Protocols for Restoring Hand Movement
- Light touch testing with cotton wisps
- Pinprick sensation assessment
- Two-point discrimination measurements
- Temperature perception checks
Mapping sensory deficits helps clinicians understand the neurological impact of the condition and guides appropriate therapy interventions.
Assessing Pain and Discomfort
Pain frequently accompanies hand impairments, potentially limiting rehabilitation participation. A thorough pain evaluation considers:
- Location (specific joints or diffuse areas)
- Quality (sharp, dull, burning)
- Intensity (using standardized scales)
- Triggers (movement, pressure, rest)
Tracking pain patterns helps therapists adjust treatment intensity and select appropriate modalities. Effective pain management often determines rehabilitation success by enabling patients to engage fully in therapeutic activities.
Functional Limitations and Impact on Daily Life
The true measure of hand impairment lies in its effect on everyday activities. Clinicians assess:
- Self-care tasks (eating, dressing, hygiene)
- Work-related demands
- Leisure activities
- Social participation
Patient interviews reveal personal perspectives about functional challenges. This collaborative approach ensures rehabilitation targets the most meaningful goals, whether that's returning to work or playing musical instruments again.
Pharmacological Interventions and Their Role

Pharmacological Approaches to Managing Anxiety
Medications serve as valuable tools in anxiety management, helping restore emotional balance. These pharmaceutical agents work by adjusting brain chemistry to reduce excessive worry and physical symptoms. Treatment selection depends on:
- Anxiety disorder type
- Symptom severity
- Patient health history
- Potential medication interactions
Common medication classes include SSRIs, SNRIs, and occasionally benzodiazepines for short-term relief. Each category offers distinct benefits and considerations.
Targeting Specific Neurotransmitter Systems
Anxiety disorders often involve imbalances in brain chemicals like serotonin and GABA. Medications aim to:
- Enhance serotonin availability (SSRIs)
- Boost both serotonin and norepinephrine (SNRIs)
- Increase GABA activity (benzodiazepines)
Understanding these mechanisms helps clinicians match medications to individual neurochemical profiles, optimizing treatment effectiveness.
Types of Medications and Their Mechanisms
SSRIs like sertraline gradually increase serotonin levels, often producing noticeable improvement within 4-6 weeks. SNRIs such as venlafaxine provide dual neurotransmitter modulation, sometimes benefiting patients who don't respond to SSRIs alone. Benzodiazepines offer rapid relief but require cautious use due to dependence risks.
Individualized Treatment Plans and Considerations
Effective medication management requires personalization. Factors influencing decisions include:
- Age and metabolism
- Co-existing medical conditions
- Medication tolerance
- Lifestyle factors
Regular provider-patient communication ensures optimal dosing and timely adjustments, maximizing benefits while minimizing side effects.
Potential Side Effects and Monitoring
While generally safe, anxiety medications may cause:
- Initial nausea or headaches
- Sleep pattern changes
- Sexual side effects
- Weight fluctuations
Ongoing monitoring helps identify and manage these effects. Most side effects diminish over time as the body adjusts, but persistent issues may warrant dosage changes or medication switches.
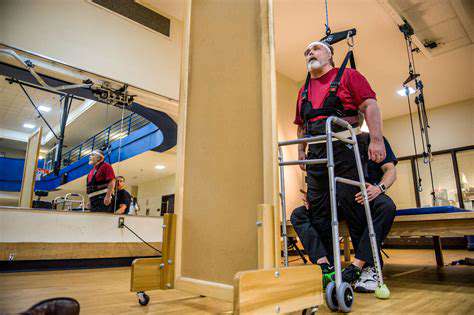
Physical Therapy Protocols for Hand Rehabilitation

Initial Evaluation and Assessment
A thorough initial assessment establishes the foundation for effective hand therapy. The evaluation process includes:
- Detailed injury/condition history
- Range of motion measurements
- Strength testing
- Sensory evaluation
- Functional capacity assessment
This comprehensive approach identifies specific impairments and guides targeted intervention strategies. Baseline measurements enable precise progress tracking throughout rehabilitation.
