Approaches to Maintain Healthy Wrist Joints
Understanding the Role of Posture in Wrist Health
Maintaining proper posture is crucial for overall well-being, and this extends significantly to the health of your wrists. Poor posture often leads to awkward positioning of the entire arm and hand, putting undue stress on the wrist joints. This can manifest in repetitive strain injuries, carpal tunnel syndrome, and other debilitating conditions. Understanding the subtle ways your body positions itself, from the alignment of your shoulders to the positioning of your forearms, is fundamental to preventing wrist problems. Addressing postural imbalances early on can significantly reduce the risk of long-term wrist pain and discomfort.
Postural issues stemming from prolonged periods of sitting, repetitive motions, or even certain sleeping positions can all contribute to wrist strain. For example, slouching at a desk, typing with your wrists bent, or sleeping with your arms awkwardly positioned can all contribute to chronic wrist pain. By consciously working to maintain a neutral spine and aligned shoulders, individuals can significantly reduce the strain placed on their wrists throughout the day. This proactive approach to posture is invaluable in preventing future wrist problems.
Practical Exercises and Stretches for Wrist Health
Incorporating simple exercises and stretches into your daily routine can significantly improve wrist health and flexibility. Regular wrist rotations, both clockwise and counter-clockwise, can help maintain joint mobility and prevent stiffness. Gentle wrist extensions and flexions, performed slowly and deliberately, can strengthen the supporting muscles and ligaments. These exercises, when performed consistently, can enhance the wrist's ability to withstand daily stresses and prevent the development of pain or discomfort.
Furthermore, incorporating wrist stretches into your routine can help alleviate tension and improve blood flow to the area. A simple wrist extension stretch, holding the position for 15-30 seconds, can help release tension in the forearm muscles and surrounding tissues. Similarly, a wrist flexion stretch, where you gently pull your hand towards your forearm, can target different muscle groups. Consistency in these stretches is key to maintaining a healthy and flexible wrist.
Beyond these basic movements, consider incorporating activities that promote overall upper body strength, such as light weightlifting or resistance band exercises. These exercises can strengthen the muscles that support the wrist, making them more resilient to injury and strain. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise program, especially if you have existing wrist conditions.
Regular stretching and exercise, combined with mindful posture awareness, form a powerful preventative strategy for maintaining a healthy wrist.
The Role of Wrist Strengthening Exercises
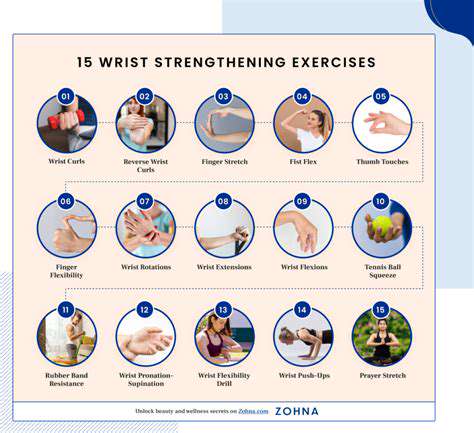
Importance of Wrist Strengthening
Wrist strengthening exercises play a crucial role in maintaining overall hand and arm health. Strengthening the muscles surrounding the wrist is vital for performing daily activities like typing, writing, and even carrying objects without experiencing pain or discomfort. These exercises improve the stability and control of the wrist joint, preventing injuries and promoting a higher quality of life. Strengthening the wrist also helps to improve grip strength, which can be beneficial for various tasks, from playing sports to performing household chores. Regular wrist exercises are a key component of a comprehensive fitness routine, addressing not only the wrist itself but also the surrounding muscles and joints.
Furthermore, wrist strengthening exercises are particularly important for individuals with existing wrist conditions. By building strength and endurance in the supporting muscles, these exercises can help alleviate pain and improve the range of motion in the affected wrist. This is often a crucial step in rehabilitation from injuries like carpal tunnel syndrome or tendonitis. Moreover, incorporating these exercises into a regular routine can help prevent future injuries, promoting long-term wrist health and functionality.
