Exploring the Impact of Overuse on Hand Tendons
Tendons: The Silent Workers of the Hand
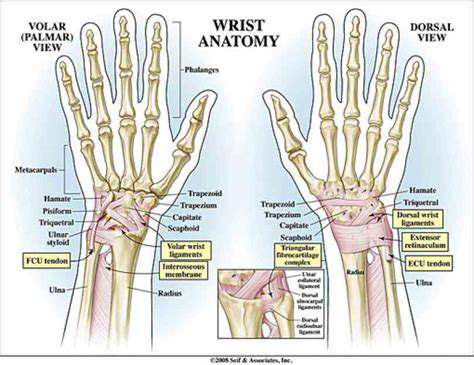
Tendons are the strong, fibrous cords that connect muscles to bones, enabling movement. In the hand, these tiny but crucial structures allow for a remarkable range of motion, from delicate fingertip manipulations to powerful gripping actions. Understanding the intricate anatomy of these tendons is paramount to comprehending how overuse injuries can develop and how to best treat them. They are essentially the silent workers, constantly transmitting forces from the muscles to the bones, allowing us to perform countless tasks without even thinking about it.
The hand's tendons are meticulously organized, each playing a specific role in the complex dance of movement. These specialized tissues, composed primarily of collagen fibers, possess a remarkable tensile strength, allowing them to withstand significant forces. However, repetitive or forceful movements can put undue stress on these delicate structures, potentially leading to inflammation, tears, and other overuse injuries.
Structure and Function of Hand Tendons
Hand tendons are categorized into flexor and extensor tendons, each responsible for different movements. Flexor tendons, positioned deep within the hand, are crucial for bending the fingers and wrist. They are encased within protective sheaths, known as tendon sheaths, which help reduce friction during movement. These sheaths are lined with synovial fluid, a lubricating substance that ensures smooth gliding of the tendons.
Extensor tendons, conversely, are responsible for straightening the fingers and wrist. They are located on the back of the hand and are also enveloped in protective sheaths. The intricate interplay between these flexor and extensor tendons allows for the precise and powerful movements essential for daily activities.
The Role of Tendon Sheaths
Tendon sheaths are crucial for the smooth functioning of hand tendons. These lubricated tunnels reduce friction between the tendons and surrounding tissues, allowing for effortless movement. This protective mechanism is essential for preventing the development of inflammation and pain, especially in the context of repetitive hand movements. Without this protective layer, tendons can easily become irritated and inflamed, leading to painful and debilitating conditions.
Problems within the tendon sheath, such as inflammation or swelling, can significantly impair the hand's ability to function. These issues, often a result of overuse, can lead to a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe pain and restricted movement.
Common Overuse Injuries to Hand Tendons
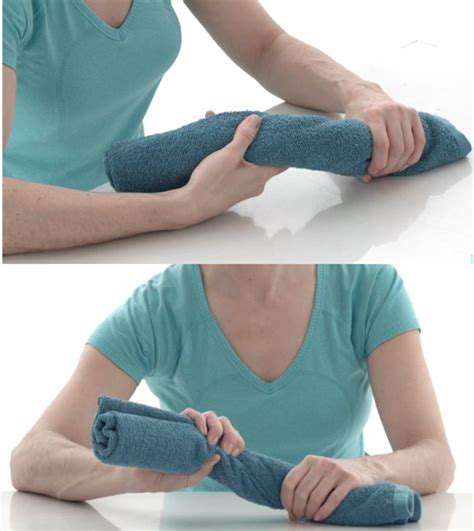
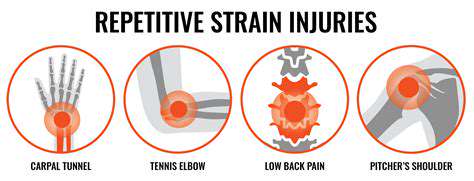
Overuse injuries to hand tendons are unfortunately quite common, particularly among individuals engaged in repetitive tasks or sports requiring significant hand movement. Carpal tunnel syndrome, De Quervain's tenosynovitis, and trigger finger are just a few examples of the types of injuries that can result from prolonged stress on the hand's tendons. Understanding the risk factors and symptoms associated with these conditions is vital for early intervention and prevention.
Proper rest, appropriate hand ergonomics, and in some cases, physical therapy, are essential for managing and preventing these injuries. Knowing the anatomy of the hand's tendons provides a vital foundation for understanding and addressing these common overuse issues.
Repetitive Strain Injuries: A Common Culprit
Understanding Repetitive Strain Injuries
Repetitive Strain Injuries (RSI) are a broad category of musculoskeletal disorders that result from repetitive motions or sustained awkward postures. These injuries often affect the hands, wrists, arms, neck, and shoulders, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced function. Understanding the root causes is crucial for effective prevention and treatment strategies. Many factors contribute to the development of RSI, from the nature of the work to the individual's physical condition and ergonomic setup.
