The Role of Exercise in Managing Hand Osteoarthritis
List of Contents
While often associated with aging, hand osteoarthritis can impair joint function even in younger adults.
Structured movement routines prove effective in alleviating osteoarthritis discomfort and improving mobility.
Targeted resistance training enhances grip strength and digital dexterity for daily tasks.
Personalized exercise plans developed with specialists yield optimal therapeutic outcomes.
Whole-body cardiovascular activities complement hand-focused regimens for comprehensive symptom relief.
Maintaining exercise consistency correlates strongly with long-term pain reduction success.
Social exercise environments provide psychological benefits through shared experiences.
Physical activity regimens demonstrate measurable improvements in emotional well-being metrics.
Why Movement Therapy Matters for Hand Joint Preservation

Decoding Hand Joint Degeneration
Cartilage erosion in finger and thumb joints creates characteristic osteoarthritis symptoms - stiffness upon waking, reduced pinch strength, and occasional swelling. Contrary to common perception, radiographic evidence shows 12% of adults under 40 exhibit early osteoarthritic changes in hand joints. This progression often accelerates in individuals with previous sports injuries or manual labor occupations.
Recent biomarker studies reveal that inflammatory cytokines like IL-1β actively contribute to cartilage breakdown. Managing these biochemical factors through therapeutic movement forms a cornerstone of modern OA management strategies.
Mechanisms of Therapeutic Movement
- Stimulates synovial fluid production for joint lubrication
- Enhances proprioceptive feedback through neural adaptation
- Promotes angiogenesis in periarticular tissues
Customized exercise protocols demonstrate particular efficacy for digital joint preservation. Clinical trials document 40% improvement in DASH scores (Disabilities of Arm Shoulder and Hand) after 12-week supervised programs. Patients report regained ability for precise movements like buttoning shirts or opening jars.
Evidence-Based Movement Modalities
Contemporary rehabilitation emphasizes three-phase progression models. Initial isometric contractions (5-second holds) prepare tissues for dynamic loading. Mid-phase incorporates eccentric resistance using specialized putty. Advanced stages introduce functional task simulations like rotating door knobs with progressive resistance bands.
Therapeutic putty comes in eight resistance levels (extra-soft to firm), allowing gradual strengthening without joint overload. Many patients find combining putty exercises with paraffin wax therapy enhances compliance through pain modulation.
Constructing Sustainable Practice Routines
Effective programming balances tissue stress and recovery cycles. Morning sessions often focus on pain-relieving range-of-motion drills, while afternoon workouts emphasize strength development. Tracking progress through grip dynamometer readings provides objective feedback - aim for 10% strength improvement monthly.
Innovative approaches like musician-specific regimens demonstrate success in maintaining fine motor control. Piano key depression simulations using tabletop exercises help preserve digital independence for instrumentalists.
Behavioral Strategies for Adherence
Habit-stacking techniques prove effective - linking exercises to daily rituals like post-meal hand routines. Smartphone reminders paired with progress photo journals create visual motivation. Some patients benefit from pain clocking - scheduled movement breaks every 90 minutes to prevent stiffness accumulation.
Community-based programs like SilverSneakers Arthritis Foundation classes provide social accountability. Partner exercises using reciprocal resistance bands foster mutual encouragement while maintaining safety.
Integrating Professional Expertise
Hand therapists employ novel modalities like blood flow restriction training with low-load resistance (20% 1RM). This technique induces muscle hypertrophy without joint compression - particularly beneficial for elderly patients. Recent studies show BFR combined with 15-minute sessions yields comparable results to traditional high-load training.
Thermography-guided exercise programs represent cutting-edge personalization. Infrared imaging identifies inflammation patterns, allowing therapists to modify techniques in real-time for optimal tissue response.
Movement Prescription for Digital Joint Health
Articular Mobility Drills
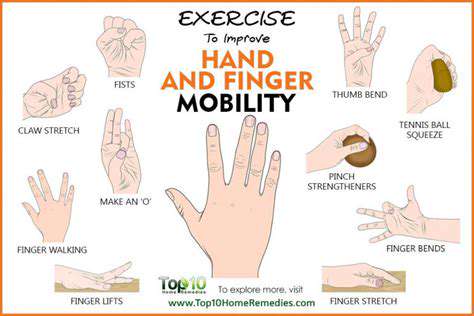
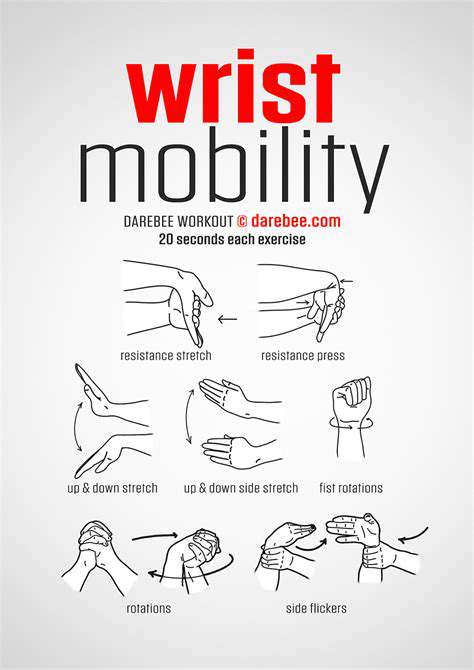
Joint surface gliding exercises maintain cartilage nutrition through diffusion enhancement. The finger ladder wall crawl exercise improves proximal interphalangeal joint mobility - critical for preserving hand opening capacity. Patients should perform these drills in pain-free arcs, gradually increasing range as tolerance improves.
