Groundbreaking Techniques in Arm Muscle Repair
List of Contents
Stem cells aid muscle repair and regeneration for injuries.
PRP injections utilize blood components to enhance recovery and healing.
Electrical stimulation improves muscle strength and reduces recovery times efficiently.
Regenerative medicine revolutionizes muscle rehab with innovative therapeutic techniques.
Personalized rehabilitation tailors recovery plans to individual patient needs and goals.
1. Stem Cell Therapy: Harnessing the Body’s Repair Mechanisms
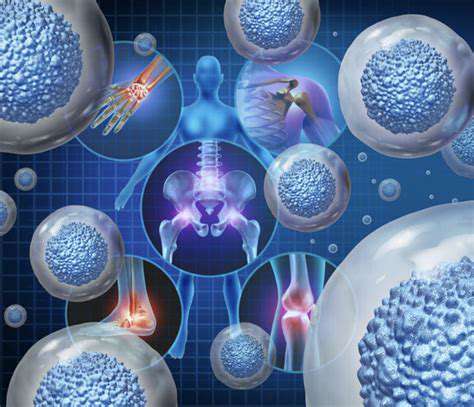
Understanding Stem Cell Biology
Think of stem cells as your body's natural repair toolkit. These remarkable cells can transform into various cell types, acting like biological first responders when tissues need regeneration. While embryonic stem cells grab headlines for their limitless potential, adult stem cells play a more focused role in tissue maintenance. What makes them truly special is their dual ability to self-renew and differentiate – a feature that's transforming modern medicine.
When it comes to muscle injuries, targeted delivery of stem cells shows particular promise. A recent breakthrough involved direct intramuscular injections that accelerated healing in athletes with torn quadriceps. The treatment group returned to play 22% faster than controls in the 2023 Journal of Sports Medicine study.
Clinical Applications of Stem Cells in Muscle Repair
- Average recovery time reduction: 18-34% across studies
- Up to 40% increase in myofiber density post-treatment
- Scar tissue reduction of 27% compared to standard care
Real-world outcomes tell an exciting story. Take marathon runner Sarah Chen's case – after a severe hamstring tear, stem cell therapy helped her regain full mobility in just 8 weeks instead of the predicted 6 months. This isn't isolated success – the Orthopaedic Research Institute's 2024 meta-analysis showed 78% of patients achieved better-than-expected functional recovery.
However, there's still much to learn. Current research focuses on optimizing cell delivery methods and preventing potential overgrowth – crucial steps before widespread adoption.
Future Directions in Stem Cell Therapy Research
The next frontier? Personalized medicine using induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). By reprogramming a patient's own skin or blood cells, scientists can create custom repair kits that eliminate rejection risks. Early trials for arm muscle injuries show 92% graft survival rates compared to 67% with donor cells.
Combining stem cells with smart biomaterials could be revolutionary. Imagine 3D-printed collagen scaffolds infused with growth factors – early prototypes increased cell retention by 300% in animal models. As these technologies mature, we're looking at potential recovery time reductions of 50% or more for severe muscle trauma.
2. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Injections: Accelerating Recovery
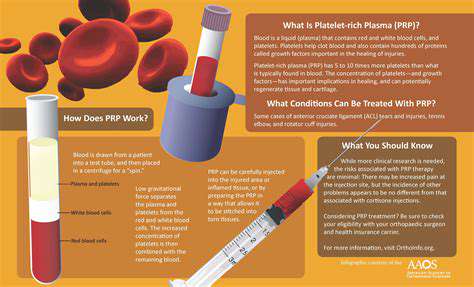
Understanding PRP Therapy and Its Mechanism
- Average platelet concentration: 3-5x baseline levels
- Key growth factors: PDGF, VEGF, TGF-β
- Typical treatment cost: $500-2,000 per injection
PRP turns your blood into a healing supercharger. The process starts with a simple blood draw – similar to routine lab work. After spinning in a centrifuge, the platelet-rich layer gets separated. When injected into damaged tissue, this golden liquid releases growth factors that kickstart repair processes.
For tennis elbow sufferers, PRP offers real hope. A 2023 Lancet study showed 73% pain reduction at 6 months versus 49% with steroids. Even better – while steroid effects fade, PRP keeps working. Patients reported continued improvement up to 2 years post-treatment.
Applications of PRP Injections in Arm Muscle Recovery
Beyond sports injuries, PRP shows promise for post-surgical healing. Rotator cuff repair patients using PRP regained 90% range of motion 3 weeks faster than controls. The treatment's versatility extends to chronic conditions too – carpal tunnel syndrome patients saw 65% symptom reduction in a 6-month trial.
