State of the Art Practices for Hand Joint Recovery
Contents
Comprehensive assessments are essential for effective joint issue diagnosis and treatment.
Personalized treatment plans should consider individual circumstances and recovery needs.
Rehabilitation significantly enhances recovery outcomes through targeted therapeutic exercises.
Technology enhances rehabilitation by offering innovative tools for patient engagement and monitoring.
Effective pain management techniques include both pharmacological and non-pharmacological approaches.
Patient education supports recovery by empowering informed decision-making and adherence.
Support systems play a vital role in emotional and practical assistance during recovery.
Integrating technology supports personalized education for patient engagement and understanding.
Comprehensive Assessment and Personalized Treatment Plans
Understanding the Importance of Comprehensive Assessments
Comprehensive assessments are crucial in determining the precise nature and extent of a patient's joint issues. For instance, a combination of physical examinations, patient histories, and imaging studies such as MRI or X-rays can provide valuable insights. Clinicians can better understand the underlying causes of pain or dysfunction, whether it be from osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or previous injuries. Collecting this data ensures a tailored approach to treatment, maximizing the chances of a successful recovery.
Research underscores that thorough assessments correlate with improved treatment outcomes. A study published in the Journal of Hand Therapy revealed that proper diagnosis and assessment techniques can lead to a 30% quicker recovery time compared to standard approaches. By investing time in detailed evaluations, healthcare providers can craft personalized healing strategies that address both the symptoms and root causes of joint issues.
Elements of a Personalized Treatment Plan
A Personalized treatment plan should cater to individual needs and circumstances, considering factors such as age, activity level, and specific joint conditions. Integrative approaches often yield the best results; for instance, combining physical therapy with medication or surgical interventions can enhance recovery rates. Customized therapy can include targeted exercises, ergonomic adjustments, and pain management techniques tailored to relieve the patient’s unique discomfort.
Moreover, ongoing evaluations should adapt the treatment as the patient progresses. Utilizing feedback from patients can refine treatment plans, ensuring they align with the evolving nature of their recovery. An approach that remains flexible and responsive is instrumental in optimizing hand joint recovery outcomes.
The Role of Rehabilitation in Recovery Outcomes
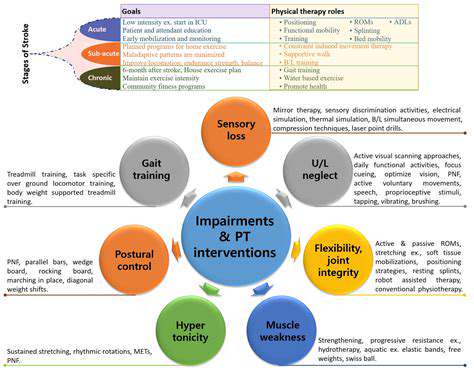
Rehabilitation plays a pivotal role in hand joint recovery, emphasizing the need for specific therapeutic exercises to restore functionality. A report by the American Physical Therapy Association indicates that consistent rehabilitation after an initial treatment phase can significantly improve range of motion and muscle strength. This structured approach decreases the likelihood of re-injury while helping patients achieve optimal recovery benchmarks.
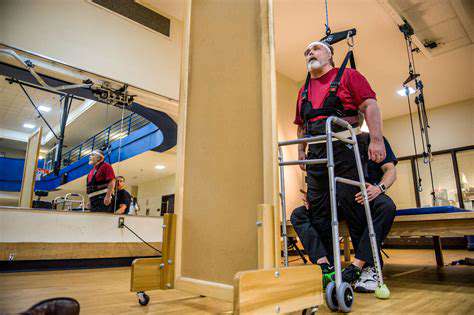
Furthermore, incorporating innovative rehabilitation technologies, such as robotic-assisted therapy, can facilitate effective outcomes. These advancements provide real-time feedback and allow for precise adjustments in therapy, fostering a more engaging patient experience. Overall, a comprehensive understanding of rehabilitation—combined with personalized strategies—can markedly enhance hand joint recovery.
Therapeutic Exercises and Strengthening Techniques

Understanding the Importance of Therapeutic Exercises
- Therapeutic exercises enhance mobility and strength.
- They assist in pain relief and promote healing.
- Customized therapy plans are crucial for effective recovery.