Effective Wrist Strengthening Exercises
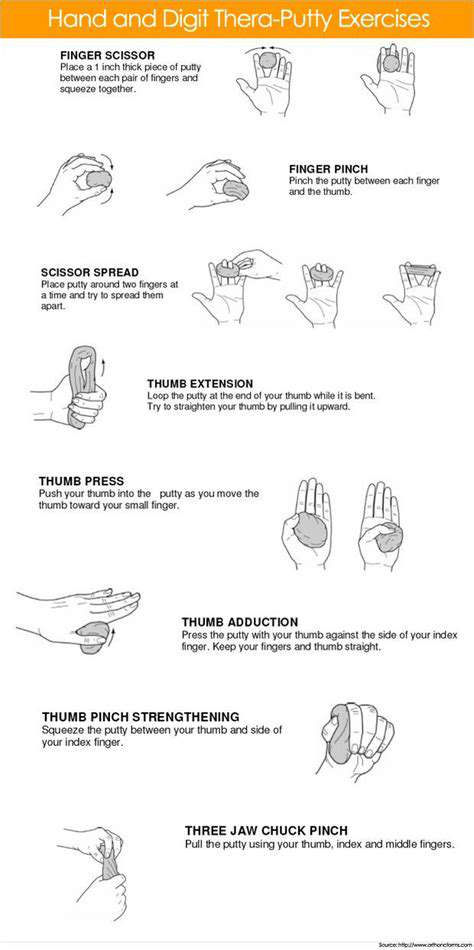
Numerous effective wrist strengthening exercises can be incorporated into a daily routine. A simple yet effective exercise is wrist curls, where you hold a weight and curl your wrist up and down. This exercise targets the muscles responsible for wrist flexion and extension. Another exercise is wrist extensions, where you hold a weight and extend your wrist upwards. These exercises work the opposing muscles, ensuring a balanced strengthening effect.
Incorporating these exercises regularly can significantly improve wrist strength and stability over time. It's essential to start with lighter weights and gradually increase the resistance as your strength improves. Proper form is crucial to avoid injuries and maximize the benefits of the exercises. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist to determine the best exercises and weight appropriate for your specific needs and conditions.
Using resistance bands or weight machines can also provide varied and effective wrist strengthening exercises. Progressive overload, increasing the difficulty of the exercises as strength improves, is key to maximizing results. Remember to listen to your body and rest when needed to prevent potential injuries. Consistency and patience are key to achieving optimal wrist strength.
Beyond simple curls and extensions, consider incorporating more complex exercises, such as wrist rotations and side-to-side movements. These exercises target different aspects of the wrist's range of motion and stability. By diversifying your routine, you can ensure a more comprehensive strengthening approach, leading to a healthier wrist over time.
Adopting a Supportive Lifestyle for Wrist Health
Understanding Wrist Anatomy and Function
The wrist is a complex joint, a crucial part of the human body's skeletal system, responsible for connecting the hand to the forearm. It's a collection of small bones, ligaments, tendons, and muscles that work in harmony to allow for a wide range of movements, from delicate fingertip manipulations to powerful hand grips. Understanding the intricate interplay of these components is paramount for maintaining optimal wrist health.
Understanding how these structures work together helps us appreciate the importance of proper posture and movement. Poor posture can put undue stress on the wrist, while repetitive motions can lead to overuse injuries. Knowledge of these anatomical elements is the first step towards a supportive lifestyle that prioritizes wrist health.
Identifying Potential Risk Factors
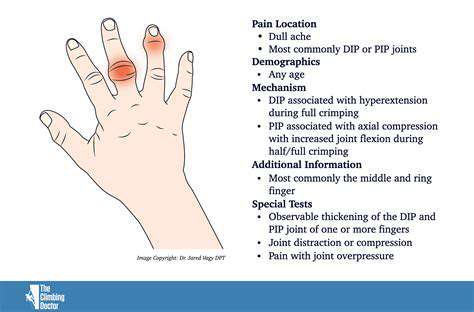
Numerous factors can contribute to wrist problems. Repetitive strain injuries, often stemming from prolonged typing, using a mouse, or engaging in certain sports, are common culprits. Furthermore, underlying medical conditions, such as arthritis or carpal tunnel syndrome, can significantly impact wrist health. Recognizing these potential risk factors is essential for implementing proactive measures to prevent or manage such issues.
Assessing individual risk factors, such as job requirements, hobbies, and family history, is critical in developing a personalized approach to wrist care. By identifying potential issues early on, individuals can take steps to mitigate the risk of developing wrist problems.
Ergonomic Considerations for Daily Activities
Ergonomics plays a vital role in maintaining wrist health. Proper workstation setup, including a well-adjusted chair, a monitor positioned at eye level, and a keyboard and mouse at an appropriate height, can significantly reduce strain on the wrist. These seemingly small adjustments can make a huge difference in preventing discomfort and injury.
Choosing the right tools and equipment can also make a notable impact. Using ergonomic keyboards and mice, for example, can help maintain a neutral wrist position, thereby minimizing the risk of repetitive strain injuries. Incorporating these ergonomic principles into daily activities is crucial for long-term wrist health.
The Importance of Proper Posture and Movement
Maintaining good posture throughout the day, whether sitting, standing, or walking, is critical for wrist health. Slouching or hunching over can put undue stress on the wrist and surrounding structures. Practicing good posture, including keeping the wrists straight and aligned with the forearms, is essential for preventing strain and injury.
Paying attention to the mechanics of daily movements is also important. Avoid twisting or forcefully bending the wrist during activities like lifting or carrying objects. Instead, use your entire body to lift, distributing the weight evenly and avoiding putting excessive pressure on the wrist.
