Understanding the Anatomy of Finger Tendons in Detail
Understanding the Anatomy of Finger Tendons
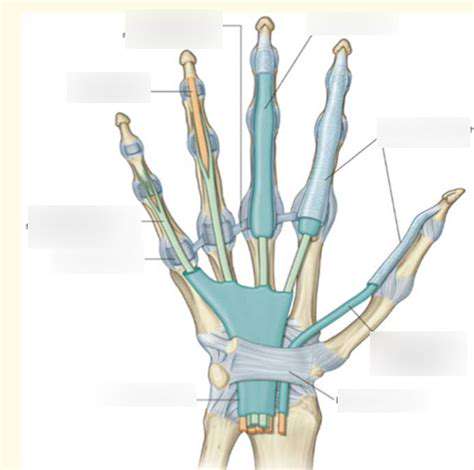
Finger tendons are essential components of the hand's intricate system for movement. These tiny, fibrous cords, connecting muscles in the forearm to the bones of the fingers, enable a wide range of actions, from delicate tasks like writing to powerful grips. Understanding their structure and function is crucial for recognizing and treating various hand conditions.
The precise arrangement and interplay of these tendons allow for the complex interplay of finger flexion and extension. Disruptions to this system, whether due to injury or disease, can significantly impact a person's ability to perform daily activities.
The Structure of Finger Tendons
Finger tendons are composed primarily of collagen fibers, arranged in a highly organized manner. This specialized structure provides the necessary strength and flexibility for the repetitive movements the hand performs throughout the day. The tendons are encased within protective sheaths, known as tendon synovial sheaths, which reduce friction and allow for smooth gliding during movement.
These sheaths contain synovial fluid, a lubricant that further minimizes friction between the tendons and surrounding structures. This intricate structure is crucial for the smooth and efficient operation of the hand.
Types of Finger Tendons
The finger tendons are categorized into flexor and extensor tendons, each playing a specific role in finger movement. Flexor tendons are responsible for bending the fingers, while extensor tendons straighten them. Understanding the specific functions of these different tendon types is essential for diagnosing and treating conditions affecting hand function.
This distinct organization allows for precise control and coordination of finger movements, enabling a wide range of actions.
The Role of Tendon Sheaths
Tendon sheaths, or synovial sheaths, are crucial for the smooth operation of finger tendons. These lubricated tunnels envelop the tendons, reducing friction and enabling effortless gliding during finger movements. Damage or inflammation within these sheaths can lead to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
The Importance of Finger Tendons in Daily Life
The delicate interplay of finger tendons is fundamental to everyday tasks. From typing on a keyboard to holding a cup of coffee, the precise control and power provided by these tendons are essential for a wide range of activities. Disruptions to these tendons can severely impact quality of life.
Common Conditions Affecting Finger Tendons
Various conditions can affect finger tendons, including tendonitis, which is inflammation of the tendons themselves. Another common issue is tenosynovitis, inflammation of the tendon sheaths, leading to pain, swelling, and stiffness. Understanding the symptoms and potential causes of these issues is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment.
These conditions can range from simple overuse to more serious injuries, requiring appropriate medical attention for prompt recovery.
Treatment Options for Tendon Injuries
Treatment options for finger tendon injuries vary depending on the severity and specific condition. Conservative approaches, such as rest, ice, and medication, often prove effective for mild cases. Physical therapy plays a critical role in restoring range of motion and strength. In more severe instances, surgical intervention might be necessary to repair or reconstruct damaged tendons.
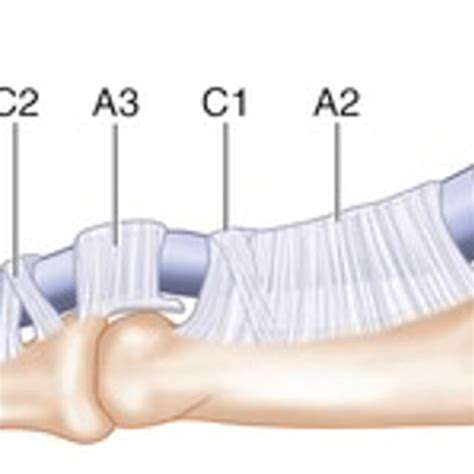
The Digital Sheaths and Their Importance
The Evolution of Digital Sheaths
Digital sheaths, encompassing everything from social media profiles to online identities, are constantly evolving in response to technological advancements and societal shifts. This evolution is characterized by an increasing complexity and interconnectedness, blurring the lines between the physical and digital realms. The sheer volume of data generated and shared online necessitates sophisticated management strategies for individuals to navigate this complex landscape effectively.
