The Impact of Inactivity on Hand and Arm Health
The Delicate Dance of Blood Flow
Our hands and arms, constantly engaged in a symphony of movement, rely on a delicate balance of blood flow to thrive. Inactivity disrupts this delicate dance. Reduced blood circulation can lead to a cascade of issues, from simple discomfort to more serious conditions. The lack of movement starves tissues of the essential nutrients and oxygen they need to function optimally, creating a silent threat to the health and well-being of our extremities.
Sustained periods of inactivity, whether from prolonged sitting, desk jobs, or simply a lack of regular exercise, can significantly impede the flow of blood to the hands and arms. This reduced circulation can lead to a variety of symptoms, ranging from numbness and tingling to a general feeling of coldness and stiffness.
Muscular Atrophy: A Silent Thief
Muscles, like any other tissue, require regular stimulation to maintain their strength and size. Prolonged inactivity allows muscle fibers to weaken and atrophy, diminishing the overall strength and functionality of the hands and arms. This gradual weakening can make everyday tasks, such as lifting objects or gripping tools, more challenging and potentially painful.
Think of it like this: if you don't use a muscle, it will shrink and lose its strength over time, much like a neglected garden. Regular movement, whether through exercise or simple everyday activities, helps maintain muscle mass and prevent this atrophy from occurring.
The Impact on Flexibility and Range of Motion
The hands and arms are designed for a wide range of motion, enabling us to perform countless tasks with precision and dexterity. Inactivity restricts this range, making it harder to perform everyday movements, from reaching for objects to writing. Over time, this lack of flexibility can lead to stiffness, pain, and even joint problems.
Nerve Compression: A Potential Culprit
Prolonged inactivity can contribute to nerve compression, a condition where nerves become trapped or squeezed. This can manifest as numbness, tingling, pain, and weakness in the hands and arms. The reduced blood flow associated with inactivity can exacerbate these conditions, making them more pronounced and persistent.
The Role of Circulation in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
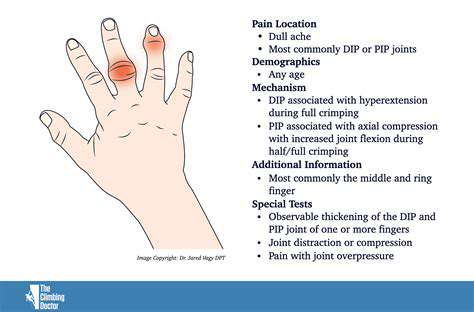
Carpal tunnel syndrome, a common condition affecting the hands and wrists, is often linked to repetitive movements. However, prolonged periods of inactivity can also contribute to the development or worsening of carpal tunnel symptoms. Impaired circulation exacerbates the pressure on the median nerve, leading to heightened discomfort.
The Importance of Movement and Exercise
Combating the silent threat of inactivity requires a proactive approach. Regular movement, encompassing stretching, light exercise, and activities that engage the hands and arms, is crucial in maintaining optimal health. Simple activities like stretching, hand exercises, and light yoga can significantly improve circulation and prevent the negative effects of inactivity.
Incorporating regular movement into your daily routine is essential for maintaining healthy hands and arms. This doesn't require extreme measures; even short bursts of activity throughout the day can make a big difference.
Preventing Future Issues
By understanding the impact of inactivity on our hands and arms, we can take proactive steps to prevent future problems. Regular movement, stretching, and exercises specifically designed for hand and arm health are essential for maintaining optimal function and preventing the onset of various ailments. A healthy lifestyle encompassing regular movement is key to maintaining overall well-being, and this includes the health of our hands and arms.
Repetitive Strain Injuries: A Common Consequence of Inactivity
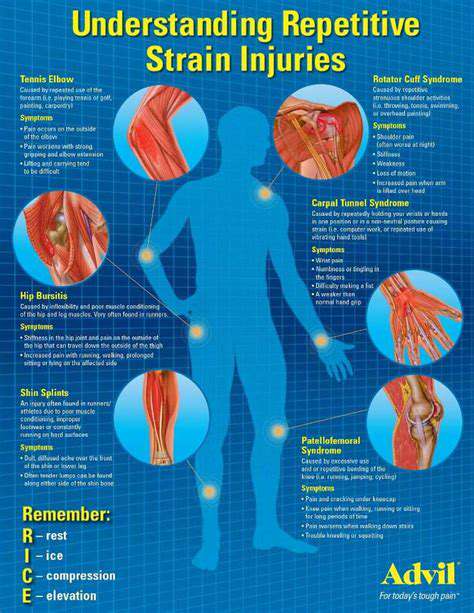
Repetitive Strain Injuries: Causes and Risk Factors
Repetitive strain injuries (RSI) are a common occupational hazard, affecting individuals who perform repetitive tasks for extended periods. These injuries are characterized by pain, stiffness, and inflammation in the muscles, tendons, and nerves of the affected area. Understanding the underlying causes and risk factors is crucial for prevention and effective treatment. The repetitive nature of the movement, combined with poor posture, inadequate rest periods, and improper tool usage, can all contribute to the development of these debilitating conditions.
A significant risk factor is prolonged exposure to forceful exertions, whether at work or during other activities. This exertion can lead to micro-tears in soft tissues, which if not properly healed, can escalate into more severe conditions. Furthermore, inadequate workspace ergonomics, such as incorrect chair height or insufficient desk adjustments, can also exacerbate the risk of RSI.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Identifying the symptoms of RSI is crucial for prompt intervention. Common symptoms include persistent pain, numbness, tingling, or weakness in the affected area. These symptoms may worsen with activity or at night. Proper diagnosis requires a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional, including a physical examination and potentially imaging studies such as X-rays or MRIs. Early diagnosis allows for timely intervention and management, potentially preventing long-term complications.
