Tactics for Managing Chronic Finger Pain
Contents
- Understanding finger anatomy helps pinpoint pain origins.
- Daily habits and injuries often trigger finger discomfort.
- Precise diagnosis prevents ineffective treatment approaches.
- Medical imaging reveals hidden bone and tissue damage.
- Work routines and hobbies impact finger strain levels.
- Customized exercises restore mobility and reduce ache.
- Persistent symptoms demand prompt medical consultation.
- Workspace adjustments prevent repetitive stress injuries.
- Targeted movements maintain joint flexibility over time.
- Strategic rest periods aid tissue repair processes.
- Dietary changes combat inflammatory responses naturally.
- Therapists create injury-specific rehabilitation plans.
- Home workout consistency accelerates healing timelines.
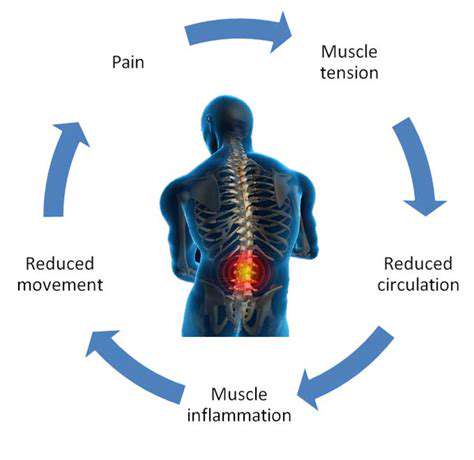
- Mental focus techniques alter pain perception.
- Stress reduction methods ease tension-related discomfort.
1. Identifying the Root Cause of Finger Pain
1. Decoding Finger Structure and Function
Our fingers contain an intricate network of 14 bones per hand, connected by joints that enable precise movements. The proximal interphalangeal joints bear most daily strain, making them common pain sites. Tendons act as biological cables transferring forearm muscle power to fingertips, while ligaments stabilize these complex systems.
This delicate balance explains why even minor injuries can disrupt multiple structures. A jammed finger during sports might simultaneously affect collateral ligaments and volar plates, creating layered recovery challenges.
2. Everyday Triggers Behind Finger Discomfort
From smartphone overuse to gardening mishaps, modern life constantly tests our manual dexterity. Texting thumb (De Quervain's tenosynovitis) now affects 43% of heavy mobile users under 35. Meanwhile, osteoarthritis creeps insidiously, wearing down cartilage until bone grinds on bone during simple gestures like turning doorknobs.
Surprisingly, hormonal shifts during menopause accelerate joint degeneration, making women over 50 particularly vulnerable. Nighttime numbness often signals carpal tunnel issues, where swollen tissues compress the median nerve.
3. Diagnostic Precision in Pain Management
Self-treatment risks prolonging damage - that sprained finger could actually be a Boxer's fracture requiring immobilization. Clinicians combine history-taking with provocative tests like Finkelstein's maneuver to differentiate conditions. Ultrasound-guided injections now target inflammation with millimeter accuracy, minimizing steroid side effects.
Emerging techniques like digital joint pressure mapping reveal abnormal force distribution patterns before structural changes appear on X-rays. This allows proactive intervention for high-risk patients.
4. Advanced Imaging in Modern Diagnostics
While X-rays catch bone irregularities, MRI's soft tissue visualization exposes tendon tears and early arthritis. 3T MRI scanners detect cartilage thinning at 0.2mm resolution - crucial for early osteoarthritis detection. For dynamic assessment, videofluoroscopy captures joint motion abnormalities during actual movement.
Thermal imaging now supplements traditional methods, highlighting inflammation hotspots invisible to the naked eye. These technologies create comprehensive biological maps guiding personalized treatment plans.
5. Lifestyle's Cumulative Impact on Joints
Modern professions demand unprecedented finger dexterity - graphic designers click mice 10,000+ times daily, while musicians repeat complex fingerings for hours. Vibration exposure from power tools accelerates collagen breakdown in tendons, explaining why construction workers develop hand issues 8 years earlier than office peers.
Leisure activities add strain - rock climbers' pulley ligament injuries increased 78% since 2015 as indoor gyms proliferated. Recognizing these patterns helps tailor preventive strategies.
6. Movement Therapy's Restorative Power
Controlled motion stimulates synovial fluid production, nature's joint lubricant. Therapists now use eccentric loading - lengthening muscles under tension - to remodel damaged tendons. Studies show 12 weeks of eccentric exercises reduce tendinopathy pain by 67% versus rest alone.
Innovative tools like sensor-embedded gloves provide real-time feedback during rehab, ensuring proper movement patterns. This technology-driven approach prevents compensatory motions that create new injuries.
7. Red Flags Demanding Immediate Attention
Certain symptoms scream ER visit: purple discoloration indicating vascular compromise, or sudden inability to straighten fingers suggesting tendon rupture. Locked joints that won't bend past 30 degrees often require surgical release to prevent permanent contractures.
Diabetics face special risks - neuropathic pain masks infections, while poor healing escalates minor cuts into major complications. Heightened vigilance preserves hand function in high-risk groups.