The Role of Wrist Strengthening Exercises
Regular wrist strengthening exercises can significantly improve wrist strength and stability, reducing the risk of injury. Simple exercises, such as wrist curls, extensions, and rotations, can be performed at home or in the office to build strength gradually. Incorporating these exercises into a daily routine can help prevent wrist pain and maintain optimal function.
Consulting with a physical therapist or occupational therapist can provide personalized exercise routines tailored to individual needs and conditions. This professional guidance can ensure that exercises are performed correctly, preventing further injury and promoting optimal wrist health.
The Significance of Rest and Recovery
Adequate rest and recovery are often overlooked but are crucial for wrist health. Allowing the wrist to rest after periods of intense use or repetitive movements is vital for preventing overuse injuries. Taking regular breaks, especially during prolonged computer work or other activities that involve repetitive wrist movements, is essential.
Listen to your body and take breaks when needed. Rest and recovery periods allow the tissues in the wrist to repair themselves, reducing the risk of inflammation and pain. Prioritizing rest is a proactive approach to maintaining wrist health.
Seeking Professional Advice When Needed
If wrist pain persists or worsens, it's crucial to seek professional medical advice. A doctor or physical therapist can diagnose the underlying cause of the pain and recommend appropriate treatment options. Early intervention can often prevent the condition from worsening and help restore wrist function.
Don't hesitate to reach out to healthcare professionals if you experience persistent wrist pain, numbness, or tingling. They can provide a proper diagnosis and create a personalized treatment plan, ensuring optimal wrist health and function.
Preventing Repetitive Strain Injuries: Key Strategies

Ergonomic Workstation Setup
Maintaining a proper workstation setup is crucial for preventing repetitive strain injuries (RSIs). A well-designed workspace minimizes strain on your muscles, tendons, and joints. This includes ensuring your monitor is at eye level, your keyboard and mouse are positioned comfortably, and your chair provides adequate lumbar support. Adjusting your chair height and monitor placement to match your body's dimensions is essential. Failing to do so can lead to prolonged stress on the body and increase the risk of RSIs.
Consider using a wrist rest to support your wrists when typing or using a mouse. A comfortable chair with proper lumbar support can significantly reduce the strain on your back and improve posture. Investing in quality ergonomic equipment can be a worthwhile investment in your long-term health and productivity.
Proper Body Mechanics
Employing correct body mechanics is vital for reducing the risk of repetitive strain injuries. This involves using your larger muscle groups to perform tasks, instead of relying on smaller muscles. For instance, when lifting objects, use your legs rather than your back. Proper lifting techniques are paramount to minimize strain on the back and reduce the risk of lower back pain.
Maintaining a neutral spine position during prolonged computer work can significantly reduce the stress on your neck, shoulders, and back. Avoid hunching or slouching, as these postures can cause muscular imbalances and lead to pain.
Regular Breaks and Stretching
Taking regular breaks is essential to prevent muscle fatigue and stiffness. Taking short breaks every 30-60 minutes can greatly reduce the risk of repetitive strain injuries. These breaks should be used to stretch your muscles and move around to improve circulation and reduce tension.
Regular stretching exercises can help maintain flexibility and reduce the risk of muscle imbalances. Stretching specific muscle groups that are frequently used during work can prevent stiffness and discomfort. Incorporate simple stretches into your daily routine to maintain flexibility and prevent strain.
Task Rotation and Variety
Rotating tasks and introducing variety into your daily work can help prevent repetitive actions from causing strain. Switching between different tasks helps to distribute the workload across various muscle groups, reducing the risk of overuse in specific areas. This can help improve overall posture and reduce pain and discomfort.
Understanding Your Limits
Recognizing your physical limitations is essential to preventing repetitive strain injuries. Knowing your limits and understanding how your body responds to different tasks is crucial for preventing injuries. It is important to avoid pushing yourself too hard and rest when needed. Listening to your body and adjusting your work schedule accordingly can help prevent injuries.
If you experience any pain or discomfort, stop the activity immediately and seek professional medical advice. Ignoring pain can lead to more serious problems in the future. Taking proactive steps to prevent strain injuries is essential for maintaining long-term health and well-being.
Seeking Professional Advice
If you are experiencing repetitive strain or are concerned about your work posture, consulting with a physical therapist or occupational therapist can provide valuable insights. They can assess your specific needs and provide tailored recommendations to address any potential issues. Seeking professional advice is a crucial step in preventing further injury and ensuring proper recovery. Early intervention can prevent the worsening of symptoms and potentially long-term health problems.
A professional can help you develop a personalized plan to address any potential risks and improve your overall well-being. This personalized approach ensures that your needs are met and that you are set up for success in preventing repetitive strain injuries.