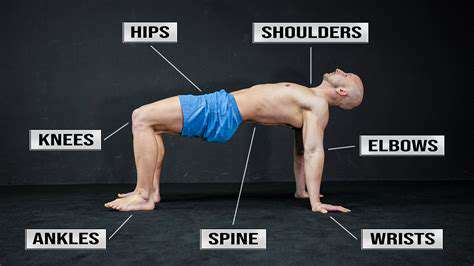
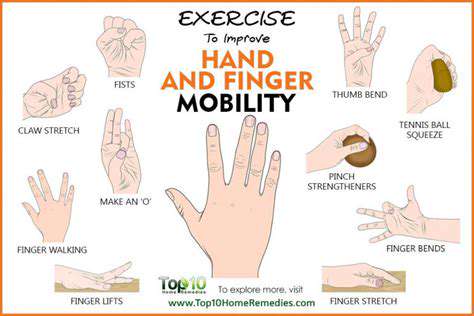
Tactics to Improve Wrist Functionality
Targeted Exercises for Wrist Strength and Flexibility
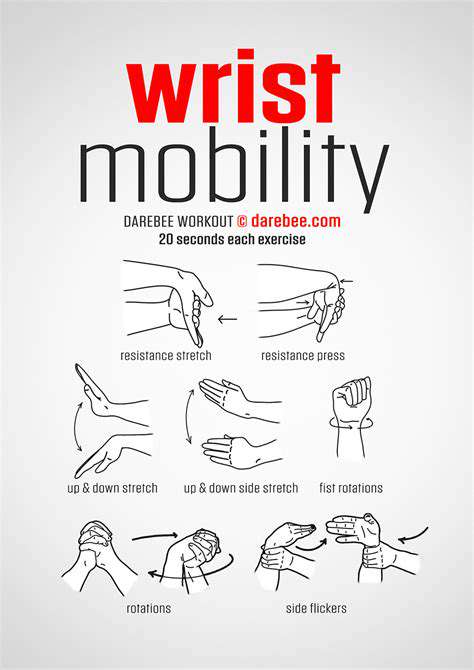
Strengthening the Wrist Extensors
Wrist extensors, located on the back of the forearm, play a pivotal role in wrist stability and injury prevention. Focusing on these muscles through targeted exercises can dramatically enhance wrist strength and durability. Effective routines often incorporate weights or resistance bands while executing controlled wrist extensions. Maintaining proper alignment is critical to prevent undue stress on adjacent hand and forearm structures.
Practical exercises include weighted wrist extensions, resistance band extensions, and reverse wrist curls. Regular training fortifies these muscles, which are essential for daily activities such as grasping objects, lifting weights, or prolonged keyboard use.
Strengthening the Wrist Flexors
The wrist flexors, positioned along the forearm's front, are equally vital for wrist functionality. Targeted training of these muscles not only prevents injuries but also promotes comprehensive wrist health. These exercises typically involve downward wrist flexion, such as using dumbbells or resistance bands for focused engagement.
Strengthening these muscles proves invaluable for repetitive tasks like typing or mouse operation. Precision in execution is paramount to avoid strain or potential injury.
Enhancing Grip Strength
A robust grip is fundamental for countless everyday actions, from carrying groceries to writing notes. Developing grip strength directly correlates with improved wrist performance and overall hand dexterity. Effective methods include squeezing stress balls, using grip trainers, or performing farmer's carries. Integrating these exercises into your regimen can transform your ability to handle daily challenges effortlessly.
Managing Wrist Discomfort
Wrist pain may arise from overuse, repetitive strain, or medical conditions. Customized exercises can mitigate discomfort by reinforcing supportive muscles and enhancing mobility. These should be adapted to address specific pain sources, often incorporating gentle stretches and controlled strengthening movements. Always seek professional medical advice before initiating any pain management exercise program.
Immediately consult a physician if you experience sharp pain or persistent symptoms. Accurate diagnosis ensures appropriate therapeutic exercises are prescribed.
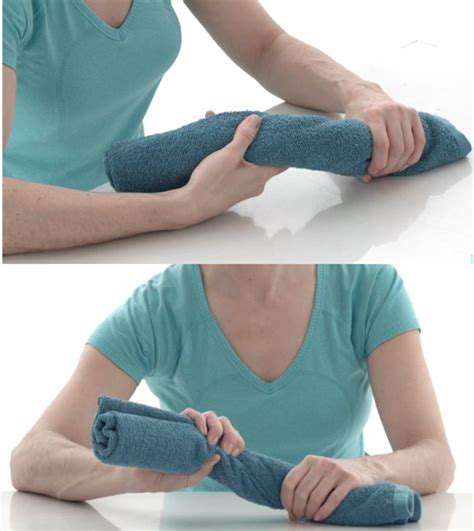
Implementing Wrist Stretches
Flexibility training is equally crucial as strength development for wrist health. Regular stretching maintains joint suppleness, prevents stiffness, and reduces injury risk. Diverse stretches target various wrist aspects, collectively improving range of motion. Consistent practice yields optimal results.
