Essential Techniques for Maximizing Finger Flexibility
The Importance of Finger Flexibility

Improving Dexterity and Fine Motor Skills
Finger flexibility plays a crucial role in enhancing dexterity, which is the ability to make precise and controlled movements with the hands. Improved dexterity is vital for a wide range of tasks, from intricate crafting projects to performing delicate medical procedures. Practicing finger exercises can significantly improve the range of motion in your fingers, allowing for greater precision and control. This increased dexterity can lead to better overall hand-eye coordination, which is beneficial for various activities in daily life.
Fine motor skills, which involve small, precise movements of the fingers and hands, are essential for everyday activities like writing, drawing, and buttoning clothes. Regularly practicing finger exercises can strengthen the muscles in the hands and fingers, leading to improved fine motor skills. The improved control and precision resulting from increased finger flexibility can make these everyday tasks easier and more efficient.
Enhancing Grip Strength and Stability
Strong, flexible fingers contribute to a firm and stable grip, allowing you to hold objects more securely. This is particularly important for activities like lifting heavy objects, playing sports, or even just carrying groceries. A good grip is essential for preventing injuries and ensuring safety in various situations. Regular stretching and exercise for your fingers can increase their strength and resilience over time.
Increased grip strength and stability can also reduce the risk of injuries, particularly in activities where you're handling objects with force. For example, gardeners will find that having a strong grip is paramount in handling tools and plants without injuring themselves. Improved stability also translates to better performance in sports and other physical activities.
Preventing Injuries and Relieving Pain
Maintaining finger flexibility can help prevent injuries, such as tendonitis, carpal tunnel syndrome, and other hand and wrist problems. These injuries often stem from repetitive motions or lack of flexibility, which can lead to inflammation and pain. By consistently working on finger flexibility, you can strengthen the supporting tissues and tendons, reducing the risk of these common injuries. This preventative measure is especially important for people who perform repetitive tasks with their hands.
Regular stretching and exercises can significantly alleviate existing pain and stiffness in the fingers and hands. If you're experiencing discomfort, consulting a physical therapist or occupational therapist can help you develop a personalized plan to improve finger flexibility and alleviate pain.
Improving Hand Coordination and Balance
Improved finger flexibility often leads to increased hand coordination, which is the ability to move your hands and fingers in a synchronized and controlled manner. This is crucial for tasks requiring precision and speed, such as playing musical instruments or using tools.
Enhanced hand coordination can also improve balance and stability. This is particularly important for activities that require a high degree of dexterity and precision, such as using tools, playing sports, or performing everyday tasks. The connection between finger flexibility and balance is not always immediately obvious, but the improved muscle control and coordination resulting from flexible fingers often leads to a more stable posture and improved balance.
Boosting Creativity and Artistic Expression
Finger flexibility is essential for artists and crafters who use their hands to create intricate designs and works of art. The ability to move the fingers with precision and control allows for a wider range of artistic expression and the creation of more detailed and nuanced pieces. This is especially true for activities like painting, sculpting, and knitting, where precise movements are necessary.
For musicians, finger flexibility is critical for playing instruments, such as the piano or guitar. The ability to move fingers quickly and precisely is essential for executing complex musical pieces. Enhancing finger flexibility can unlock a new level of musical expression and skill for musicians.
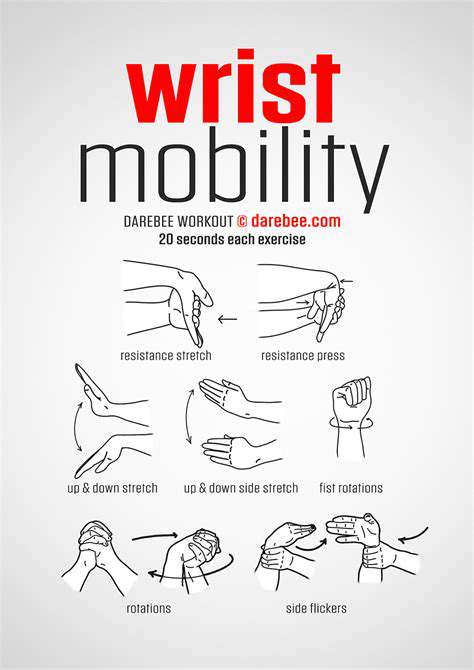
Simple Exercises for Improved Range of Motion

Warm-up Stretches
Before embarking on any exercise routine, it's crucial to prepare your body with some gentle stretches. These stretches help increase blood flow to your muscles, reducing the risk of injury and preparing your body for the workout ahead. A simple yet effective warm-up routine could involve dynamic stretches like arm circles, leg swings, and torso twists. These movements gradually increase your range of motion and get your muscles ready for more intense activity.
