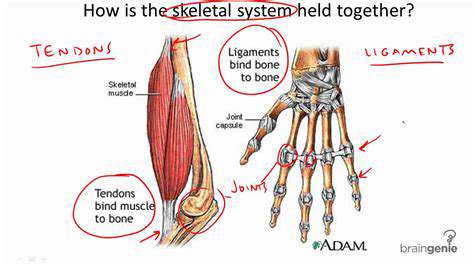
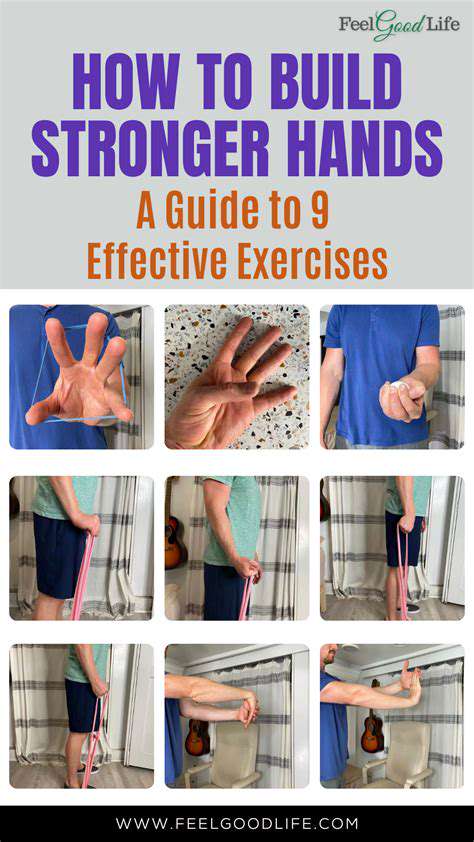
Preventing Hand Fatigue in Office Workers: Tips and Tricks

Identifying the Root Causes of Corrosion
Corrosion, a pervasive issue affecting various materials, stems from a complex interplay of environmental factors and material properties. Understanding these underlying causes is crucial for effective prevention and mitigation strategies. Corrosion often involves electrochemical reactions, where a metal loses electrons and undergoes oxidation, ultimately leading to deterioration. This process can be accelerated by the presence of moisture, oxygen, and electrolytes, which facilitate the transfer of electrons.
Identifying the specific culprits behind corrosion requires a thorough investigation into the surrounding environment. Factors like humidity, temperature, and the presence of corrosive substances like acids or salts all significantly influence the rate of corrosion. Understanding the specific chemical composition of the environment is also critical to determining the most appropriate protective measures.
Types of Corrosion Mechanisms
Various mechanisms contribute to the degradation of materials due to corrosion. One common type is uniform corrosion, where the metal deteriorates at a relatively consistent rate across its surface. Another significant mechanism is pitting corrosion, characterized by localized damage in the form of small pits, often leading to significant material loss over time. Galvanic corrosion, which occurs when dissimilar metals are in contact in an electrolyte solution, is another crucial mechanism that can cause severe structural damage.
Understanding the specific types of corrosion affecting a particular application is essential for devising targeted preventative measures. Different corrosion mechanisms require different mitigation strategies. For instance, uniform corrosion might be addressed by applying a protective coating, while pitting corrosion might require altering the environment or using specialized alloys.
Environmental Factors Influencing Corrosion
Environmental factors play a pivotal role in determining the rate and extent of corrosion. Moisture, in particular, is a critical element, as it provides a medium for electrochemical reactions to occur. The presence of oxygen is also crucial, as it acts as the electron acceptor in the corrosion process, further accelerating the deterioration of the material. The presence of electrolytes, like salts and acids, further enhances the conductivity of the solution, leading to a faster corrosion rate.
Temperature fluctuations also significantly impact corrosion rates. Higher temperatures often increase the rate of corrosion, as they enhance the kinetic energy of the reacting species, leading to faster reactions. Understanding these environmental influences is critical for predicting and preventing corrosion in various applications. Careful consideration of these factors is essential for designing effective preventive measures.