Early digital sheaths were relatively simple, primarily focused on personal information. Today, however, they encompass a vast array of digital footprints, including online activity, social interactions, and even financial transactions. This evolution reflects the growing importance of digital presence in modern life.
Impact on Personal Identity
The digital sheath significantly impacts how we perceive and present ourselves to the world. The curated narratives we construct online often differ from our real-life experiences, leading to a potential disconnect between our online and offline identities. This can create both opportunities and challenges, influencing our relationships, career prospects, and overall well-being.
Security and Privacy Concerns
The increasing reliance on digital sheaths raises serious security and privacy concerns. Protecting sensitive personal data from unauthorized access and misuse is paramount. Robust security measures and informed decision-making regarding data sharing are crucial for mitigating these risks. Users must actively manage their digital footprints and be aware of the potential vulnerabilities inherent in online interactions.
Data breaches and cyberattacks pose substantial threats, impacting individuals and organizations alike. Protecting personal information and safeguarding digital assets is a continuous challenge in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
The Role of Digital Sheaths in Professional Life
Digital sheaths play an increasingly important role in professional contexts. Online presence and reputation management have become integral components of career development. Navigating the professional landscape effectively requires a strategic approach to managing one's digital sheath. This includes carefully curating online content and proactively addressing potential reputational risks.
Professional networking and recruitment processes often rely heavily on digital platforms, requiring individuals to present a professional and trustworthy image.
Ethical Considerations
The use and management of digital sheaths raise numerous ethical considerations. Issues of data ownership, privacy rights, and algorithmic bias are becoming increasingly important. Transparency and accountability in the collection, use, and dissemination of personal data are crucial for establishing ethical standards in the digital realm.
Furthermore, the potential for manipulation and misinformation within digital sheaths necessitates critical thinking and media literacy skills. Users must be equipped to discern credible information from potentially misleading content.
Clinical Significance and Potential Injuries

Clinical Significance of Neurological Disorders
Neurological disorders encompass a wide range of conditions affecting the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. These conditions can manifest in various ways, from subtle cognitive impairments to debilitating motor deficits. Understanding the clinical significance of these disorders is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Early detection and intervention can significantly impact the course of the disease, improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
The clinical significance extends beyond the immediate symptoms. Neurological disorders often have long-term consequences, impacting daily activities, social interactions, and the overall well-being of individuals and their families. Addressing these broader implications is essential for comprehensive patient care.
Potential Impact on Patient Outcomes
The potential impact of neurological disorders on patient outcomes is substantial. The specific impact varies considerably depending on the disorder, its severity, and the individual's response to treatment. Effective treatment strategies aim to maximize functional independence and minimize disability.
Interventions targeted at restoring lost function, managing symptoms, and promoting adaptation to the condition are crucial for optimizing patient outcomes. This often requires a multidisciplinary approach, involving neurologists, therapists, and other healthcare professionals.
Diagnosis and Treatment Approaches
Accurate diagnosis of neurological disorders relies on a combination of clinical evaluation, neurological examinations, and advanced diagnostic tools. These tools can include imaging techniques, electrophysiological studies, and laboratory tests. Early and precise diagnosis is essential for timely intervention and to provide the most effective treatment approach.
Importance of Early Intervention
Early intervention in neurological disorders is of paramount importance. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can significantly impact the progression of the disease and prevent further deterioration. This can lead to improved outcomes, reduced disability, and a better quality of life for the affected individual.
Recognizing the early warning signs and symptoms is vital for seeking timely medical attention. This allows for prompt initiation of appropriate therapies and management strategies.
Role of Rehabilitation Therapies
Rehabilitation therapies play a crucial role in managing neurological disorders. These therapies are tailored to the individual's specific needs and goals, focusing on restoring lost function, improving mobility, and enhancing overall well-being. Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy are often integral components of a comprehensive rehabilitation program.
Prognosis and Long-Term Management
The prognosis for neurological disorders varies greatly depending on the specific condition, its severity, and the individual's response to treatment. Long-term management often necessitates ongoing medical care and support. This can involve regular follow-up appointments, medication adjustments, and adaptations to daily living to support the ongoing needs of the patient.
Public Health Implications
The public health implications of neurological disorders are significant. These conditions pose a substantial burden on healthcare systems and individuals and families affected by the conditions. Investing in research and support services is essential for improving the lives of those with neurological disorders and their families. Public awareness campaigns can help promote early diagnosis and encourage individuals to seek medical attention if they experience concerning symptoms.