Creative Approaches to Enhance Finger Coordination
Unlocking the Hidden Potential of Your Fingers
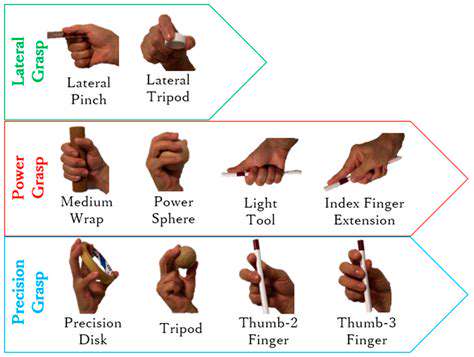
While traditional exercises have their place, there's a world of untapped potential waiting in your fingers. Each finger is unique, with its own strengths and weaknesses, and recognizing these differences allows for more targeted development. By focusing on individualized training, you'll notice faster progress in dexterity and control compared to generic drills.
Embracing the Power of Rhythm and Flow
Instead of practicing isolated movements, consider how musicians blend notes into melodies. This rhythmic approach creates natural flow that improves both timing and coordination. When you incorporate varied rhythmic patterns into your practice, you'll develop a more musical understanding of finger movement that transcends mechanical exercises.
Utilizing Technology for Personalized Feedback
Modern tools offer insights we never had before. Motion capture software and specialized apps can analyze your technique in real-time, highlighting areas that need adjustment. This immediate feedback lets you make precise corrections during practice sessions rather than developing bad habits.
The Importance of Visual Learning and Kinesthetic Awareness
Watching expert demonstrations while paying attention to the physical sensations in your hands creates powerful learning connections. This dual approach helps develop intuitive control that goes beyond intellectual understanding. Many find they progress faster when combining visual examples with focused physical practice.
Exploring Non-Musical Applications of Finger Mastery
The benefits extend far beyond musical instruments. Surgeons, artists, and craftspeople all rely on advanced finger control. Even everyday activities like typing or smartphone use become easier when you develop this specialized coordination through targeted practice.
Cultivating a Holistic Approach to Finger Training
True mastery involves more than physical technique. Managing performance anxiety, maintaining focus, and developing patience all contribute to better results. The mental aspects of practice often determine long-term success more than raw physical ability alone.
Integrating Movement and Mindfulness for Enhanced Focus
Slow, deliberate practice while fully attending to each movement builds neural pathways more effectively than rushed repetitions. This mindful approach leads to cleaner technique and helps prevent fatigue or injury from tense, inefficient movements.
Art and Craft: Sculpting with Precision
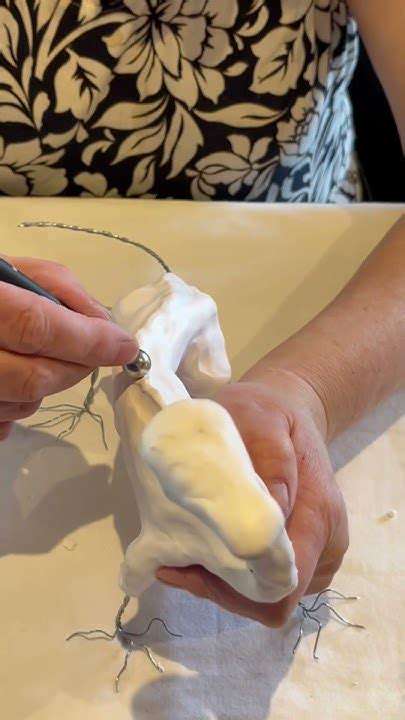

Exploring the Essence of Precarious Sculpting
This daring art form challenges our expectations about permanence in art. By working with fragile materials that might shift or collapse, artists capture the beauty of impermanence. These pieces often feel alive, changing with their environment in ways that static sculptures cannot.
Materials and Techniques in Precarious Sculpting
Artists might use anything from delicate ice crystals to carefully balanced found objects. The material choice becomes part of the artwork's meaning, with some pieces designed to gradually transform over their exhibition period. This requires deep understanding of material properties and creative problem-solving.
Conceptual Frameworks in Precarious Sculpting
These works often explore profound themes about existence and change. They make us confront how everything - including ourselves - exists in a temporary state. Some pieces deliberately incorporate elements of chance, allowing natural processes like weathering to complete the artistic statement.
Historical Context and Influences
While the concept feels modern, artists have explored impermanence for centuries. Japanese flower arranging (ikebana) and Tibetan sand mandalas both embrace transience. Contemporary precarious sculpture builds on these traditions while incorporating new materials and technologies.
The Role of the Viewer in Precarious Sculpting
These works create unique viewing experiences. You become aware that you're witnessing the artwork at a specific moment in its lifespan. This awareness creates a more active, thoughtful engagement than with permanent pieces.
The Future of Precarious Sculpting
As artists gain access to new responsive materials and interactive technologies, this field will continue evolving. We'll likely see more works that change based on viewer interaction or environmental conditions, creating ever more dynamic artistic experiences.
Gaming and Simulation: Virtual Challenges
Immersive Experiences in Gaming
Today's games create astonishingly real virtual worlds. Advanced VR systems now track full body movement, while haptic feedback lets players feel virtual objects. This immersion creates powerful learning environments where skills transfer more effectively to real-world applications.
Simulation for Skill Development
From medical students practicing surgeries to mechanics troubleshooting virtual engines, simulations provide safe training spaces. The ability to instantly reset after mistakes removes performance anxiety, allowing focused skill development. Many professionals now train this way before working with actual patients or equipment.
Realistic Environments and Challenges
The most effective simulations include unpredictable elements that mimic real-world complexity. A flight simulator that only presents perfect weather conditions wouldn't prepare pilots for actual emergencies. Good simulations balance structured learning with authentic challenges.
Impact on Finger Coordination
Precision gaming requires and develops remarkable finger control. Studies show that expert gamers develop hand-eye coordination rivaling that of surgeons. The varied input methods across different games - from touchscreens to complex controller combinations - create comprehensive finger training.
Training and Education Applications
Interactive simulations are transforming education. History students can walk through ancient cities, while chemistry students conduct virtual experiments too dangerous for classrooms. This experiential learning leads to better retention than traditional textbook methods.
Creative Approaches to Virtual Challenges
The best simulations incorporate compelling narratives that motivate users to push their skills. Rather than dry repetition, challenges unfold as part of engaging stories. This game design philosophy is being adopted by corporate trainers and educators seeking more effective teaching tools.