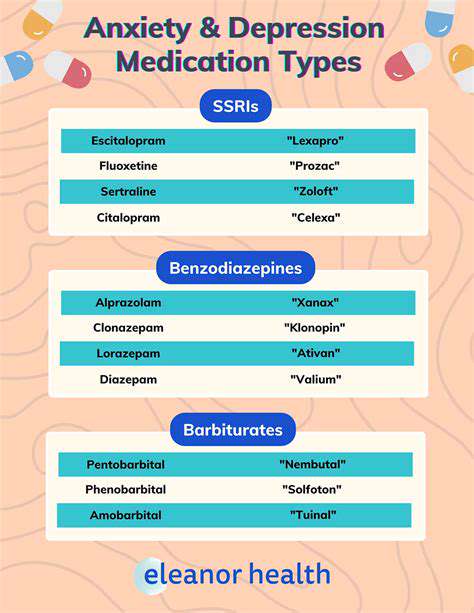
Modern Techniques in Hand Transplant Surgery
Modern surgical techniques have undergone a transformative shift with the rise of minimally invasive approaches. Unlike traditional open surgeries, these methods utilize smaller incisions, significantly reducing tissue damage and blood loss. Clinical studies confirm that patients undergoing these procedures experience dramatically shorter recovery periods. This paradigm shift hasn't just improved surgical outcomes—it's fundamentally changed patient expectations and quality of life post-operation.
Diverse Applications of Minimally Invasive Techniques
The medical field now employs these advanced techniques across numerous specialties. Laparoscopic procedures, for instance, allow surgeons to operate within the abdominal cavity through tiny openings. Similarly, thoracoscopic techniques provide access to the chest cavity, while arthroscopic methods enable precise joint interventions. The choice of technique depends entirely on the specific anatomical region requiring treatment and the nature of the medical condition.
Why Patients Prefer Minimally Invasive Options
The benefits of these advanced surgical methods extend far beyond the operating room. Patients consistently report significantly less post-operative pain compared to traditional surgeries. The reduced incision size not only minimizes visible scarring but also dramatically lowers infection risks—a critical factor in successful recoveries. Additionally, most patients can resume normal activities much sooner, with many experiencing shorter hospital stays that often translate to lower medical costs.
Technological Advancements Driving Progress
Cutting-edge instrumentation has been instrumental in advancing these surgical techniques. High-definition cameras provide surgeons with magnified, crystal-clear views of internal structures. Robotic assistance systems offer unprecedented precision, while specialized micro-instruments allow manipulation of delicate tissues with minimal trauma. These technological innovations collectively enhance surgical accuracy while reducing potential complications.
Optimizing Patient Outcomes Through Preparation
Successful outcomes begin long before the actual procedure. Comprehensive preoperative evaluations ensure patients understand all aspects of their upcoming surgery. Necessary dietary adjustments and medication modifications are carefully coordinated. This thorough preparation, combined with the inherent advantages of minimally invasive techniques, typically results in smoother recoveries with fewer post-operative challenges compared to conventional surgical approaches.
Economic and Practical Considerations
From a healthcare economics perspective, these techniques often prove more cost-effective despite their technological sophistication. The reduced hospitalization requirements and faster return to productivity create substantial savings across the healthcare system. However, availability remains inconsistent, as these procedures require specialized equipment and highly trained surgical teams that may not be universally accessible.
The Evolving Landscape of Surgical Innovation
Surgical technology continues its rapid advancement, with robotic systems becoming increasingly sophisticated. Emerging imaging technologies promise even greater visualization capabilities, while novel instrument designs push the boundaries of what's possible. These continuous improvements suggest we're only beginning to realize the full potential of minimally invasive techniques. As these technologies mature, they'll undoubtedly redefine standards of care across surgical specialties worldwide.
Precision Tissue Engineering for Enhanced Regeneration
The Science Behind Precision Tissue Engineering
This groundbreaking field represents the convergence of multiple scientific disciplines, combining advanced biomaterials with cutting-edge cellular biology. Unlike conventional approaches, precision tissue engineering focuses on meticulously controlling every aspect of the regeneration process at the molecular level. This level of control enables the creation of tissue constructs that more accurately mimic natural anatomy and physiology, particularly crucial for complex structures like those found in the hand.
The implications for hand injury treatment are profound, offering potential solutions that could reduce rehabilitation periods while improving functional outcomes. Each treatment can be customized based on the patient's specific injury pattern and biological characteristics.
Innovative Biomaterials Driving Progress
The foundation of successful tissue engineering lies in the development of sophisticated scaffold materials. These constructs must precisely replicate the mechanical and biological properties of native tissues. Modern materials range from temperature-sensitive hydrogels to nanocomposite polymers, each engineered to provide optimal support for different tissue types. Their gradual degradation must synchronize perfectly with new tissue formation—a delicate balance critical for successful integration.
Harnessing Cellular Potential for Regeneration
Contemporary approaches leverage various cell types to drive tissue regeneration. Pluripotent stem cells offer remarkable versatility, while tissue-specific progenitor cells provide targeted differentiation potential. Scientists can now precisely guide these cells' development using carefully calibrated biochemical signals. This level of control is particularly valuable for recreating the hand's intricate network of tendons, nerves, and vascular structures.
Supplemental growth factors and signaling molecules further enhance regeneration quality while helping prevent immune rejection—a persistent challenge in transplantation medicine.
3D Bioprinting: Creating Complex Living Structures
Additive manufacturing technologies have revolutionized tissue engineering capabilities. Modern bioprinters can deposit living cells with micron-level precision, building three-dimensional structures layer by layer. This technology proves invaluable for recreating the hand's complex anatomical features, from the delicate arrangement of finger joints to the specialized structures of nail beds. The ability to customize each construct to match a patient's exact anatomical dimensions represents a significant leap forward in personalized medicine.
Personalized Treatment Paradigms
The most significant advantage of modern tissue engineering lies in its capacity for personalization. Treatment strategies now consider numerous patient-specific factors, including genetic predispositions, metabolic profiles, and even lifestyle considerations. This comprehensive approach enables the creation of truly customized therapeutic solutions that account for each individual's unique biological context and recovery potential.
Clinical Implementation for Hand Injuries
Practical applications in hand trauma management are already demonstrating promising results. From complex tendon reconstructions to articular cartilage repair, these techniques show potential to restore function where traditional methods fall short. As clinical adoption increases, we're seeing improved outcomes including enhanced mobility, reduced pain, and more natural tissue integration. However, widespread implementation requires navigating complex regulatory landscapes and addressing valid ethical considerations surrounding these advanced therapies.