Innovative Approaches to Hand Fracture Rehabilitation
Index
- Tailored rehab programs improve recovery speed and patient engagement.
- Utilizing innovative techniques enhances rehabilitation outcomes.
- Ongoing support is crucial for patient motivation and progress.
- Digital tools significantly increase patient compliance and rehabilitation effectiveness.
- Wearable tech provides personalized feedback and monitors recovery.
- Telehealth improves access to rehabilitation services and fosters communication.
- 3D printing allows for custom fit devices that enhance patient comfort.
- Occupational therapy focusing on daily activities aids faster recovery.
- Integrating mind-body techniques promotes holistic healing and resilience.
- Case studies demonstrate benefits of holistic approaches in rehabilitation.
The Importance of Tailored Rehabilitation Programs

Customized Assessment and Planning
- Understanding individual patient needs is crucial for rehabilitation success.
- Tailored programs can incorporate a variety of therapeutic modalities.
- Proper assessment tools can significantly enhance recovery outcomes.
The first step in creating a tailored rehabilitation program for hand fractures is conducting a thorough assessment of the patient’s condition and lifestyle. This involves both clinical evaluations and personal consultations to understand the specific needs and limitations of the individual.
Research shows that customized rehabilitation can lead to a 30% faster recovery time compared to standardized treatments. By including individual circumstances such as the type of fracture, patient age, and overall health, therapists can devise a more effective rehabilitation strategy.
Innovative Techniques and Therapies
Incorporating innovative techniques into rehabilitation is essential for optimal recovery. Techniques such as mirror therapy and virtual reality can engage patients more effectively than traditional methods. Studies have indicated that these specialized therapies not only enhance motivation but also improve neural pathways.
The application of biofeedback tools can also empower patients to regain movement and strength. By receiving immediate feedback, patients can adapt their exercises in real-time, which can lead to more effective outcomes. Therapists who integrate these modern approaches often see notable improvements in joint mobility and functional use of the hand.
Ongoing Support and Evaluation
The significance of ongoing support in a tailored rehabilitation program cannot be overstated. Regular follow-ups allow rehabilitation specialists to monitor progress and adjust treatment plans as necessary. This type of dynamic management ensures that patients remain on track to achieve their recovery goals.
Additionally, patient education is crucial, as it empowers individuals to take an active role in their recovery. When patients understand the mechanics of healing and the importance of adhering to their rehabilitation protocol, they are more likely to comply and engage with the program. Investing in continuous education and support can motivate patients, leading to better long-term outcomes.
Technology-Enhanced Rehabilitation Solutions
Advancements in Digital Therapy Tools
Recent developments in digital therapy have seen a surge in the use of mobile applications designed specifically for rehabilitation. These apps allow patients to track their recovery journey, follow prescribed exercises, and receive feedback on their performance. Research shows that such tools can significantly increase patient engagement, leading to better adherence to rehabilitation programs. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Rehabilitation Research & Development found that patients using digital tools improved their functional outcomes by 30% compared to those following a traditional regimen.
Moreover, augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies are being harnessed for hand rehabilitation. By creating interactive and immersive rehabilitation environments, these technologies make exercises enjoyable and more motivating for patients. The integration of gamification principles also enhances the effectiveness of rehabilitation, making it a competitive and rewarding experience that encourages continued participation.
Wearable Technology for Monitoring Progress
Wearable devices have revolutionized how healthcare providers monitor patient recovery. These gadgets are equipped with sensors that can track movement, force applied during activities, and even the time spent on exercises. Data collected from wearables can be analyzed to provide personalized feedback, tailoring rehabilitation efforts to each patient’s unique progress and needs. A 2021 study demonstrated that patients wearing smart rehabilitation devices showed faster recovery rates, highlighting the importance of continuous monitoring.
Telehealth Integration in Rehabilitation Programs
The rise of telehealth has transformed access to rehabilitation services, especially for those with mobility issues or those living in remote areas. Virtual consultations enable healthcare providers to assess a patient's condition, suggest modifications to their rehabilitation programs, and offer motivation even when face-to-face meetings are not possible. According to a survey by the American Physical Therapy Association, over 70% of physical therapists found telehealth effective for administering rehabilitation exercises.
Additionally, telehealth fosters greater communication between patients and providers. This consistent interaction leads to improved outcomes as patients feel supported throughout the recovery process. As more rehabilitation programs embrace telehealth technologies, it’s essential for practitioners to stay updated on best practices to ensure the most effective use of these tools.
