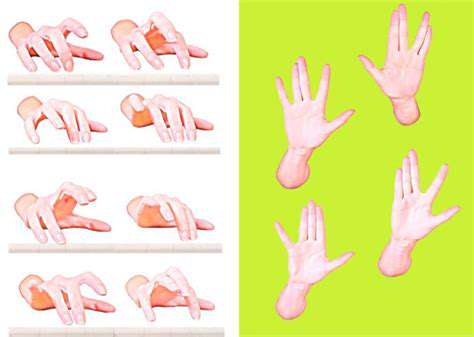
The Role of Genetic Testing in Predicting Hand Disorders
The Role of Genetic Testing in Early Detection and Prevention

Genetic Testing and Hearing Loss
Genetic testing plays a crucial role in understanding and diagnosing hearing loss, a condition affecting millions worldwide. Identifying the specific genetic mutations responsible for hearing impairment allows for more accurate diagnoses, personalized treatment strategies, and potentially, preventative measures in future generations. This knowledge is vital for families affected by inherited hearing loss.
Understanding the genetic basis of hearing loss is transforming how we approach diagnosis and management. It's no longer just about treating symptoms; it's about addressing the root cause and offering more targeted interventions.
Types of Genetic Tests for Hearing Loss
Various genetic tests are available to detect different types of hearing loss. These tests can analyze specific genes known to be associated with auditory function, looking for mutations or variations that may cause hearing impairment. Some tests focus on specific genes linked to particular forms of hearing loss, while others utilize broader panels to screen for a wider range of genetic causes.
Comprehensive genetic testing can identify the underlying genetic defects responsible for hearing loss, guiding medical decisions and family counseling. The choice of test depends on the patient's specific situation and the suspected genetic cause of the hearing loss.
Diagnostic Accuracy and Precision
Genetic testing offers a high degree of diagnostic accuracy, particularly when combined with other clinical evaluations. By identifying the specific gene mutation, clinicians can provide a more definitive diagnosis and understand the potential severity and progression of the hearing loss.
This precision is invaluable for tailoring treatment plans and providing accurate prognosis for individuals and families affected by hearing loss. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for facilitating appropriate interventions and counseling.
Predictive Testing and Family Counseling
Genetic testing isn't just about diagnosing current hearing loss; it also allows for predictive testing in at-risk family members. This is especially important for individuals with a family history of hearing loss, as they may be carriers of the same genetic mutations, potentially leading to the same condition. This knowledge empowers families to proactively address their health concerns.
Predictive testing enables proactive strategies for managing hearing health within families. This approach helps in early intervention and potentially reduces the severity of hearing loss in future generations. Genetic counseling plays a critical role in interpreting results and discussing implications for family members.
Personalized Treatment Strategies
Knowing the specific genetic cause of hearing loss enables the development of Personalized treatment strategies. Different genetic mutations may respond to distinct therapies or management approaches. This personalized approach aims to maximize treatment effectiveness and minimize potential side effects.
This level of individualized care is essential for optimizing outcomes and improving the quality of life for individuals with hearing loss. It represents a significant advancement in the field, moving towards a more precise and targeted approach to treatment.
Prenatal Genetic Testing
Prenatal genetic testing for hearing loss can identify potential hearing problems before birth. This allows parents to prepare for the possibility of hearing impairment and make informed decisions regarding prenatal care and potential interventions. Early detection is crucial for implementing appropriate support and interventions.
Ethical Considerations of Genetic Testing
While genetic testing for hearing loss offers significant advantages, ethical considerations are paramount. Privacy, confidentiality, and the potential psychological impact of results on individuals and families need careful consideration. Genetic testing should be approached with a comprehensive understanding of its implications, and proper counseling should be provided.
Informed consent and ethical guidelines for genetic testing are critical for protecting patient rights and ensuring responsible use of this powerful technology. Careful consideration of the potential social and psychological implications of genetic testing results is paramount.
Personalized Treatment Strategies Based on Genetic Profiles
Tailored Approaches to Patient Care
Personalized treatment strategies are becoming increasingly crucial in modern healthcare. This approach recognizes that individuals respond differently to various treatments due to genetic predispositions, environmental factors, and lifestyle choices. By considering these unique characteristics, healthcare providers can develop more effective and efficient treatment plans, leading to better patient outcomes and reduced side effects. This personalized approach fosters a more proactive and collaborative relationship between patients and their care teams, empowering patients to take an active role in their own well-being. Ultimately, the goal is to tailor interventions to the specific needs of each patient, optimizing treatment effectiveness and minimizing potential harm.
A key component of personalized treatment involves thorough assessments to understand the individual's specific circumstances. This includes gathering detailed medical histories, conducting genetic testing when appropriate, and considering lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and stress levels. By integrating all these data points, healthcare professionals can gain a deeper understanding of the patient's unique profile and how it interacts with the condition being treated. This deep understanding allows for the development of targeted treatment plans that are more likely to achieve desired outcomes and minimize unnecessary complications.
Optimizing Treatment Outcomes through Precision Medicine
Precision medicine plays a vital role in implementing personalized treatment strategies. It leverages advanced technologies and data analysis to identify the specific genetic and molecular characteristics of a disease in an individual patient. This allows for the development of targeted therapies that are more likely to be effective and well-tolerated, compared to traditional, one-size-fits-all approaches. By tailoring treatments to the specific genetic makeup of each patient, precision medicine aims to minimize adverse effects and maximize the effectiveness of care.
The integration of genomic data and other relevant information into treatment decisions is a key aspect of precision medicine. This data-driven approach empowers healthcare professionals to make more informed choices about the most appropriate therapies for each patient, potentially leading to improved treatment outcomes and increased patient satisfaction. Moreover, the use of biomarkers to monitor treatment response can help healthcare providers adjust treatment plans as needed, allowing for a more dynamic and personalized approach to care. This dynamic approach is essential for optimizing treatment outcomes and ensuring patient well-being.
Another crucial element of precision medicine is the use of advanced computational tools to analyze large datasets of patient information. This allows for the identification of patterns and relationships that would be impossible to discern through traditional methods. By analyzing these patterns, researchers can develop new hypotheses and refine existing models of disease progression, ultimately leading to more effective and targeted treatments. This advanced data analysis is critical to the continual advancement and refinement of personalized treatment strategies.