Engaging in a short warm-up routine is a significant step in preventing potential injuries during your workout. Consistent warm-up routines will contribute to a greater range of motion and improve overall flexibility.
Cardiovascular Activities
Incorporating cardiovascular activities into your routine is essential for improving overall fitness and range of motion. Activities like brisk walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling elevate your heart rate, improving blood circulation and delivering oxygen to your muscles. This increased blood flow helps to nourish your muscles, contributing to a greater range of motion and flexibility.
Cardiovascular exercises not only enhance your overall well-being but also enhance your body's ability to adapt to new movements. Consistent cardiovascular exercises also contribute to a healthier body composition and improve your overall physical function.
Resistance Training
Resistance training, whether using weights or resistance bands, is crucial for building strength and increasing muscle mass. Stronger muscles provide more support for your joints, reducing stress and strain, which ultimately contributes to a greater range of motion. Exercises like squats, lunges, push-ups, and rows are excellent examples of resistance training exercises that can be easily incorporated into your routine.
Resistance training is a key component in improving your range of motion and overall physical health. It is important to start with lighter weights and gradually increase the intensity as you progress. Proper form is crucial to prevent injuries and maximize results.
Flexibility Exercises
Stretching is a vital component of any exercise program aimed at improving flexibility and range of motion. Stretching helps increase the elasticity of your muscles and tendons, allowing them to move through a wider range of motion without pain or stiffness. Static stretches, held for 15-30 seconds, are particularly beneficial for improving flexibility. Examples include hamstring stretches, quad stretches, and chest stretches.
Regular stretching can significantly improve your flexibility and range of motion. Incorporating stretching into your routine helps maintain a healthy range of motion, reducing the risk of injury and promoting overall well-being.
Balance Exercises
Balance exercises are often overlooked but play a significant role in maintaining a healthy range of motion. Exercises that challenge your balance, such as standing on one leg, heel-to-toe walking, or using a balance board, improve proprioception, which is your body's awareness of its position in space. This improved awareness helps you move more efficiently and safely, reducing the risk of falls and improving overall mobility.
Progressive Overload
Progressive overload is a key principle for any exercise program. Gradually increasing the intensity, duration, or difficulty of your exercises over time is essential for continued improvement in range of motion. This could involve lifting heavier weights, performing more repetitions, or increasing the duration of your cardio sessions. Progressive overload ensures that your body is constantly challenged, promoting adaptation and improvement.
By progressively increasing the difficulty of your exercises you can effectively increase your range of motion and overall fitness. Consistent practice of progressive overload is essential for seeing tangible results over time.
Targeted Stretches for Specific Finger Limitations

Targeted Stretches for Hip Flexors
Hip flexors are a group of muscles crucial for everyday movements like walking, running, and sitting. Tight hip flexors can lead to a cascade of issues, including lower back pain, knee pain, and even posture problems. Addressing hip flexor tightness through targeted stretching is essential for overall mobility and pain relief. It's important to remember that consistency is key; regular stretching sessions will yield the best results.
Specific stretches for hip flexors often involve bringing the knee towards the chest, like the kneeling hip flexor stretch. This stretch targets the iliopsoas muscle, a primary hip flexor, and helps to lengthen and release tension in the area. Proper form is paramount to avoid straining other muscles and ensure effective stretching.
Targeted Stretches for Hamstrings
Hamstring stretches are vital for maintaining flexibility and preventing injuries, particularly in athletes. Tight hamstrings can affect running form, limit range of motion, and contribute to back pain. Consistent hamstring stretching can significantly improve athletic performance and reduce the risk of strains or tears. The importance of proper form cannot be overstated when stretching hamstrings.
A common hamstring stretch involves bending one knee and reaching for the foot. Holding this stretch for 30 seconds can promote muscle relaxation and improve flexibility. This stretch can be done while standing or seated, depending on individual preference and comfort level.
Targeted Stretches for Quads
Quads, or quadriceps muscles, are powerful muscles located at the front of the thighs. These muscles are essential for activities like jumping, running, and squatting. Tight quads can restrict movement and potentially lead to knee pain or discomfort. Regular stretching can help maintain flexibility and promote overall leg health.
