Approaches to Enhance Arm Rehabilitation
Utilizing Assistive Devices and Adaptive Techniques
Assistive Devices for Enhanced Range of Motion
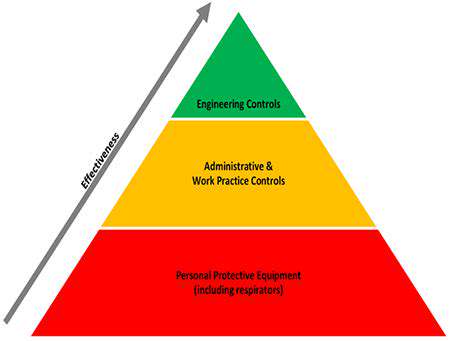
Assistive devices play a crucial role in improving range of motion during arm rehabilitation. These devices can provide support and stability, allowing individuals to perform exercises and activities that would otherwise be difficult or impossible. From lightweight splints designed to maintain a specific position to more complex motorized systems that assist with repetitive movements, the range of assistive devices available is constantly expanding. Proper selection and use of these devices, under the guidance of a physical therapist, is essential for maximizing their effectiveness and minimizing potential complications.
Consideration of the specific needs and limitations of each individual is paramount. Different types of assistive devices cater to various impairments and goals. For instance, a lightweight wrist splint might be appropriate for a patient recovering from a minor fracture, while a more sophisticated robotic arm system could be utilized in cases of significant neurological damage. Choosing the right device is not merely about functionality; it's also about user comfort and safety.
Adaptive Techniques for Exercise Modification
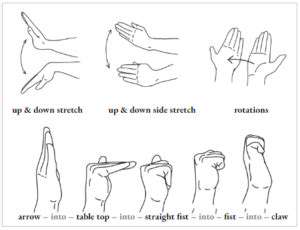
Adaptive techniques are crucial for modifying exercises to accommodate limitations in strength, dexterity, or endurance. These techniques allow individuals to safely and effectively engage in therapeutic activities, even when complete independence is not immediately achievable. This includes adjusting the weight, resistance, and complexity of exercises, as well as modifying the position and posture of the patient. For example, performing exercises with a modified grip using larger handles or utilizing resistance bands to gradually increase strength and endurance are both adaptive techniques that can be employed during arm rehabilitation.
Adaptive techniques are often tailored to the specific needs of the individual. This personalized approach ensures optimal progress and prevents potential harm. For instance, using a specialized mirror to enhance the visual feedback during exercises, employing adaptive tools to adjust the height of exercise equipment, or modifying the environment to create a safe and supportive space for rehabilitation are all valuable examples.
Furthermore, incorporating adaptive techniques can also significantly enhance patient motivation and engagement. By making exercises more manageable and accessible, patients are more likely to participate consistently and actively in their rehabilitation program. This active engagement is crucial for achieving optimal outcomes.
Strategies for Enhancing Motor Control and Skill Development
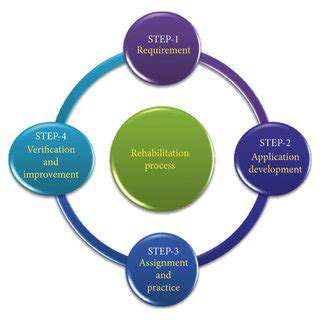
Strategies for enhancing motor control and skill development are essential components of arm rehabilitation. These strategies focus on restoring and improving the brain's ability to control and coordinate the movements of the affected arm. Techniques can involve specific exercises that target the re-training of neural pathways and the development of new motor skills. These techniques often involve targeted repetition and progressive challenges to foster neuroplasticity and motor learning. Implementing these strategies carefully under the supervision of a qualified healthcare professional is essential for ensuring safety and effectiveness.
Repetitive practice is frequently used to reinforce newly acquired motor skills, gradually increasing the complexity and speed of movements as the patient progresses. This progressive overload principle is crucial for stimulating the brain and promoting neural adaptations. Visual and tactile cues can also play a significant role in improving motor control. Using visual feedback, such as mirrors or video recordings, can help patients understand and correct their movements more effectively. Tactile feedback from specialized equipment or tools can also contribute to a more refined motor response.