Understanding the Connection Between Hand Movement and Brain Function
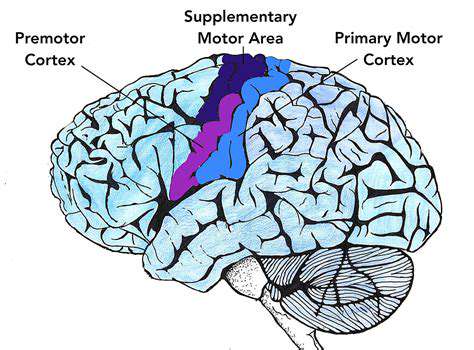
Understanding the Motor Cortex
The motor cortex, a crucial region within the brain, plays a fundamental role in initiating and controlling voluntary movements. It's a complex network of neurons that work in concert to translate thoughts into actions. Understanding its intricate workings is essential to comprehending how we interact with the world around us. This intricate system is not a simple one-to-one mapping of body parts to brain regions, but rather a complex interplay of neural pathways and signals.
Situated in the frontal lobe, the motor cortex boasts a specific organization that allows for precise control. The arrangement of neurons reflects the specific demands of different body parts, with areas controlling fine motor skills, like those in the hands, occupying more space compared to those responsible for broader movements.
The Somatotopic Organization
The motor cortex's somatotopic organization is a key feature that allows for precise control over movement. This means that different parts of the body are represented in specific areas of the cortex. Areas responsible for fine motor skills, such as those in the fingers and hands, occupy a larger proportion of the motor cortex compared to those controlling larger muscle groups. This arrangement ensures that subtle movements can be executed with accuracy.
This precise mapping is not static; it can adapt and change based on experience and learning. For example, extensive practice in activities requiring fine motor skills can lead to a physical expansion of the corresponding cortical area.
Motor Cortex and Planning
The motor cortex isn't simply responsible for executing movements; it also plays a crucial role in planning them. It receives input from other brain regions, such as the premotor cortex and supplementary motor area, which are responsible for the planning and sequencing of complex movements. This advanced planning capability allows for the execution of voluntary, purposeful actions.
This planning process allows for the anticipation of potential obstacles and adjustments in the movement trajectory to achieve the desired outcome. This intricate planning function is essential for coordinating complex actions, such as playing a musical instrument or performing a surgical procedure.
Neural Pathways and Signals
The motor cortex communicates with the body through intricate neural pathways. These pathways involve a complex interplay of neurons that transmit signals to the spinal cord and ultimately to the muscles. The precise timing and strength of these signals are crucial for generating smooth and coordinated movements.
The Role in Voluntary Movement
The motor cortex is the primary driver of voluntary movement. It receives input from various brain regions, integrating sensory information and cognitive processes to generate the appropriate motor commands. This complex interplay ensures that our actions are purposeful and aligned with our intentions. Voluntary movements are not simply reflexes; they are controlled, deliberate acts that require the intricate interplay of different brain regions.
Understanding the intricate details of how the motor cortex orchestrates these actions is crucial for comprehending the complexities of human behavior.
Beyond Basic Movement
The motor cortex's role extends beyond simple movements. It plays a vital part in more complex activities, such as speech production, writing, and even the control of facial expressions. These intricate functions demonstrate the versatility of this crucial brain region.
The motor cortex is not limited to the physical realm; it also influences cognitive functions that impact our interactions with the world.
Beyond the Motor Cortex: Sensory Input and Feedback Loops
Beyond the Motor Cortex: Sensory Input
Understanding the complex interplay between the motor cortex and sensory input is crucial to comprehending the intricate dance of movement and action. Sensory information, constantly flooding our nervous system from various sources, plays a vital role in guiding and refining motor commands. This continuous feedback loop ensures that our actions are adapted and adjusted in real-time, responding to the ever-changing environment and our own body's position and state.