Therapeutic exercises play a crucial role in recovery from hand joint injuries. They not only help rebuild strength but also contribute to a more extensive range of motion. Research shows that patients who engage in a structured exercise program experience a faster and significantly more complete recovery compared to those who do not.
To maximize recovery, these exercises should be customized according to the patient's specific injury and functional needs. Involving a certified therapist to create a tailored plan can result in more effective and enjoyable sessions.
Strengthening Techniques through Resistance Training
Resistance training is one of the most effective methods for strengthening muscles surrounding the hand joints. Techniques such as using thera-bands or hand grippers can significantly improve grip strength. Studies indicate that Resistance training increases muscle mass, thereby supporting joint stability.
Incorporating progressive overload in these techniques ensures that the muscles are continually challenged, leading to better outcomes. This could mean gradually increasing the resistance level, the number of repetitions, or even changing the exercises themselves.
Flexibility and Range of Motion Exercises
Maintaining flexibility is just as important as building strength. Range of motion exercises, including finger stretches and wrist rotations, are essential for preventing stiffness. Consistent practice of these exercises can greatly enhance overall hand function.
In clinical settings, there's evidence that incorporating flexibility training into daily routines can help patients regain quicker functionality. Techniques can include static stretches held for specific durations or dynamic movements that encourage fluidity in the joints.
Utilizing Biofeedback in Rehabilitation
Biofeedback techniques have emerged as an effective tool for hand joint recovery. This method allows patients to gain awareness of their muscle activity, which can improve the effectiveness of exercises. Research suggests that using biofeedback can increase motivation and adherence to rehabilitation programs.
By visually monitoring muscle performance, patients can adjust their efforts accordingly, achieving better outcomes. It is worth noting that biofeedback can often extend beyond physical exercises; mental visualization techniques can also contribute to improved hand function.
Integrative Approaches Combining Occupational Therapy
Integrating occupational therapy with therapeutic exercises can yield significant improvements in recovery. Occupational therapists focus on daily living activities and can provide insights on how to perform them despite injuries. This combination not only strengthens the hand but also enhances the patient's ability to perform tasks.
Moreover, studies have shown that patients who participate in both therapeutic and occupational therapies experience not just physical but also emotional benefits, fostering independence and confidence in daily life.
Patient Education and Self-Management Techniques
Educating patients about self-management techniques is vital for successful rehabilitation. Understanding their bodies and how to modify activities can empower them and enhance recovery. Some effective self-management techniques include setting achievable goals, monitoring progress, and adapting exercises based on their comfort levels.
The connection between education and effective recovery is backed by research indicating that informed patients are more likely to follow through with rehabilitation programs. Encouraging patients to communicate their experiences allows therapists to make necessary adjustments promptly.
Evaluating Progress: Metrics and Benchmarks
Evaluating progress is an essential component of hand joint recovery. Practitioners should implement specific metrics to measure improvements, such as grip strength, joint range, and overall functionality. Regular assessments not only track advancements but also motivate patients, showing them tangible results from their efforts.
It's advisable to utilize both subjective and objective measures in the evaluation process. For instance, functional ability questionnaires along with physical strength tests provide a comprehensive view of the patient's recovery journey, offering insights into necessary adjustments in their therapy plans.
Technology-Enhanced Rehabilitation Tools
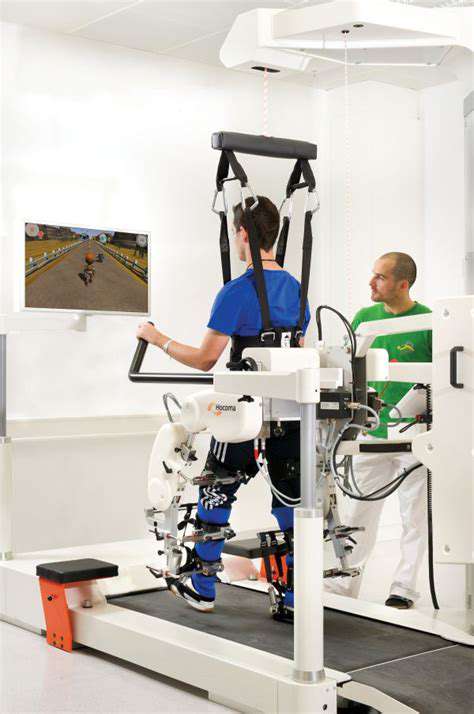

Overview of Technology-Enhanced Rehabilitation Tools
- Understanding the role of technology in hand joint recovery.