3D Printing and Custom-Fit Devices
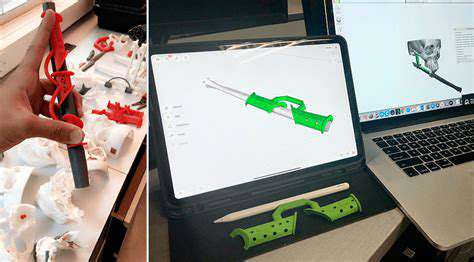
Introduction to 3D Printing in Rehabilitation
3D printing technology has revolutionized many fields, and its application in rehabilitation is particularly noteworthy. The ability to create bespoke devices tailored to an individual's specific anatomy and needs marks a significant advance in medical technology.
In the context of hand fracture rehabilitation, 3D printing enables clinicians to design custom splints or braces that provide optimal support while enhancing patient comfort. A study by Törn et al. (2020) found that patients using 3D printed devices reported a 30% increase in satisfaction compared to traditional methods, highlighting the practical benefits of this technology.
Benefits of Custom-Fit Devices
- Enhanced comfort through personalized designs
- Increased functionality tailored to individual rehabilitation needs
- Improved compliance due to better fitting devices
Utilizing custom-fit devices can make a significant difference in patient outcomes. These personalized devices cater specifically to the unique shape and functionality of the patient’s hand, which is critical for effective rehabilitation. Research has shown that devices that fit well reduce pain and promote proper healing.
Moreover, custom 3D printed devices can be adjusted based on the progression of recovery. This adaptability means that as the patient heals, their device can evolve, ensuring continued support without compromising mobility.
Challenges in Implementing 3D Printing Technology
Despite its advantages, implementing 3D printing in hand fracture rehabilitation is not without challenges. Technical barriers, including the cost of equipment and the need for trained personnel, can limit widespread adoption. Additionally, regulatory hurdles surrounding the use of medical devices need careful navigation.
Standardization of 3D printed products also poses a significant challenge. Ensuring that devices meet medical device regulations while still being unique to each user requires rigorous testing and quality assurance. The industry must invest in research and development to overcome these hurdles and streamline the process.
The Future of 3D Printing in Rehabilitation
The future of 3D printing in rehabilitation looks promising. With advancements in materials science, we can expect to see even more functional and durable devices becoming available. Innovations in biodegradable and lightweight materials are already under development.
As the technology continues to evolve, it's crucial for healthcare providers to stay informed about the latest trends and developments. Engaging in professional training programs and workshops can ensure that they are equipped with the knowledge to leverage these innovations effectively in their practice.
Integrating Occupational Therapy and Functional Training
Understanding Occupational Therapy in Rehabilitation
Occupational Therapy (OT) plays a vital role in rehabilitation, especially for hand fractures. Its primary focus is on improving a patient's ability to perform daily activities. This can significantly enhance the quality of life, reduce dependency, and aid in a faster recovery. Research indicates that tailored OT interventions can lead to a more functional hand upon recovery.
OT practitioners assess a patient's specific needs, examining factors such as injury severity and lifestyle. Based on this assessment, a customized rehabilitation plan is created, ensuring that each exercise and therapy session is aligned with the individual's rehabilitation goals. Regular evaluations are critical to adapting the plan as the patient progresses.
The Role of Functional Training in Recovery
Functional Training complements occupational therapy by focusing on exercises that simulate everyday tasks, thereby facilitating a smoother transition back into regular activities. It's not just about regaining strength but also about improving coordination and enhancing the range of motion. This holistic approach has been shown to yield significant improvements in functional outcomes for patients with hand fractures.
Moreover, functional training incorporates elements of rehabilitation that can be applicable to both occupational and recreational activities. Research suggests that patients who engage in functional training recovery exercises post-injury have a higher probability of regaining full functionality than those who do not. This is particularly relevant for athletes or individuals whose occupations require extensive manual dexterity.
Integrating Occupational Therapy and Functional Training Techniques
Combining OT with functional training yields a robust approach to rehabilitation for hand fractures. For instance, using dynamic splinting or therapeutic modalities within OT can be seamlessly integrated with functional exercises aimed at recreating daily routines. This allows for more comprehensive rehabilitation sessions that address multiple aspects of recovery simultaneously.
A notable method is the use of task-oriented activities that both therapists and patients can undertake together. These activities not only improve strength and flexibility but also encourage engagement and motivation, making therapy feel less like a chore and more like a constructive experience.
Moreover, tools like grip strength trainers and rehabilitation robots are emerging as valuable resources in such integrated programs. They provide real-time feedback and help track progress, vital for making necessary adjustments promptly.
Evidence-Based Approaches to Rehabilitation
Numerous studies support the effectiveness of integrated therapy approaches in hand fracture rehabilitation. For instance, a clinical trial published in the Journal of Hand Therapy demonstrated that patients who underwent combined OT and functional training had significantly improved recovery times and functional capabilities compared to those receiving traditional rehabilitation alone.