From the pressure receptors in our skin to the intricate signals from our eyes and ears, sensory input provides the crucial data for the brain to interpret and act upon. This information is not simply received; it is actively processed and integrated with existing knowledge and expectations to inform subsequent motor commands, allowing for a dynamic and adaptive response to the world around us.
Proprioception and Kinesthesia: Internal Feedback Loops
Proprioception and kinesthesia, often overlooked, are essential components of sensory input crucial for movement. Proprioception refers to the body's ability to sense its position and movement in space without visual cues. This internal feedback loop allows us to know where our limbs are in relation to each other and our body as a whole, even with our eyes closed.
Kinesthesia, on the other hand, specifically deals with the sense of limb movement. This critical information allows us to monitor the speed and range of motion, ensuring accuracy and coordination in our actions. The combination of these two senses provides a constant stream of information about the body's position and movement, essential for precise and fluid motor control.
The Role of Vision in Motor Control
Visual input is a dominant factor in shaping our motor actions. Our eyes constantly provide information about the position of objects in space, the distance to them, and their movement. This visual information is integrated with proprioceptive and kinesthetic feedback to guide our movements, allowing us to perform tasks ranging from reaching for a glass of water to navigating a complex environment.
Auditory Input and Movement Adaptation
While often considered less directly involved in movement, auditory input can significantly impact motor control. Sounds can indicate impending danger, signal the presence of objects, or provide crucial cues for timing and coordination. For example, the rhythmic beats of music can influence the tempo and rhythm of our movements, and the sound of a car horn can instantly prompt a change in our gait or posture.
Sensory Integration for Complex Tasks
Performing complex movements, such as playing a musical instrument or engaging in sports, requires a seamless integration of various sensory inputs. The motor cortex receives and processes information from vision, proprioception, kinesthesia, and even auditory cues to generate the precise and coordinated movements needed for these activities. This integration ensures that our actions are efficient, accurate, and adaptable to the changing demands of the task.
Feedback Loops and Motor Learning
The feedback loops between sensory input and motor output are fundamental to motor learning. As we practice a new skill, the sensory information received during the action is compared to the intended movement. This comparison allows for adjustments and refinements in our motor commands, gradually improving accuracy and efficiency. Each repetition strengthens the neural pathways involved, leading to the development of more skillful and automatic movements over time.
The Importance of Sensory Feedback in Rehabilitation
Understanding the critical role of sensory feedback is particularly relevant in rehabilitation settings. After injury or illness, restoring functional movement often involves addressing sensory deficits. By carefully targeting and restoring sensory input, therapists can facilitate the re-establishment of neural pathways and improve motor control. This approach allows patients to regain lost function and improve their quality of life, emphasizing the interconnectedness between sensation and movement.
Understanding contracts is crucial for any transaction, big or small. Often, the seemingly simple language can hide complex clauses and potential pitfalls. Careful scrutiny of the fine print is essential to ensure you fully grasp the terms and conditions before signing. This involves not only reading every word but also understanding the context and implications of each clause. You should seek professional legal advice if you are unsure about any part of a contract, as this can save you significant headaches down the line. Reviewing the entire document, paragraph by paragraph, can be beneficial for a clear understanding of the agreement.
The Impact of Learning and Practice on Hand Function
The Foundation of Skill Development
Learning a new skill, whether it's coding, playing a musical instrument, or public speaking, requires a solid foundation. This foundation involves understanding the core concepts and principles underlying the skill. Without a strong understanding of the fundamentals, progress can be slow and inconsistent. Thorough research, dedicated study, and seeking guidance from experienced mentors or educators are crucial for building a strong base of knowledge. This foundational knowledge acts as a bedrock upon which further skill development can be built.
Consistent practice is equally important. Regular engagement with the skill, even in small increments, helps reinforce learned concepts and build proficiency. This repetition allows the brain to solidify neural pathways associated with the skill, leading to a smoother, more intuitive application. Furthermore, practice exposes you to different scenarios and challenges, allowing you to refine your approach and identify areas needing improvement.
