Groundbreaking Approaches in Hand Pain Management

Beyond the Basics of Non-Surgical Interventions
Non-surgical interventions are increasingly popular for addressing a range of health concerns, offering a less invasive alternative to traditional surgery. These methods often involve therapies, procedures, and lifestyle adjustments to alleviate symptoms, promote healing, and improve overall well-being. Understanding the nuances of these approaches is crucial for informed decision-making and maximizing their potential benefits.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
Minimally invasive procedures are a key component of non-surgical interventions. These procedures often use smaller incisions, specialized instruments, and advanced imaging techniques, leading to less trauma, faster recovery times, and reduced scarring compared to traditional surgical methods. This approach minimizes the risk of complications and promotes a quicker return to daily activities.
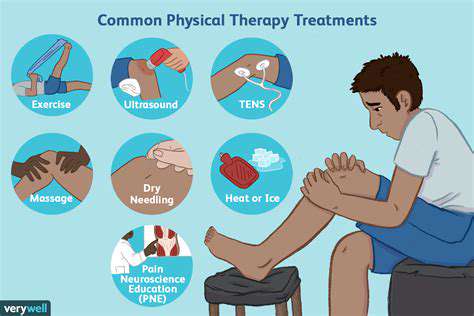
Therapeutic Exercises and Physical Therapy
Therapeutic exercises and physical therapy play a vital role in non-surgical treatment plans. Tailored programs, often incorporating targeted stretches, strengthening exercises, and mobility drills, can help restore function, alleviate pain, and improve overall physical well-being. These methods are crucial for rehabilitation and long-term maintenance of health, particularly for conditions like back pain and joint injuries.
Dietary Modifications and Nutritional Support
Dietary modifications and nutritional support can significantly impact the effectiveness of non-surgical interventions. Adjusting macronutrient intake, incorporating specific vitamins and minerals, and eliminating potential allergens can positively influence the body's ability to heal and recover. Proper nutrition is essential for overall well-being and can substantially aid in the recovery process for many conditions.
Complementary and Alternative Therapies
Complementary and alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, massage therapy, and herbal remedies, are increasingly recognized for their potential to support non-surgical interventions. These therapies often work by addressing underlying imbalances, promoting relaxation, and reducing pain and inflammation. Many patients find that integrating these therapies into their treatment plans enhances their overall experience and outcomes.
Lifestyle Changes and Behavioral Interventions
Lifestyle changes and behavioral interventions are crucial components of non-surgical management strategies. Adopting healthy habits, such as regular exercise, stress management techniques, and sufficient sleep, can significantly impact overall health and well-being. These changes can be instrumental in preventing future issues and supporting the body's natural healing processes. It is often necessary to modify daily routines and behaviors to achieve positive outcomes.
Patient Education and Empowerment
Patient education and empowerment are essential to the success of any non-surgical intervention. Educating patients about their condition, treatment options, and potential side effects empowers them to actively participate in their care. This collaborative approach fosters better understanding, promotes compliance with treatment plans, and ultimately leads to more positive outcomes. Active participation and a thorough understanding of the plan by the patient are key to a successful recovery.

The Rise of Regenerative Medicine: Stimulating Natural Healing
Harnessing the Body's Innate Repair Mechanisms
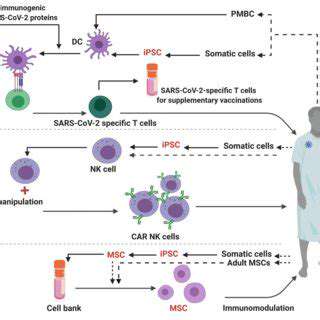
Regenerative medicine, a burgeoning field of biomedical research, aims to restore, maintain, or enhance damaged tissues and organs. Central to this approach is the understanding and stimulation of the body's natural healing processes. This innovative approach diverges from traditional treatments that primarily focus on symptom management, instead striving to address the underlying causes of disease and injury. By mimicking and enhancing the body's own regenerative capabilities, regenerative medicine promises to revolutionize healthcare, offering more effective and less invasive treatments for a wide range of conditions, from spinal cord injuries to diabetes.
The focus on stimulating natural healing mechanisms is a significant departure from the past. Traditional medical approaches often involve replacing damaged tissue or organs with synthetic alternatives. However, these methods frequently come with their own set of complications, including the risk of rejection or infection. Regenerative medicine, in contrast, seeks to foster the body's own inherent ability to repair itself, which minimizes these risks and potentially leads to more durable and long-lasting results.
Advancements in Cell and Tissue Engineering
A key component of regenerative medicine is cell and tissue engineering. This field involves manipulating cells and tissues to repair or replace damaged or diseased ones. Researchers are actively exploring various methods to cultivate and differentiate cells into specific tissue types, paving the way for the creation of functional replacements for damaged organs and tissues. This meticulous process often necessitates careful consideration of the cellular microenvironment to ensure optimal growth and function of the engineered tissues.
One of the most promising avenues within cell and tissue engineering is the development of biocompatible scaffolds. These scaffolds provide a supportive framework for cells to adhere to and proliferate, facilitating the regeneration of complex tissues. Advancements in materials science have led to the creation of sophisticated scaffolds that mimic the natural extracellular matrix, further enhancing cell growth and differentiation. This approach holds tremendous potential for treating a wide range of conditions affecting various parts of the body.
The future of regenerative medicine is bright. As research continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative applications of cell and tissue engineering. This will lead to improved treatment options for a wider range of diseases and injuries, potentially offering hope for individuals suffering from debilitating conditions.
From skin grafts to organ replacement, the potential applications of regenerative medicine are vast. This innovative approach may transform the way we approach healthcare, offering personalized and effective solutions for a multitude of conditions.
The promise of regenerative medicine is built upon the fundamental principle of harnessing the body's own remarkable capacity for healing. This innovative approach has the potential to fundamentally change how we treat disease and injury.
In conclusion, the advancements in regenerative medicine are significant and hold the promise of revolutionizing healthcare.