Mastering Technique and Progressive Training
Precision in execution is absolutely vital for wrist exercises. Improper form may cause injuries and impede progress. Begin with minimal resistance, gradually intensifying as strength develops. This measured approach allows physiological adaptation while minimizing injury potential.
Dedication produces results. Combining consistent practice with proper technique and progressive overload leads to substantial improvements in wrist capability and overall function.
The Importance of Posture and Ergonomic Practices
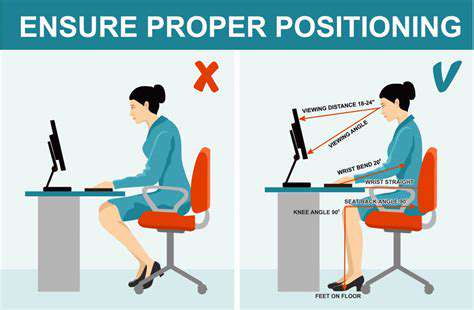
Sustaining Proper Alignment for Health
Optimal posture forms the foundation of physical wellbeing, particularly in our increasingly sedentary lifestyles. Suboptimal alignment can trigger a domino effect of issues, from temporary discomfort to chronic musculoskeletal disorders. Recognizing posture's significance and consciously maintaining it throughout daily activities prevents long-term complications and enhances quality of life.
Conscious postural maintenance during sitting and standing significantly diminishes back, neck, and related discomfort risks. Beyond physical benefits, proper alignment fosters body confidence and spatial awareness.
Workplace Ergonomics Essentials
Office environments profoundly influence our physical health. Thoughtful ergonomic implementation substantially reduces bodily stress and prevents occupational injuries. Critical factors include adjustable seating, optimal monitor placement, and workstation configuration. Businesses prioritizing these elements cultivate healthier, more productive workforces.
Investing in ergonomic solutions and employee education yields substantial returns through reduced absenteeism, enhanced comfort, and improved work output.
Posture's Systemic Health Impact
Chronic poor posture affects multiple body systems beyond the musculoskeletal framework. Persistent misalignment contributes to chronic pain, restricted movement, and decreased functional capacity. These limitations often extend beyond physical symptoms, diminishing overall life quality and daily performance.
Additionally, postural deficiencies may precipitate spinal issues, tension headaches, and even breathing pattern disturbances. Comprehensive understanding of these relationships enables proactive health management.
Posture's Psychological Influence
Emerging research reveals posture's significant psychological effects. Physical alignment directly influences emotional state and self-perception. Maintaining upright posture correlates with improved mood and heightened confidence, while slumped positions may reinforce negative emotional states.
This mind-body connection suggests that postural correction benefits extend beyond physical health, potentially enhancing mental wellbeing and self-image.

Comprehensive Strategies for Wrist Wellness
Wrist Anatomy Fundamentals
The wrist's intricate architecture comprises eight carpal bones connecting forearm to hand. Optimal function requires seamless coordination between bones, tendons, and muscles. Detailed anatomical knowledge informs effective preventive strategies and supports sustained wrist performance. This understanding guides lifestyle decisions that preserve joint integrity and minimize injury risks.
Ergonomic Lifestyle Adjustments
Many wrist issues originate from repetitive stress and improper positioning during routine activities. Essential ergonomic principles include neutral wrist positioning during computer use, regular activity breaks, and proper input device selection. Conscious movement integration and workspace optimization profoundly impact long-term wrist health.
Consider ergonomic accessories like wrist rests during extended computer or smartphone use. These simple modifications prevent excessive pressure accumulation and reduce repetitive strain risks.
Weight Control and Physical Activity
Healthy weight maintenance benefits all joints, including wrists. Excess body mass increases joint stress, elevating arthritis and degeneration risks. Balanced nutrition combined with wrist-specific exercises like controlled curls enhances stability and prevents injuries.
Safe Lifting Protocols
Improper lifting techniques frequently cause wrist sprains and related injuries. Fundamental principles include knee bending, back straightening, and proper weight distribution. These mechanics prevent excessive wrist strain during lifting tasks.
Nutritional Support for Joints
Nutrient-dense diets rich in anti-inflammatory compounds support joint health. Emphasize colorful fruits, vegetables, and quality proteins in your diet. While supplements like glucosamine may offer benefits, always consult healthcare providers before beginning any supplementation program.
Stress Reduction Techniques
Chronic tension negatively impacts musculoskeletal health, including wrists. Relaxation practices like mindful breathing, yoga, or meditation help manage stress. Concurrent postural awareness prevents unnecessary wrist strain from poor alignment during daily activities.