Next Generation Protocols for Arm Rehabilitation Success

Neurorehabilitation Techniques for Neurological Recovery
Neurorehabilitation encompasses a diverse range of techniques aimed at maximizing functional recovery and improving quality of life for individuals experiencing neurological impairments. These methods are tailored to the specific needs of each patient, considering the type and extent of neurological damage, as well as individual goals and preferences. Effective neurorehabilitation programs often integrate various approaches to address motor, sensory, cognitive, and emotional aspects of recovery. This multifaceted approach can lead to significant improvements in daily activities and overall well-being.
Rehabilitation is not a one-size-fits-all process; it's a personalized journey guided by trained professionals. The process is often long-term and demanding, requiring dedication and commitment from both the patient and the rehabilitation team. The goal is not just to restore lost function but also to empower individuals to adapt and thrive in their new circumstances. Successful rehabilitation programs prioritize safety, efficacy, and patient satisfaction.
Promoting Motor Function Recovery
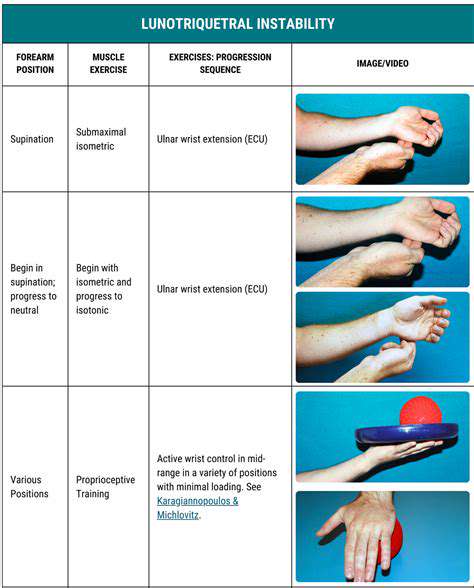
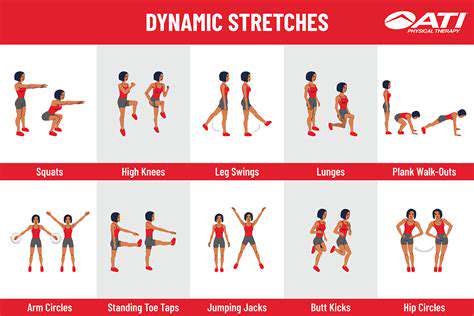
Techniques for promoting motor function recovery often involve a combination of physical exercises, occupational therapy, and assistive devices. These strategies focus on restoring strength, coordination, balance, and range of motion. Specific exercises are carefully designed to target specific muscle groups and neurological pathways, promoting neuroplasticity and the brain's ability to rewire itself.
Occupational therapy plays a crucial role in helping individuals adapt to their new abilities and develop compensatory strategies. This might involve learning to use adaptive equipment, modifying daily tasks, and developing new approaches to activities previously taken for granted.
Sensory Integration and Cognitive Enhancement
Sensory integration therapies aim to address sensory processing difficulties that can arise from neurological conditions. These therapies help individuals learn to organize and interpret sensory information, which can lead to improvements in attention, concentration, and overall cognitive function. For example, specific sensory activities might be used to help patients better process tactile, visual, or auditory stimuli.
Cognitive rehabilitation focuses on restoring or improving cognitive functions like memory, attention, problem-solving, and executive functioning. These therapies often incorporate various techniques, such as memory aids, problem-solving exercises, and cognitive training programs, to help patients regain lost cognitive abilities.
Addressing Emotional Well-being and Quality of Life
Neurological conditions can significantly impact emotional well-being, leading to feelings of frustration, anxiety, and depression. Neurorehabilitation programs should address these emotional aspects to ensure holistic recovery. Addressing emotional challenges can be a key component in achieving successful rehabilitation outcomes.
Support groups and counseling can play a vital role in helping individuals and their families cope with the emotional and social challenges associated with neurological conditions. These resources provide a safe space for sharing experiences, receiving support, and developing coping mechanisms.
Innovative Assistive Technologies: Empowering Independent Function
Assistive Robotics for Enhanced Mobility
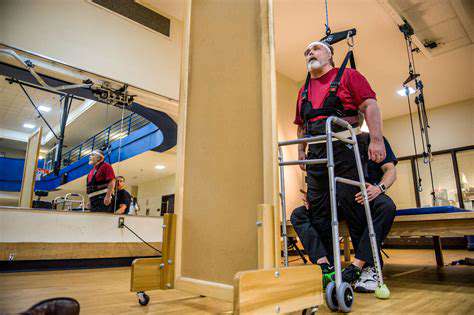
Assistive robotics are revolutionizing the way individuals with mobility limitations interact with their environment. These advanced technologies, ranging from lightweight exoskeletons to sophisticated robotic wheelchairs, offer a new level of independence and freedom of movement. The development of more intuitive and user-friendly interfaces is crucial, allowing users to seamlessly control these robotic systems through simple gestures or even direct brain-computer interfaces. This innovation promises to significantly improve the quality of life for individuals facing mobility challenges, enabling them to participate more fully in daily activities and social interactions.
Beyond simply providing physical support, assistive robotics are increasingly integrating cognitive and sensory enhancements. For example, some robots are designed to anticipate user needs, proactively adjusting their movements to ensure smooth transitions and prevent potential obstacles. This proactive approach not only enhances safety but also promotes a greater sense of autonomy and control for the user, reducing reliance on external assistance and fostering a more independent lifestyle. The future of assistive robotics holds immense potential for improving the lives of countless individuals.
Cognitive Enhancement Technologies
Emerging assistive technologies are not limited to physical support; they are also addressing cognitive impairments. These technologies utilize various approaches, from specialized software applications to advanced brain-computer interfaces, to aid individuals in managing tasks, remembering information, and communicating effectively. These systems can be tailored to specific cognitive needs, providing personalized support and fostering greater independence in daily life activities.
From personalized memory aids and reminders to tools that assist with organization and scheduling, these technologies are designed to empower users to take control of their daily routines. This personalized approach to cognitive support is crucial for individuals facing a wide range of cognitive challenges, enabling them to manage their lives more effectively and maintain their independence.
Personalized Communication Solutions
The advancement of assistive technologies has also led to innovative solutions for individuals with communication impairments. These technologies range from sophisticated speech-generating devices to advanced augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) systems. The increasing sophistication of these tools allows for greater flexibility and nuance in communication, bridging the gap between individuals and their social environment. Improved accessibility and user-friendliness of these tools are crucial for ensuring effective and natural communication.
Furthermore, integrating these communication tools with other assistive technologies creates a seamless and comprehensive support system. This interconnectedness allows for a more holistic approach to communication, empowering individuals to participate fully in social and professional settings. These innovations are not only changing the way individuals communicate but also transforming the way they interact with the world around them.