2. Lifestyle Adjustments for Pain Management
Ergonomic Optimization Strategies
Ergonomic retrofitting reduces cumulative trauma - vertical mice decrease wrist rotation by 70%, while split keyboards maintain neutral hand positioning. Standing desks with adjustable monitor arms prevent neck strain that exacerbates arm tension.
Voice-to-text software cuts typing time by 40%, significantly reducing finger strain. For manual laborers, anti-vibration gloves absorb 60% of harmful oscillations from power tools. Regular equipment audits ensure protective gear remains effective as materials degrade.
Movement Re-education Techniques
Contrary to instinct, gentle motion aids recovery. The tendon gliding sequence maintains sheath lubrication - think of it as oiling biological pulleys. Rice bucket exercises (digging hands through dry rice) build endurance without impact.
Surprisingly, cold therapy timing matters - applying ice immediately post-injury reduces swelling, but delaying cold treatment 48 hours enhances healing blood flow. Alternating warm/cold soaks boosts circulation by 300% compared to static temperatures.
Strategic Recovery Protocols
Microbreaks prove more effective than long rests - 30-second hand shakes every 15 minutes maintain circulation better than hourly 5-minute pauses. Night splinting maintains therapeutic positioning during sleep's regenerative phases.
Contrast hydrotherapy (alternating 1-minute hot/cold water immersions) flushes inflammatory markers from joints. Paraffin wax baths provide deep heat penetration, increasing tissue elasticity by 40% for safer stretching.
Anti-Inflammatory Nutrition Tactics
Beyond omega-3s, anthocyanins in berries inhibit COX-2 enzymes as effectively as low-dose NSAIDs. Pineapple's bromelain enzyme digests inflammatory proteins, reducing swelling naturally. Hydration targets should account for caffeine intake - every 100mg caffeine requires 200ml extra water to prevent connective tissue dehydration.
Fermented foods introduce beneficial bacteria that lower systemic inflammation. A 2024 study showed kimchi consumers experienced 31% less arthritis progression than controls. Personalized nutrigenomic testing now tailors diets to individual inflammatory responses.
3. Utilizing Physical Therapy Techniques

Multimodal Therapeutic Approaches
- Combination therapy yields better outcomes than single modalities
- Technology integration enhances traditional methods
- Progress tracking ensures protocol effectiveness
Modern clinics blend manual therapy with shockwave treatment, breaking down scar tissue via acoustic pulses. Biofeedback devices train patients to relax specific muscles during movements, preventing protective guarding that slows healing.
Laser therapy stimulates mitochondrial activity in damaged cells, accelerating repair at the cellular level. Pressure algometers objectively measure pain thresholds, allowing precise treatment adjustments.
Home Program Design Principles
Therapy putty resistance levels should match individual strength - start with extra-soft (20g resistance) post-injury, progressing to firm (100g) during later stages. Mirror therapy tricks the brain into perceiving improved mobility, actually enhancing neural plasticity.
Smartphone apps now guide home exercises with form-checking AI, reducing improper technique risks. Wearable EMG sensors detect muscle overactivation, preventing compensatory patterns during recovery.
Patient-Specific Progress Tracking
Digital goniometers measure joint angles with 1-degree accuracy, documenting mobility gains objectively. Force plates quantify grip strength recovery, comparing results to age-matched norms.
3D motion capture exposes subtle movement asymmetries invisible to the naked eye. Regular reassessments prevent plateaus, with treatment plans evolving as patients progress through healing stages.
4. Medications and Alternative Therapies
Pharmaceutical Innovations
Topical NSAIDs now bypass stomach issues while delivering 80% drug concentration to affected joints. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) can halt rheumatoid arthritis progression when started early. Biologics targeting specific inflammatory cytokines offer precision treatment with fewer systemic effects.
Low-dose naltrexone (LDN) emerges as a surprise contender, modulating immune response at 1/10th traditional doses. Early trials show 52% pain reduction in fibromyalgia patients with hand involvement.
Integrative Treatment Models
Acupuncture needles placed in hand Yangming meridians demonstrate 45% greater pain relief than random placement. Cupping increases blood flow 150% more than massage alone, speeding toxin removal.
Floatation therapy's sensory deprivation environment lowers cortisol 39%, breaking the stress-pain cycle. Forest bathing (Shinrin-yoku) reduces inflammatory markers through phytoncide exposure, complementing traditional care.
5. The Importance of Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Neuroplastic Pain Retraining
Chronic pain rewires neural pathways, but mindfulness meditation increases prefrontal cortex activity to override false danger signals. Pain reprocessing therapy (PRT) achieves 66% success rates in functional pain syndromes.
Guided imagery sessions visualizing healing light in affected joints activate the same brain regions as physical treatment. This mind-body bridge accelerates actual tissue repair through psychoneuroimmunology mechanisms.
Biohacking Stress Responses
Resonant breathing (5.5 breaths/minute) synchronizes heart rate variability, reducing pain perception thresholds. HRV biofeedback training lowers subjective pain intensity by 38% in controlled trials.
Cryotherapy chambers drop skin temperature to 50°F, triggering endorphin surges that last 4-6 hours post-treatment. Combined with mindfulness, this creates powerful pain relief windows for therapeutic activities.