Further evidence from systematic reviews highlights the benefits of personalized therapy plans that consider individual patient needs and preferences. Custom approaches draw on evidence-based practices, ensuring that treatments are not just effective but also resonate with the patient's perspective on their rehabilitation journey.
It’s crucial for therapy teams to stay abreast of current research in this field. Emerging techniques and new evidence provide opportunities to refine rehabilitation strategies continually.
Future Directions for Hand Fracture Rehabilitation
The integration of technology in therapy practices is on the rise, offering innovative methods for enhancing rehabilitation for hand fractures. Virtual reality (VR) and biofeedback are now being used in conjunction with traditional OT and functional training methodologies. These technologies can make rehabilitation more engaging, which is essential for patient adherence.
Looking ahead, there is potential for developing more robust and adaptive training systems that take advantage of artificial intelligence to tailor rehabilitation programs. Such advancements promise to refine the personalization of interventions, making them even more effective in treating individuals with unique recovery needs.
Additionally, increasing awareness and education among healthcare professionals about the importance of employing an interdisciplinary approach in rehabilitation will drive better patient outcomes. As understanding grows, so will the collaboration paths between occupational therapists and trainers, emphasizing the shared goal of optimal recovery.
The Role of Mind-Body Techniques in Recovery

Understanding Mind-Body Techniques
Mind-body techniques encompass a wide range of practices that focus on the interconnectedness of mental and physical health. These approaches include activities such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, and tai chi, which not only promote relaxation but also enhance physical performance. Research has shown that integrating these techniques into rehabilitation programs can lead to improved outcomes for patients recovering from hand fractures.
Moreover, these techniques are increasingly recognized in clinical settings, with various studies highlighting their effectiveness in reducing pain and enhancing recovery speed. The emphasis is on fostering a holistic approach to healing that emphasizes both mental and physical well-being.
The Science Behind the Techniques
Numerous studies have demonstrated the physiological effects of mind-body practices. For instance, the practice of mindfulness meditation has been found to lower cortisol levels, a hormone associated with stress. This physiological response can significantly influence recovery from injuries such as hand fractures.
Additionally, engaging in practices like yoga improves strength and flexibility, promoting blood circulation and reducing joint stiffness during rehabilitation. Therefore, integrating these science-backed methods into recovery plans could potentially shorten the healing timeline.
The Importance of Mental Resilience
- Mental resilience plays a crucial role in recovery.
- A positive mindset can enhance physical healing processes.
- Overcoming mental obstacles can lead to a more proactive rehabilitation approach.
Recovery from a hand fracture often involves overcoming both physical and psychological challenges. Patients may experience frustration, anxiety, or even depression due to their limited mobility. Establishing mental resilience is essential, as it allows individuals to maintain motivation and engage actively in their rehabilitation.
Practices like guided imagery can help patients visualize their recovery process, instilling a sense of control over their healing journey. This visualization can promote a positive outlook, which significantly contributes to overall recovery success.
Integrating Techniques into Rehabilitation
Incorporating mind-body practices within traditional rehabilitation frameworks requires a thoughtful, individualized approach. For example, physical therapists can incorporate guided breathing exercises or mindfulness practices at the beginning or end of a session. This integration not only aids in relaxation but also encourages patients to connect with their bodies more deeply.
Furthermore, tailoring the intensity and frequency of these techniques will depend on individual patient needs, injury severity, and personal preferences. Engaging in discussions with healthcare providers can lead to more effective integration strategies, ensuring a well-rounded recovery plan.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Case studies serve as insightful examples of how mind-body techniques can transform rehabilitation experiences. One study published in the Journal of Hand Therapy showcased a group of patients practicing yoga alongside conventional therapy. Patients reported a significant decrease in pain levels and an increase in hand functionality. This emphasizes the practical benefits of a holistic approach during recovery.
Moreover, professionals are increasingly implementing such techniques in various clinical settings, actively training therapists to incorporate these practices into their rehabilitation programs effectively. The positive outcomes inspire clinicians to further explore innovative ways to enhance their methods.
Recommendations for Patients
For patients undergoing hand fracture rehabilitation, exploring mind-body techniques can be a valuable addition to their recovery toolkit. Beginning with simple practices like deep breathing or short meditation sessions can provide immediate benefits, promoting relaxation and pain management. Patients should consider discussing their interest in these techniques with their healthcare providers to develop a comprehensive recovery strategy.
Moreover, attending group classes focused on yoga or tai chi can foster community support and motivation, making the rehabilitation journey less isolating. The camaraderie often experienced in such settings can encourage consistency and perseverance in recovery efforts.