A simple quad stretch involves pulling one heel towards your buttock, keeping your knee straight. Holding this stretch for a moderate duration, around 20-30 seconds, can effectively lengthen and release tension in the quadriceps muscles.
Targeted Stretches for Calves
Calf stretches are important for maintaining ankle mobility and preventing injuries, especially for runners and those participating in activities requiring a lot of movement. Tight calf muscles can hinder proper running form and increase the risk of strains or tears. Improving calf flexibility is crucial for overall lower body function. Consistent stretching can also reduce the risk of plantar fasciitis.
The classic calf stretch involves placing one leg behind the other while keeping your heels on the ground and leaning forward. Holding the stretch for 30 seconds, while keeping the front leg straight, can effectively stretch the calf muscles. This stretch is effective in targeting the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles.
Targeted Stretches for Lower Back
Stretching the lower back is crucial for maintaining proper posture and alleviating pain. Tight muscles in the lower back can lead to stiffness, discomfort, and even sciatica. Regular stretching can promote better blood flow to the area and reduce tension in the muscles. This can result in long-term relief and improved spinal mobility.
Lower back stretches often involve gently arching the back or twisting the torso. It is important to listen to your body and avoid any movements that cause sharp pain. Gentle stretches, like the child's pose, can be highly effective in relieving lower back tension.
The Role of Hand Therapy and Professional Guidance
Understanding Hand Therapy's Role in Recovery
Hand therapy plays a crucial role in the rehabilitation process for various hand injuries and conditions. A skilled hand therapist utilizes a range of specialized techniques, including exercises, splints, and modalities, to restore function, reduce pain, and improve dexterity. This personalized approach addresses the specific needs of each patient, tailoring treatment plans to maximize recovery potential. Understanding the complexity of the hand's intricate structure and its diverse functions is paramount to crafting effective treatment strategies.
From simple sprains to complex fractures and nerve damage, hand therapy addresses a wide spectrum of conditions. The expertise of a hand therapist extends beyond simply treating injuries. They educate patients on proper hand care, injury prevention strategies, and techniques to maintain optimal hand function in daily life. This holistic approach empowers individuals to actively participate in their recovery journey.
The Importance of Professional Guidance in Hand Care
Seeking professional guidance in hand care is essential for achieving optimal recovery and preventing further complications. A qualified hand therapist possesses the knowledge and experience to accurately diagnose hand problems, develop tailored treatment plans, and monitor progress effectively. This expertise ensures that interventions are targeted and efficient, leading to faster healing and improved outcomes.
Beyond physical treatment, professional guidance provides crucial education. Patients learn about the condition affecting their hand, its potential impact on daily activities, and strategies to manage discomfort or limitations. This knowledge empowers them to actively participate in their rehabilitation and achieve a higher quality of life.
Assessment and Diagnosis in Hand Therapy
Accurate assessment and diagnosis are critical first steps in effective hand therapy. A thorough evaluation by a hand therapist involves a detailed history, physical examination, and potentially imaging studies to identify the specific injury or condition. This process enables the therapist to understand the extent of the damage and the individual patient's needs.
Analyzing range of motion, strength, sensation, and dexterity provides valuable information. This comprehensive approach ensures that treatment plans are tailored to the specific needs of the individual, maximizing the likelihood of a successful recovery. Precise diagnostic tools are vital to ensure appropriate treatment protocols are implemented.
Tailoring Treatment Plans for Optimal Results
A key aspect of hand therapy is the development of personalized treatment plans. These plans are tailored to address the unique needs of each patient, considering factors such as the nature of the injury, the patient's overall health, and their lifestyle. This individualized approach ensures that interventions are targeted and effective in promoting healing and restoring function.
Utilizing a combination of exercises, splints, and modalities, therapists aim to improve strength, flexibility, and dexterity. The plan is regularly reviewed and adjusted as needed to ensure that it remains aligned with the patient's progress and goals. This adaptable approach fosters a collaborative partnership between the therapist and the patient to achieve the best possible outcomes.
Long-Term Management and Prevention Strategies
Effective hand therapy extends beyond acute treatment. Long-term management strategies focus on maintaining the gains achieved during rehabilitation and preventing future injuries. This often involves ongoing exercises, self-care techniques, and education to promote long-term hand health.
Educating patients about proper hand use, ergonomic principles, and injury prevention strategies empowers them to maintain optimal hand function in their daily lives. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of recurrence and ensures that patients can continue to perform essential tasks with ease and comfort. The commitment to ongoing education and prevention strategies is crucial for maximizing the positive impact of hand therapy.