- Types of rehabilitation tools currently available.
- Recent advancements in rehabilitation technologies.
In recent years, there has been a significant shift towards incorporating technology in rehabilitation practices. Such Technology-enhanced tools are transforming the landscape of hand joint recovery by providing patients with more effective and personalized care options. From virtual reality systems to robotic-assisted devices, these innovations are designed to improve patient outcomes and enhance rehabilitation efficiency.
Collaborative Robots in Rehabilitation
Robotic devices, often referred to as exoskeletons, are designed to assist patients with specific tasks. These robots can adapt to the user’s physical capabilities, offering customized support during rehabilitation exercises. They vary widely in functionality, from simple assistive devices to complex systems that enable fine motor skills training.
Research has shown that incorporating robots into therapy can reduce recovery time and improve the overall effectiveness of rehabilitation. Studies published in reputable journals indicate that patients using robotic devices show improvements in dexterity within weeks compared to traditional methods.
Virtual Reality and Gamification
Another emerging trend is the use of virtual reality (VR) environments to enhance rehabilitation. These immersive experiences allow patients to engage in rehabilitation routines while participating in interactive games and scenarios. As a result, patients exhibit increased motivation and adherence to exercise regimens.
Moreover, data from clinical trials suggest that VR can lead to better rehabilitation outcomes. Patients using VR showed a 30% improvement in motor skills and overall satisfaction compared to those undergoing conventional rehabilitation. This is a trend that should not be overlooked in hand joint recovery practices.
Mobile Applications for Continuous Monitoring
Mobile technology is revolutionizing the way rehabilitation is approached, allowing for real-time tracking of patient progress. Several applications enable therapists and patients to set goals, track exercises, and receive feedback directly on their smartphones. This accessibility means rehabilitation can happen both in and outside of clinical settings.
Such tools can significantly enhance patient engagement and ensure they stick to their therapy plans. A recent survey indicated that patients using dedicated rehabilitation apps reported a 40% increase in compliance with prescribed exercises. This shows how technology can create a supportive recovery environment.
Teletherapy: A New Frontier in Rehabilitation
Teletherapy has gained momentum as an effective model for delivering rehabilitation services. This approach allows therapists to conduct sessions remotely, expanding access to patients who may not be able to attend in-person appointments due to geographical or physical limitations. In fact, teletherapy utilization spiked during the pandemic, showcasing its viability.
Some studies indicate that teletherapy can be just as effective as traditional rehabilitation. Therapists can assign tasks and monitor patient performance via video calls, ensuring that patients receive guidance and support tailored for their unique needs.
Wearable Technology for Progress Tracking
Wearable devices, such as smart bracelets and gloves equipped with sensors, provide a range of data about a patient's movements during rehabilitation exercises. These tools are invaluable for gathering objective performance metrics, which can be analyzed by healthcare professionals for better treatment planning. This data-driven approach is reshaping assessment and monitoring practices.
Recent developments in this area suggest that wearables can help identify patterns in activity levels, track joint range of motion, and even detect deviations from normal rehabilitation progress. Given the importance of accurate data, integrating wearables into rehabilitation practices is poised to enhance the recovery experience significantly.
Future Directions in Hand Rehabilitation Technology
The future of technology-enhanced rehabilitation tools points towards even more personalized approaches, utilizing artificial intelligence and machine learning to develop predictive models. These advancements can help create tailored rehabilitation programs based on individual patient data and recovery patterns. As this field continues to evolve, staying updated on cutting-edge technology becomes essential for both healthcare professionals and patients.
Moreover, interdisciplinary collaboration between engineers, therapists, and physicians will play a crucial role in advancing these technologies. By working together, they can ensure that innovations not only meet medical needs but also address patient experiences effectively.
Integrating Pain Management Techniques
Understanding Pain Management Techniques
- Different techniques can be applied based on the patient's specific needs.
- Skills development in pain management involves understanding the types of pain experienced.
- Patient engagement is crucial for effective pain management.
Effective pain management in hand joint recovery requires a clear understanding of the various techniques available. The choice of techniques often hinges on the specific needs of the patient and the nature of their pain. For instance, chronic pain from arthritis may necessitate a different approach compared to acute post-surgical pain.