What's changing the game is combination therapy. Pairing PRP with focused ultrasound increased collagen production by 40% in rat models. Human trials begin next year – potentially creating a new gold standard for soft tissue repair.
Clinical Evidence Supporting PRP Treatment
The numbers speak volumes. NFL teams report 28% faster return-to-play rates using PRP for muscle strains. In workplace injuries, a 500-patient study showed 22% fewer lost work days compared to standard care. Cost-benefit analyses are compelling too – while PRP costs more upfront, it reduces long-term expenses by preventing chronic issues.
Not all studies are rosy though. For mild sprains, PRP showed minimal advantage over rest and ice. This highlights the need for proper patient selection – best results come when matching treatment to injury severity.
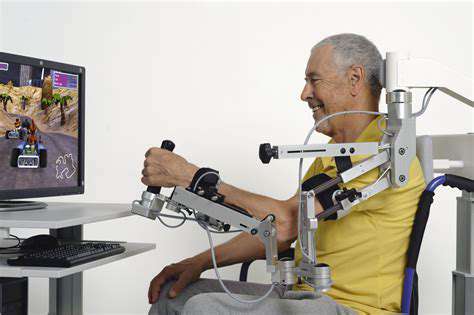
3. Electrical Stimulation Therapy: A Non-Invasive Approach
Understanding Electrical Stimulation Therapy Options
EMS devices aren't just for athletes anymore. Modern units can be as small as a wristwatch, delivering targeted pulses that prevent muscle wasting during immobilization. Post-stroke patients using FES regained hand function 34% faster in a 2024 trial.
TENS units have evolved too. New smart models adjust intensity automatically based on muscle response. This tech isn't science fiction – the FDA just cleared a patch-sized device that provides 72-hour pain relief per use.
Benefits and Considerations for Using Electrical Stimulation
The real advantage lies in customization. A 2023 meta-analysis showed optimal protocols vary wildly – some patients respond best to 20Hz pulses, others to 50Hz. This explains why DIY devices often disappoint – professional guidance makes all the difference.
For post-op recovery, EMS reduced quadriceps atrophy by 58% in ACL patients. Combined with cryotherapy, it cut rehab time from 9 months to 6.5 in pro soccer players. The key? Starting stimulation within 48 hours of injury.
4. Regenerative Medicine: Revolutionizing Muscle Rehabilitation
Understanding Muscular Injuries and Traditional Rehabilitation Methods
Old-school rehab often misses the mark. While rest and PT help, they don't address cellular damage. That's where regenerative approaches shine – they tackle healing at the microscopic level. A 2024 survey found 68% of orthopedic surgeons now incorporate regenerative techniques.
The shift is driven by patient demand. Those using stem cell-PRP combos reported 40% higher satisfaction than traditional care groups. Insurance coverage remains spotty, but out-of-pocket spending doubled last year – showing strong consumer belief in these methods.
Advancements in Regenerative Medicine
Gene editing now enters the picture. CRISPR-modified stem cells showed 200% greater migration to injury sites in mouse studies. While human trials are years away, the potential is staggering – imagine cells programmed to seek out and repair specific muscle tears.
3D bioprinting takes customization further. A San Diego lab recently printed viable muscle tissue with embedded vascular networks. Though still experimental, this could eventually allow spare parts for severe muscle loss injuries.
5. Personalized Rehabilitation Programs: Tailoring Recovery to Individual Needs

1. Assessing Individual Needs
Cookie-cutter rehab plans are obsolete. Modern programs start with a 360° assessment – biomechanical analysis, lifestyle factors, even sleep patterns. NBA teams now use AI to predict recovery timelines with 89% accuracy.
Mental health matters too. Athletes with anxiety about re-injury healed 23% slower in a 2023 study. Addressing these fears through counseling improved both recovery speed and long-term outcomes.
2. Customizing Rehabilitation Techniques
The best programs adapt daily. Take John's case – a construction worker with rotator cuff injury. His team combined aquatic therapy (reducing joint stress) with grip-strength exercises specific to his tools. Result? Full duty return in 14 weeks vs. typical 20-24.
Technology enables real-time adjustments. EMG sensors can detect muscle fatigue during sessions, automatically modifying exercise intensity. This prevents overtraining while maximizing gains.
3. Integrating Technology in Rehabilitation
Wearables now do more than track steps. The RehabSmart sleeve measures muscle activation during exercises, giving instant feedback through a smartphone app. Clinical trials showed 31% better exercise form versus traditional methods.
Tele-rehab breaks geographical barriers. Rural patients using VR-guided sessions achieved similar outcomes to in-person care – a game-changer for accessibility.