These injuries can range from mild discomfort to severe pain that significantly impacts daily life. Proper recognition and early intervention are essential to prevent long-term complications and promote recovery.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Numerous factors can contribute to the development of RSI. Repetitive tasks, such as typing, assembly line work, or using tools, can place excessive stress on specific muscle groups and tendons. Sustained awkward postures, improper workstation setup, and lack of regular breaks can exacerbate the risk. Additionally, pre-existing conditions, such as arthritis or carpal tunnel syndrome, can make individuals more susceptible to developing these injuries.
Poor posture, insufficient rest periods, and inadequate ergonomic support can significantly increase the likelihood of developing RSI.
Using tools or equipment without proper training or inadequate hand placement can lead to repetitive micro-trauma, culminating in RSI.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms of RSI is crucial for timely intervention. Common symptoms include pain, stiffness, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the affected area. Symptoms often worsen with continued use of the affected body part, and can be accompanied by swelling and reduced range of motion. Early diagnosis is essential to ensure appropriate treatment and prevent further complications.
A comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional is necessary to accurately diagnose RSI. This may include physical examinations, imaging tests (such as X-rays or MRIs), and neurological assessments to identify the specific cause and extent of the injury.
Prevention Strategies
Implementing preventative measures is crucial to reduce the risk of developing RSI. Ergonomic assessments of workstations and tools are essential to ensure proper posture and minimize strain on the body. Regular breaks and stretching exercises can help alleviate muscle fatigue and prevent repetitive strain on soft tissues.
Using appropriate tools and equipment designed to reduce strain is vital. Proper training and education on safe work practices are equally important. Promoting awareness about the importance of maintaining good posture and taking regular breaks is crucial for both employers and employees.
Treatment and Recovery
Treatment options for RSI vary depending on the severity and location of the injury. Conservative approaches, such as rest, ice, and pain medication, are often the first line of treatment. Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and assistive devices may also be utilized to improve function and alleviate pain.
In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to address underlying structural problems. A multidisciplinary approach involving healthcare professionals, employers, and employees is often crucial for a successful recovery and return to work. Emphasis on proper rehabilitation techniques and ongoing monitoring are essential for long-term well-being.
Symptoms and Diagnosis: Recognizing the Signs

Initial Symptoms and Their Potential Significance
Identifying the initial symptoms of a potential medical condition is crucial for prompt diagnosis and treatment. Early detection allows for more effective intervention and often leads to better outcomes. Many conditions, while seemingly minor, can have significant underlying causes that require attention. Paying close attention to unusual changes in your body is essential, even if they seem insignificant at first.
Common initial symptoms can include fatigue, persistent headaches, unexplained weight changes, or changes in bowel or bladder habits. It is important to remember that these symptoms can sometimes be indicative of various conditions, and it's essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
Various diagnostic tests and procedures are employed to pinpoint the underlying cause of the symptoms. These tests range from simple blood tests to more complex imaging techniques, such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs. The specific tests ordered will depend on the nature of the suspected condition and the patient's overall health status.
Laboratory tests, like blood counts and biochemical profiles, can provide valuable insights into the body's internal functions and help identify potential abnormalities. Furthermore, imaging studies can visualize internal structures and help detect any structural or anatomical issues that might be contributing to the symptoms.
Importance of a Comprehensive Medical History
A detailed medical history is a cornerstone of the diagnostic process. This includes information about past illnesses, surgeries, allergies, medications, family medical history, and lifestyle factors. This comprehensive overview provides crucial context for understanding the current symptoms and potential contributing factors.
Gathering this information helps healthcare professionals form a more complete picture of the patient's overall health and identify potential risk factors or predispositions to certain conditions. A thorough medical history is vital for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans.
Physical Examination Techniques
A thorough physical examination is another critical aspect of the diagnostic process. This involves a detailed evaluation of the patient's vital signs, including blood pressure, heart rate, and temperature. Furthermore, the examination includes a systematic assessment of various body systems, such as the cardiovascular, respiratory, and neurological systems.
Physical examination findings, combined with the patient's medical history and diagnostic test results, provide a comprehensive picture of the patient's condition. This integrated approach allows for a more accurate and nuanced understanding of the underlying cause of the symptoms.
Differential Diagnosis and Consideration of Various Conditions
Differential diagnosis involves considering several potential conditions that could explain the observed symptoms. This process helps to narrow down the possibilities and focus on the most likely causes. Careful consideration of various conditions is crucial to avoid overlooking potentially serious underlying issues.
The physician will weigh the various possibilities based on the gathered information. This process involves evaluating the likelihood of each condition given the patient's unique presentation. This comprehensive approach to diagnosis is essential for providing the most accurate and effective treatment plan.
The Role of Patient Education and Collaboration
Patient education plays a critical role in the diagnostic process. Understanding the symptoms, the diagnostic process, and the potential conditions being considered can empower patients to actively participate in their care. This active engagement enhances the diagnostic process by providing valuable insights and facilitating a collaborative approach to finding a solution.
Open communication between the patient and healthcare provider is essential to ensure both parties are on the same page regarding the diagnosis and treatment plan. Patients should feel empowered to ask questions and express their concerns, fostering a collaborative relationship that leads to a more effective and satisfying outcome.