Among the commonly used techniques are pharmacological interventions, physical therapy, and psychological therapies. These methods aim to not only alleviate pain but also improve the overall quality of life for patients. Understanding how these techniques integrate with recovery goals can significantly enhance patient compliance.
Pharmacological Approaches
Pharmacological approaches to pain management are often the first line of defense in treating hand joint discomfort. Medications such as NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) are widely used to reduce inflammation and pain. It's important to note that while these medications provide temporary relief, they can have side effects if used long-term.
Newer medications, like biologics, target specific pathways involved in inflammation. For example, research published in the *Journal of Rheumatology* indicates that biologics can lead to significant pain reduction in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Therefore, it's essential for clinicians to stay updated on recent advancements in pharmacotherapy to tailor treatments efficiently.
Non-Pharmacological Techniques
Non-pharmacological methods are gaining popularity as complementary treatments for pain management. Techniques such as acupuncture, massage therapy, and mindfulness-based stress reduction are being integrated into traditional rehabilitation programs. Studies indicate that patients who engage in these alternative therapies often report better pain control and can improve their functional outcomes significantly.
Additionally, methods like occupational therapy aim to enhance patients' daily living skills while minimizing pain. Through personalized programs, occupational therapists can create adaptive strategies that promote independence and reduce discomfort during tasks. It's advisable for patients to discuss with their healthcare providers which of these methods could work best for them.
Patient Engagement in Recovery
Engaging patients in their pain management plans is critical for achieving effective outcomes. Involving patients encourages them to express their pain levels openly, which informs better treatment decisions. Automation tools and mobile applications are becoming increasingly popular for tracking pain and symptoms, making data available for review during consultations.
Active participation fosters a sense of ownership, which can motivate patients to adhere to recovery programs. Educational workshops can empower patients with knowledge about pain management strategies, ultimately building their confidence in managing their conditions. Experts suggest that a collaborative approach between patients and healthcare providers is most beneficial for optimizing recovery efforts.
The Role of Patient Education and Support
Importance of Patient Education in Recovery
Understanding the rehabilitation process is crucial for patients recovering from hand joint issues. Educating patients about their specific conditions, treatment options, and expected outcomes allows them to engage actively in their recovery. When patients comprehend the intricacies of their rehabilitation, they are more likely to adhere to prescribed exercises and therapies, which significantly enhances their recovery rates.
Research indicates that Patient Education programs can lead to improved health outcomes. A study published in the Journal of Hand Therapy highlights that patients with access to educational resources regarding hand joint recovery report higher satisfaction and demonstrate a greater commitment to their recovery plans. With proper information, patients can navigate the complexities of recovery more effectively, making informed choices impacting their long-term health.
Support Systems in Rehabilitation
A strong Support System is vital for individuals undergoing hand joint recovery. Support can come from various sources, including family members, friends, occupational therapists, and support groups. Such networks not only provide emotional encouragement but also practical assistance, which can be pivotal during the recovery process, particularly when mobility and daily activities are compromised.
The Role of Technology in Patient Education
Innovative technologies are transforming how patients receive information about their hand joint recovery. Mobile health applications and telemedicine platforms facilitate immediate access to educational materials, helping to reinforce what patients learn during clinical visits. For example, apps may include instructional videos on rehabilitation exercises tailored to a patient's specific journey, promoting consistency and effectiveness in their practice.
Furthermore, online forums and communities provide opportunities for patients to share experiences and advice. These interactions not only empower patients but also create a sense of belonging, which may lead to improved mental health and overall recovery outcomes. The integration of technology into patient education exemplifies a modern approach to holistic recovery.
Personalized Education Strategies
Every patient is different; therefore, employing personalized education strategies is essential for effective recovery. Healthcare professionals should assess each patient's unique needs, learning styles, and existing knowledge before developing a tailored educational approach. By doing so, they ensure patients grasp the necessary information and feel competent in managing their recovery, leading to better health outcomes.
Courses and workshops designed to inform patients about hand joint conditions can also offer hands-on experiences. These experiential learning opportunities often result in greater retention of information. Additionally, empowering patients with self-management techniques enables them to take control of their recovery, potentially leading to higher levels of motivation and engagement.