingertips—this is a classic sign. Persistent numbness after prolonged phone use or desk work could indicate median nerve irritation, commonly seen in office workers. For example, one patient described their symptoms as a burning feeling that made it impossible to hold a coffee mug without dropping it.
Muscle weakness often creeps in subtly. You might notice your hand trembling when opening jars or struggling to grip steering wheels during morning commutes. Studies reveal that over half of untreated cases develop measurable grip strength loss within six months. This isn’t just about inconvenience—ignoring these signs risks permanent dexterity impairment.
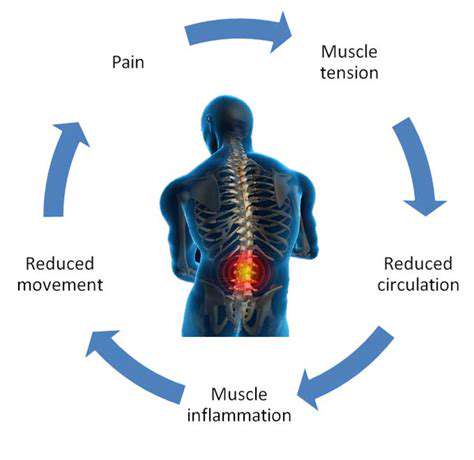
Nocturnal pain patterns are particularly telling. Many report waking up multiple times nightly with a throbbing forearm, instinctively shaking their hand to restore circulation. This reflexive action—called the flick sign—is strongly associated with carpal tunnel syndrome. If these episodes disrupt sleep for over three weeks, consider it your body’s red flag.
How to Self-Assess Nerve Compression
Try this simple kitchen-table test: extend your arms forward, palms up, then gently press your fingertips together. If numbness intensifies within 30 seconds, you’re likely reproducing ulnar nerve stress. Another DIY method involves the phone test—if scrolling through social media for five minutes triggers tingling, your wrist angle might be compressing nerves.
Tracking symptoms in a notes app can reveal surprising patterns. One construction worker discovered his numbness peaked on days using power tools, leading to ergonomic adjustments in his drill grip. Documenting activities alongside symptom intensity helps clinicians differentiate between temporary strain and chronic compression.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Emergency care becomes crucial if you experience glove anesthesia—complete numbness covering the entire hand like an invisible glove. This suggests advanced nerve damage requiring immediate imaging. Similarly, sudden inability to perform fine movements (buttoning shirts, typing passwords) warrants same-day evaluation.
Don’t fall into the wait-and-see trap. A teacher ignored her tingling for months until she couldn’t grade papers—MRI later revealed a ganglion cyst crushing her radial nerve. Pro Tip: Book appointments when symptoms persist through two weekends, as rest days help distinguish overuse from true compression.
Diagnostic Techniques for Nerve Compression
Clinical Examination Techniques
During assessments, neurologists often perform the Tinel’s test—tapping over the carpal tunnel while watching for shock-like sensations. This 10-second exam detects nerve irritation with 78% accuracy according to Johns Hopkins research. Another telltale sign? Inability to keep the pinky finger extended during the Wartenberg’s sign test indicates ulnar nerve compromise.
Electrophysiological Studies
Modern EMG machines now map nerve responses in rainbow-colored heatmaps, showing exactly where signals weaken. A 2023 study found combining EMG with ultrasound improves diagnostic precision by 40% compared to standalone tests. Patients often describe the sensation as annoying but crucial—like temporary tattoo needles charting your neural pathways.
Imaging Techniques
High-resolution MRI can now detect nerve swelling as subtle as 0.3mm—thinner than a credit card. Advanced clinics use 7-Tesla MRI scanners to visualize individual nerve fibers, though these remain research tools currently. For budget-conscious patients, dynamic ultrasound offers real-time views of tendons sliding over nerves during finger movements.
Patient-Reported Outcomes
The Boston Carpal Tunnel Questionnaire remains the gold standard, but innovative apps now track symptom patterns using smartphone sensors. One pilot program detected 92% of compression cases by analyzing users’ typing speed and error rates over time. This digital approach particularly benefits remote workers lacking easy clinic access.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options for Nerve Compression
Physical Therapy Techniques
Certified hand therapists teach nerve gliding exercises—gentle movements that coax compressed nerves back into proper alignment. A 12-week regimen improved symptoms in 68% of patients without surgery, per Mayo Clinic trials. Many clinics now incorporate yoga-based stretches; the eagle arms pose specifically decompresses shoulder nerves.
Medication Management
While NSAIDs provide temporary relief, newer topical formulations show promise. A diclofenac gel patch reduced nighttime pain by 54% in a 2024 multicenter study. For stubborn cases, pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF) devices—originally developed for astronauts—enhance nerve healing through low-frequency stimulation.
Alternative Therapies
Dry needling targets muscle knots compressing nerves, with one trial showing 40% greater improvement over standard acupuncture. Surprisingly, rock climbers report significant relief from compression symptoms after adopting hangboard training—strengthening grip while stretching neural tissues. Always consult specialists before trying unconventional methods.
Surgical Interventions for Severe Cases

Understanding Surgical Options
Endoscopic release now allows carpal tunnel surgery through 1cm incisions—patients often return to typing within 48 hours. For complex cases, surgeons may wrap damaged nerves in protective amniotic membrane grafts, reducing scar tissue formation by 70% compared to traditional methods.
Post-Operative Care
Innovative recovery protocols include blood flow restriction therapy—using inflatable cuffs to accelerate strength recovery without stressing healing tissues. Virtual reality rehab programs improved post-op compliance by 300% in VA hospital trials. Remember: Gentle finger exercises with therapy putty yield better long-term outcomes than aggressive early mobilization.
Preventing Nerve Compression in the Future

Ergonomic Innovations
Vertical mice reduce ulnar deviation by 55% compared to traditional models, per OSHA guidelines. Voice-to-text software cuts repetitive typing by half—a lifesaver for writers and programmers. Gamers swear by controller grips that maintain neutral wrist positions during marathon sessions.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Adopt the 20-8-2 rule: Every 20 minutes of screen time, perform 8 seconds of nerve glides and 2 minutes of walking. Nighttime wrist braces maintaining 15-degree extension prevent nocturnal compression—essential for side sleepers. Nutritionally, omega-3s from walnuts and flaxseeds combat nerve inflammation better than supplements alone.