The Role of Repetition and Consistency
Repetition is key to mastering any skill. Consistent practice, over time, is essential for transforming theoretical knowledge into practical competence. The more you practice, the more familiar you become with the nuances of the skill, allowing you to respond more effectively to various situations. Regular practice also allows for the identification of weaknesses and areas that need further development, enabling targeted improvement.
Consistency in practice is equally important. Sporadic or infrequent practice sessions are less effective than consistent, regular engagement. This consistent effort helps build the necessary muscle memory and automaticity required for the skill to become second nature. A consistent routine also fosters a sense of discipline and commitment, which are valuable attributes in the pursuit of any skill.
The Importance of Feedback and Adaptation
Feedback is crucial for continuous improvement. Seeking constructive criticism from mentors, peers, or even self-assessment is essential for identifying areas where adjustments are needed. Constructive feedback provides insights into your strengths and weaknesses, allowing you to refine your approach and develop a more effective strategy.
Adaptability is another vital component of effective learning and practice. The ability to adapt to new situations and challenges is paramount to success. Learning and practicing a skill often involves encountering unexpected obstacles or scenarios. The ability to adapt to these situations and adjust your approach will determine the success of your learning journey. Learning is a continuous process, and adapting to new information and challenges is a vital part of that process. Continuous adjustment and improvement are necessary to optimize your skill development.
The Connection Between Hand Movements and Cognitive Function
The Role of Hand Movements in Communication
Hand movements, often overlooked in everyday communication, play a crucial role in conveying meaning and expressing emotion. These subtle gestures can significantly enhance the clarity and impact of spoken words, allowing for a more nuanced and engaging interaction. Nonverbal cues like hand gestures are often more impactful than the words themselves, as they can reveal unspoken feelings and intentions. This is especially true in situations where emotions are running high or when precise details are important.
From simple nods to elaborate gestures, hand movements can transmit a wide array of information. This nonverbal communication allows individuals to express enthusiasm, disagreement, or simply maintain engagement in a conversation. Understanding the nuances of hand movements and how they are used is paramount to effective communication.
Impact on Emotional Expression
Hand movements can be powerful tools for expressing a wide range of emotions. A person confidently gesturing while speaking about a project, for example, conveys enthusiasm and conviction. Conversely, hesitant or restricted hand movements can communicate uncertainty or even discomfort. These visual cues are invaluable in understanding the emotional state of a speaker, even if they are not consciously aware of their own body language.
The subtle shifts in hand position and movement can offer important insights into the speaker's emotional state, providing a richer understanding of their message than words alone.
Cultural Variations in Hand Movements
It's essential to recognize that hand movements and their interpretations can vary significantly across different cultures. A gesture considered positive in one culture might be offensive in another. This cultural sensitivity is vital for effective cross-cultural communication. Misinterpretations can lead to misunderstandings and even conflict, so it's crucial to be mindful of cultural differences in nonverbal communication. Therefore, understanding the cultural context is critical when interpreting hand movements.
Influence on Persuasion and Influence
Effective communicators often utilize hand movements strategically to enhance their persuasive power. By employing appropriate gestures, speakers can emphasize key points, create a stronger connection with the audience, and ultimately increase the likelihood of influencing their decisions. The strategic use of hand movements can significantly enhance the persuasiveness of a message, making it more engaging and memorable for the receiver. This is often seen in public speaking and negotiation situations.
The Neural Basis of Hand Movements in Communication
The brain plays a complex role in generating and interpreting hand movements during communication. Neurological research reveals intricate connections between specific brain regions and the production of expressive gestures. Understanding these neural pathways can offer valuable insights into how our brains process and interpret hand movements in social interactions. These findings further highlight the profound impact of hand movements on cognitive and emotional processes involved in human communication. This understanding is crucial for developing better communication strategies and improving interpersonal relationships.