Therapeutic Exercises and Activities
Hand therapy incorporates progressive exercise regimens:
- Early-phase: Gentle range of motion
- Mid-phase: Strengthening exercises
- Late-phase: Functional task practice
Activity-based therapy bridges the gap between clinical exercises and real-world function, helping patients regain practical skills for daily living and work tasks.
Manual Therapy Techniques
Hand therapists employ specialized manual techniques including:
- Joint mobilization for stiffness
- Soft tissue release for tight structures
- Nerve gliding for irritated nerves
These hands-on methods complement exercise programs, addressing specific tissue restrictions that limit recovery.
Patient Education and Compliance
Successful rehabilitation depends on patient understanding and participation. Key educational components include:
- Condition explanation
- Home exercise instruction
- Activity modification guidance
- Pain management strategies
Clear communication and collaborative goal-setting enhance treatment adherence and outcomes. Patients who understand their rehabilitation process typically achieve better results.
Imagine strolling beside Venetian waterways, where gentle waves kiss ancient stone walls in rhythmic harmony. The atmosphere blends aromas of fresh-baked bread, blooming flowers, and savory spices drifting from neighborhood trattorias. This sensory symphony creates the perfect backdrop for romantic moments along Venice's enchanting canals.
Surgical Interventions: When Necessary for Optimal Outcomes
Minimally Invasive Techniques
Modern surgical approaches increasingly favor minimally invasive methods offering significant advantages:
- Smaller incisions
- Reduced tissue trauma
- Faster recovery
- Lower infection risk
Advanced technologies like laparoscopy and robotic systems enhance surgical precision. These techniques continue evolving, expanding their applications across surgical specialties.
Open Surgical Procedures
Traditional open surgery remains essential for certain complex cases. Advantages include:
- Direct visualization
- Complete access
- Flexibility for unexpected findings
While requiring longer recovery, open techniques provide unparalleled access when dealing with extensive pathology or complicated anatomy.
Post-Operative Care and Rehabilitation
Comprehensive recovery programs incorporate:
- Pain control
- Wound care
- Early mobilization
- Gradual strengthening
Multidisciplinary teams coordinate care to optimize healing and functional restoration. Rehabilitation progresses through phases tailored to each patient's recovery timeline.
Adaptive Devices and Assistive Technologies
Adaptive Devices for Hand Movement Restoration
Specialized tools help compensate for impaired hand function, ranging from simple splints to sophisticated robotic aids. These devices:
- Support weakened movements
- Protect healing structures
- Enable functional tasks
Occupational therapists guide device selection based on individual needs and recovery goals.
Assistive Technology for Enhanced Dexterity
Innovative technologies aid hand function through:
- Adaptive utensils
- Specialized computer interfaces
- Task-specific tools
These solutions empower users to maintain independence in daily activities despite physical limitations.
Ergonomic Considerations in Hand Rehabilitation
Effective device use requires attention to:
- Proper fit
- Comfortable positioning
- Efficient movement patterns
Ergonomic optimization prevents secondary strain and promotes sustained functional gains.
Neuroplasticity and Adaptive Devices
Therapeutic devices stimulate the nervous system's adaptability by:
- Providing sensory feedback
- Encouraging purposeful movement
- Gradually increasing challenges
Consistent, targeted practice promotes neural reorganization and functional improvement.
Protocols for Using Adaptive Devices
Structured usage guidelines ensure:
- Safe progression
- Optimal benefit
- Timely adjustments
Therapists customize protocols based on ongoing assessments of recovery progress.
Monitoring and Evaluation of Progress
Regular assessments track improvements in:
- Functional capacity
- Device proficiency
- Independence levels
Data-driven adjustments maintain rehabilitation momentum toward meaningful goals.
Ethical Considerations in Assistive Technology
Important ethical principles include:
- Accessibility
- Affordability
- User autonomy
- Cultural sensitivity
Technology solutions should respect individual dignity while promoting maximum functional independence.