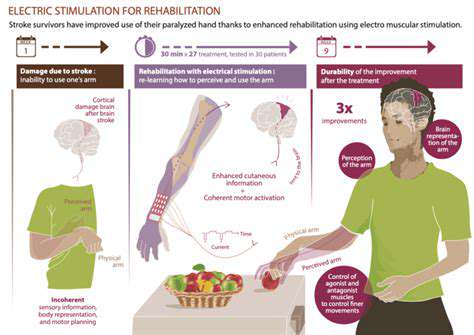
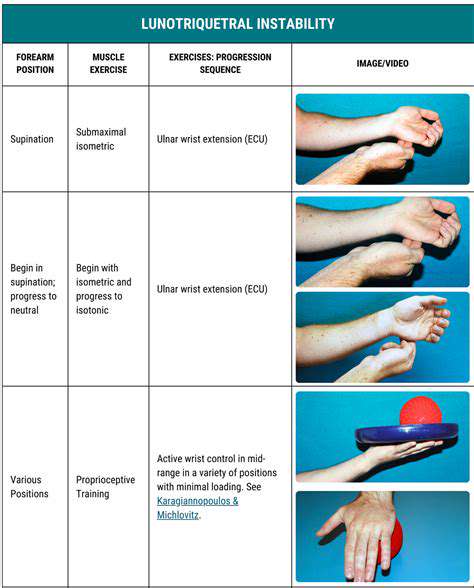
Methods to Enhance Hand Sensory Function


Utilizing Assistive Technologies for Sensory Enhancement
Braille Displays for Enhanced Tactile Input
Braille displays offer a tangible and highly effective method for sensory enhancement, particularly for individuals with visual impairments. These devices translate text into tactile patterns of raised dots, allowing users to read information by touch. The precise arrangement of dots provides a direct and immediate connection to the written word, fostering a strong sense of agency and independence in accessing and comprehending information.
Beyond basic text, Braille displays can be integrated with various software applications, providing access to a wide range of digital content, including emails, documents, and even interactive learning materials. This accessibility extends beyond simple reading and writing, enabling users to fully participate in digital environments.
Auditory Aids for Improved Sound Recognition
Auditory aids, such as hearing amplifiers and assistive listening devices, are crucial for enhancing the ability to perceive and interpret sounds. These devices can amplify faint sounds, reducing the strain on the auditory system and making conversations, environmental cues, and other important sounds clearer and more accessible. Effective use of auditory aids can dramatically improve communication skills and participation in social situations, fostering a greater sense of inclusion and connectedness.
Furthermore, specialized software can transform visual information into auditory signals, enabling users with visual impairments to navigate their surroundings and access digital information through sound. This conversion allows for the creation of a comprehensive auditory landscape that complements the tactile and other sensory inputs.
Tactile Graphic Displays for Multisensory Learning
Tactile graphic displays provide a powerful avenue for multisensory learning. By translating visual information into tactile representations, these devices allow individuals to experience complex concepts and patterns through touch. This approach can be incredibly beneficial for individuals with visual impairments, but also offers advantages for all learners, enhancing understanding and retention through a more immersive and engaging learning experience.
Imagine a map with raised textures representing elevation changes, or a scientific diagram with different materials providing tactile feedback for various elements. These tactile representations can deepen the understanding of complex data and concepts.
Assistive Technology for Spatial Awareness
Assistive technologies play a significant role in improving spatial awareness for individuals with disabilities. For example, GPS-based navigation systems with verbal guidance or visual aids can significantly improve orientation and movement in unfamiliar environments. These tools provide clear and concise instructions, helping users navigate their surroundings with greater confidence and independence.
Furthermore, specialized software can use haptic feedback to simulate physical sensations, enhancing users' awareness of their surroundings through a more engaging and responsive interaction.
Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC) Systems
Augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) systems provide alternative methods for individuals with communication impairments to express themselves. These systems can range from simple picture boards to sophisticated speech-generating devices. AAC systems empower individuals to participate in conversations, express their needs, and participate fully in social interactions.
AAC systems also support learning and development, enabling individuals to express their thoughts and ideas, ask questions, and share experiences with others. This fosters greater independence, self-expression, and inclusion.
Sensory Integration Tools for Multimodal Stimulation
Sensory integration tools can be utilized to create a more comprehensive and stimulating learning environment. These tools often incorporate a variety of sensory input modalities, such as visual, auditory, and tactile stimulation. This approach is particularly helpful for individuals with sensory processing differences, allowing them to regulate their sensory intake and learn more effectively.
By carefully integrating different sensory inputs, these tools can create a more engaging and supportive learning experience for all individuals, leading to improved focus, concentration, and overall learning outcomes.
Assistive Listening Devices for Enhanced Sound Recognition
Assistive listening devices are vital tools for individuals with hearing impairments or in situations with background noise. These devices amplify sounds, reduce background noise, and improve sound clarity, making communication more effective and enjoyable. This can have a profound impact on overall participation in social and educational activities.
Whether it's in a classroom, at work, or in social settings, these devices can improve the understanding and comprehension of spoken words and sounds, leading to improved communication, engagement, and understanding.