Material Properties and Their Impact
Material properties also significantly contribute to the susceptibility of a material to corrosion. The chemical composition of the material, including the presence of alloying elements, directly influences its corrosion resistance. For example, stainless steel, with its chromium content, exhibits excellent corrosion resistance compared to plain carbon steel. The microstructure of the material, including grain size and crystallographic orientation, can also influence corrosion susceptibility.
The surface condition of the material is another important factor. Damage or defects in the surface can create localized points of vulnerability, accelerating corrosion. Therefore, maintaining a smooth and intact surface is crucial for enhancing corrosion resistance. Proper surface treatment and protective coatings can significantly improve the material's ability to withstand corrosive environments.
Repetitive Strain Injury Prevention: Breaking the Cycle

Ergonomic Workstation Setup
Maintaining a proper ergonomic workstation setup is crucial in preventing repetitive strain injuries. This involves adjusting your chair, desk, and monitor to promote a neutral posture. A properly adjusted chair supports the natural curves of your spine, reducing strain on your back and neck. Ensuring your keyboard and mouse are positioned comfortably within easy reach helps to minimize awkward movements and repetitive stress on your wrists and hands.
Consider using a wrist rest to support your wrists when typing or using a mouse. An adjustable monitor arm allows you to position your screen at eye level, further reducing strain on your neck and shoulders. Regular adjustments and proper positioning are key to preventing the development of RSI.
Regular Breaks and Movement
Taking regular breaks is essential for preventing repetitive strain injuries. Short breaks every 30-60 minutes can significantly reduce the risk of developing muscle fatigue and pain. These breaks should include stretching and moving around to improve circulation and reduce muscle tension.
Engage in simple stretches, such as wrist rotations, shoulder shrugs, and neck stretches. Walking around or performing some light exercises during your breaks can help improve blood flow and reduce the risk of stiffness and pain in your muscles and joints. This active approach to breaks is far more effective than simply sitting passively.
Proper Lifting Techniques
Proper lifting techniques are critical for avoiding strain injuries. When lifting objects, always bend at your knees, not your back. Keep the load close to your body and use your leg muscles to lift, not your back. This helps distribute the weight evenly and minimizes stress on your back and spinal column.
Assess the weight and size of the object before attempting to lift it. If the object is heavy or awkward, ask for assistance to avoid straining your back or other parts of your body. Remember, prevention is better than cure when it comes to lifting injuries.
Keyboard and Mouse Usage
Proper keyboard and mouse usage is crucial for preventing wrist and hand strain. Ensure your keyboard and mouse are positioned comfortably within easy reach to avoid awkward postures and repetitive movements. Using a split keyboard, if necessary, can help to maintain a more neutral wrist position.
Take frequent breaks to rest your hands and wrists, and consider using ergonomic keyboards and mice designed to reduce strain. Adjust the sensitivity of your mouse to your needs and avoid rapid or jerky movements.
Importance of Posture
Maintaining good posture throughout the workday is essential for preventing repetitive strain injuries. Poor posture can lead to muscle imbalances and strain on your joints, increasing your risk of developing RSI. Pay attention to your posture throughout the day, ensuring your back is straight, your shoulders are relaxed, and your head is aligned with your spine.
Understanding Your Body
Listening to your body is crucial in preventing repetitive strain injuries. Pay attention to any signs of pain or discomfort, and address them promptly. Don't ignore minor aches, as they can escalate into more serious problems if left unaddressed. Early intervention is key to preventing further injury and reducing the need for more extensive treatment later.
If you experience pain or discomfort, consult a healthcare professional to determine the cause and receive appropriate guidance on how to manage the condition and prevent future occurrences.
Encouraging picky eaters to try new foods often hinges on how the food is presented. Instead of simply placing a plate of broccoli and carrots in front of them, consider arranging the vegetables in fun shapes using cookie cutters or creating a colourful mosaic. A visually appealing plate can spark curiosity and make the food seem more exciting and less intimidating. This simple act can make a world of difference in getting them to sample new flavours and textures.