It is important to seek medical advice if you experience these symptoms, as they can indicate a variety of conditions, not just RSI. A doctor will be able to determine if the symptoms are caused by RSI or another underlying issue.
Treatment Options
Treatment options for RSI vary depending on the severity and location of the injury. Rest and activity modification are often the initial steps, followed by physical therapy to improve flexibility and range of motion. Pain management strategies such as over-the-counter medications or topical creams may also be recommended. In some cases, more invasive treatments like injections or surgery might be necessary to address chronic or severe conditions.
Prevention Strategies
Implementing effective prevention strategies is paramount to minimize the risk of developing RSI. Proper ergonomics in the workplace, including adjustable chairs and desks, are crucial for maintaining good posture and minimizing strain on the body. Taking regular breaks and incorporating stretching exercises into the workday can help prevent muscle fatigue and maintain flexibility. It is also important to use appropriate tools and techniques to reduce strain and exertion.
Impact on Daily Life
Repetitive strain injuries can significantly impact an individual's daily life, causing discomfort, limiting mobility, and hindering productivity. The pain and discomfort associated with RSI can interfere with work, household chores, and social activities. The impact on quality of life can be profound, affecting not only physical well-being but also emotional and mental health. Addressing the condition effectively is essential to restoring a normal lifestyle.
Occupational Health and Safety
Workplace safety measures play a vital role in mitigating the risk of RSI. Employers have a responsibility to provide a safe and healthy work environment for their employees. This includes implementing ergonomic assessments to identify potential hazards and providing appropriate training to employees on proper techniques and tool usage. Proactive measures, such as regular health screenings and ergonomic evaluations, can help in the early detection of risk factors. This proactive approach can minimize the likelihood of RSI occurrence and promote employee well-being.
Long-Term Management
Long-term management of RSI involves a multifaceted approach focusing on sustained recovery and preventing recurrence. This includes ongoing physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, and stress management techniques. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, plays a crucial role in supporting the body's healing process. Furthermore, addressing any underlying stress or anxiety can help in managing the condition effectively.
Thorough packing is crucial for a stress-free trip. Consider the activities you'll be engaging in, the climate of your destination, and the length of your stay when packing. A well-organized suitcase or backpack will minimize the hassle of finding items during your journey, ensuring you can focus on enjoying your experience rather than fumbling with your luggage. Making a detailed packing list in advance can help you avoid overpacking and ensure you have everything you need, and nothing you don't.
The Importance of Incorporating Movement: Simple Strategies for Maintaining Hand and Arm Health
Understanding the Importance of Movement
Maintaining healthy hand and arm function relies heavily on regular movement. Prolonged periods of inactivity, whether due to work, hobbies, or lifestyle choices, can lead to stiffness, reduced range of motion, and even the development of repetitive strain injuries. Regular movement helps to circulate blood, delivering vital nutrients to the tissues and removing waste products. This process is crucial for maintaining healthy muscle tone, flexibility, and overall hand and arm health.
Incorporating even simple movements into your daily routine can significantly contribute to preventing these issues. Think about tasks like gently stretching your fingers, rotating your wrists, or performing light hand exercises. These seemingly small actions can make a world of difference over time.
Targeted Exercises for Hand and Wrist Health
Specific exercises can address particular areas of concern. For example, gently flexing and extending your fingers, making a fist and then opening your hand, and rotating your wrists in both directions are excellent ways to maintain flexibility and strength. Performing these exercises regularly, perhaps for just a few minutes several times a day, can significantly enhance hand and wrist health.
Consider incorporating light resistance exercises, such as squeezing a stress ball or using hand grip strengtheners. These can help build strength in the smaller muscles of the hand, improving dexterity and reducing the risk of injury.
The Role of Posture in Hand and Arm Health
Maintaining proper posture throughout the day is essential for minimizing strain on the hand and arm. Poor posture, especially when engaging in repetitive tasks, can lead to muscle imbalances and discomfort. Ensuring your wrists are in a neutral position and avoiding awkward angles during work or other activities will help prevent potential injuries.
Consider your workspace setup. Ensure your chair provides adequate support, your monitor is at eye level, and your keyboard and mouse are positioned comfortably within reach to avoid unnecessary strain on your hands and arms.
Integrating Movement into Your Daily Routine
Incorporating movement doesn't require dedicating hours to strenuous workouts. Simple strategies like taking short breaks every hour to stretch your hands, arms, and neck can significantly impact your overall well-being. Even a few minutes of gentle movement can help to prevent stiffness and discomfort. For example, try doing a few wrist rotations or finger stretches while waiting for a meeting or during a phone call.
The Benefits of Stretching and Flexibility
Stretching routines are crucial for maintaining flexibility and range of motion in your hands and arms. Gentle stretching exercises can improve blood flow to the muscles and reduce stiffness. Regular stretching can help prevent the onset of muscle tension and reduce the risk of injuries associated with overuse.
Include stretches that target specific areas such as your fingers, wrists, and forearms. Hold each stretch for 15-30 seconds to allow the muscles to lengthen and relax. Consistency is key, aiming for several stretching sessions throughout the day.
Preventing Repetitive Strain Injuries (RSI) Through Movement
Prolonged repetitive movements, common in many occupations and hobbies, significantly increase the risk of repetitive strain injuries (RSI). By incorporating regular movement breaks and incorporating exercises into your daily routine, you can mitigate the risk of developing these injuries. This includes ensuring proper posture, utilizing ergonomic tools, and taking frequent breaks to allow your muscles to recover.
Regular movement and mindful posture help in reducing the strain on your hands and arms. This proactive approach can prevent discomfort and pain associated with RSI, ensuring long-term hand and arm health.