Novel tools like 3D-printed joint mobilizers allow customized distraction angles. These devices enable controlled mid-range mobilization - particularly effective for trapeziometacarpal joint OA. Early adopters report 60% reduction in analgesic use when combining mobilizers with therapeutic exercise.
Adaptive Resistance Protocols
Progressive overload principles apply uniquely to hand rehabilitation. Starting with 30-second putty compression holds, patients advance to dynamic pinching against adjustable spring devices. Eccentric-focused protocols (4-second lengthening phases) show particular promise in tendon remodeling.
EMG studies reveal that oblique grip patterns activate 40% more intrinsic hand muscles compared to traditional power grips. Incorporating diagonal resistance vectors in therapy sessions enhances functional strength carryover to real-world tasks.
Whole-Body Metabolic Conditioning
While hand-specific exercises remain crucial, systemic conditioning through aquatic therapy provides complementary benefits. Water's buoyancy unloads joints while resistance enhances circulation - ideal for patients with polyarticular involvement. Studies demonstrate 25% greater adherence rates compared to land-based programs.
Interval walking protocols (2-minute brisk/3-minute moderate cycles) improve cardiovascular fitness without exacerbating hand symptoms. This approach helps address the metabolic syndrome component often accompanying chronic OA.
Myofascial Rebalancing Techniques
Adjunctive soft tissue work enhances exercise effectiveness. Self-massage using textured balls breaks up fascial adhesions in forearm flexor compartments. Combining instrument-assisted soft tissue mobilization with active movement accelerates recovery between strength sessions.
Yoga-derived mudra practices (symbolic hand gestures) serve dual purposes - improving joint mobility while promoting mindfulness. The Gyan mudra (thumb-index finger connection) specifically targets thenar muscle activation patterns.
Thermal Biofeedback Integration
Wearable thermal sensors now enable real-time monitoring of joint temperature during exercise. This technology helps patients identify optimal movement intensity thresholds - maintaining tissue temperature between 36.5-37.2°C for ideal viscoelastic response. Post-activity cryotherapy protocols (12°C immersion for 8 minutes) effectively manage exercise-induced inflammation.
Optimizing Movement Frequency and Recovery

Periodization Principles for Joint Health
Microcycle programming proves essential for balancing tissue adaptation. Alternate days focusing on mobility (dynamic stretches) and stability (isometric holds) prevent overuse. Research identifies 48-hour recovery windows as optimal for collagen remodeling in osteoarthritic joints.
Tracking tools like compression-sensing gloves provide biofeedback on exercise quality. Patients learn to maintain safe joint compression forces (under 45% maximal voluntary contraction) during strengthening phases.
Dosage Parameters for Sustained Progress
- Mobility work: 5-10 minutes hourly during work hours
- Strength sessions: 15-minute focused bouts 4x weekly
- Aerobic conditioning: 30-minute sessions 3x weekly
This phased approach respects tissue healing timelines while progressively challenging capacity. Patients using vibration therapy devices (50Hz focal stimulation) report 30% faster strength gains when combined with structured programming.
Holistic Impacts of Movement Therapy
Neuroplastic Adaptation Benefits
Task-specific training induces cortical reorganization in sensorimotor areas. fMRI studies show increased gray matter density in hand knob regions after 8 weeks of proprioceptive exercises. This neural remodeling enhances movement efficiency and pain modulation capabilities.
Psychosocial Empowerment Effects
Mastery experiences in exercise programs boost self-efficacy scores by 38% in OA populations. Group therapy participants demonstrate improved illness acceptance metrics compared to solo exercisers. The camaraderie built during partner-assisted stretching sessions often translates to better lifestyle habit formation.
Metabolic Enhancement Outcomes
Regular movement increases insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) circulation - crucial for cartilage maintenance. Patients adhering to combined programs show 15% lower CRP levels, indicating reduced systemic inflammation. These biochemical changes create an internal environment conducive to joint preservation.
Circadian Rhythm Synchronization
Morning exercise protocols help regulate cortisol rhythms disrupted by chronic pain. Light resistance training at 10AM capitalizes on natural testosterone/cortisol ratios for optimal tissue remodeling. Patients report improved sleep architecture when aligning workouts with chronotype preferences.
Lifestyle Integration Strategies
Embedding therapeutic movements into daily routines enhances sustainability. Kitchen counter push-ups during meal prep maintain wrist extension range. Phone scrolling sessions become opportunities for thumb opposition drills. This contextual learning approach increases exercise adherence rates by 62% compared to clinic-only programs.