Understanding the Role of the Median Nerve in Hand Function
Origins and Course
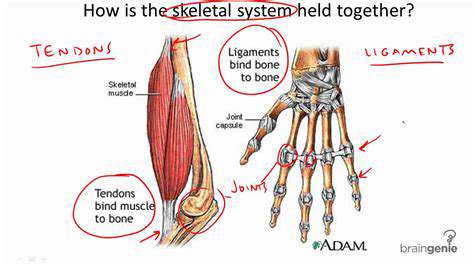
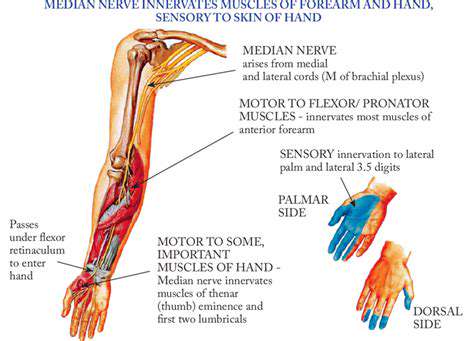
The median nerve, a crucial component of the brachial plexus, originates from the medial and lateral cords. Its journey through the arm is intricate, encompassing various anatomical structures. This nerve plays a pivotal role in the sensation and motor function of the hand and forearm. It's essential for proper hand dexterity and fine motor skills.
Tracing the median nerve's course, it descends through the arm, passing through the coracobrachialis and biceps brachii muscles. Its trajectory is carefully orchestrated to ensure its function in the upper extremity. The nerve's path is often vulnerable to injury, especially in areas of compression or trauma.
Branches and Distribution
The median nerve distributes its function through several branches, each targeting specific muscle groups and sensory areas of the forearm and hand. Understanding the branches is vital for diagnosing and treating conditions affecting the nerve's function. These branches supply motor innervation to the flexor muscles of the forearm and the intrinsic muscles of the hand.
The sensory distribution of the median nerve is equally important. It provides sensation to the thumb, index, middle, and lateral half of the ring finger. This sensory input is vital for touch, pain, and temperature perception. Disruptions to this distribution can result in a range of sensory impairments.
Relationship to Other Structures
The median nerve's path is closely linked to several other anatomical structures. It frequently interacts with the brachial artery and vein, often running alongside them. This close proximity can be significant in cases of compression or injury, where damage to one structure can affect the others.
Furthermore, the median nerve passes through the carpal tunnel, a narrow passageway in the wrist. The delicate nature of this passage makes it susceptible to compression, a condition known as carpal tunnel syndrome. This compression can lead to significant pain and numbness in the hand.
Clinical Significance
The median nerve's clinical significance is high due to its crucial role in hand function. Conditions affecting the nerve, such as carpal tunnel syndrome, can lead to significant disability and pain. Diagnosis and treatment of these conditions often require careful evaluation of the nerve's function and structure. This includes nerve conduction studies and electromyography.
Moreover, injuries to the median nerve, either from trauma or other causes, can result in motor and sensory deficits. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial for optimal recovery. Physical therapy and surgical interventions may be necessary in severe cases.
Potential Injuries and Conditions
The median nerve, due to its vulnerable position, is prone to various injuries. Trauma, such as fractures or lacerations, can directly damage the nerve. Compression, often from repetitive motions or prolonged pressure, can also lead to nerve dysfunction. Compression syndromes like carpal tunnel syndrome are a common concern.
Conditions such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and certain infections can also affect the median nerve. Understanding these predisposing factors is critical for early detection and intervention. This comprehensive knowledge helps in developing appropriate preventative measures and treatment strategies.
Motor Functions: Enabling Precise Hand Movements
Motor Cortex Activation
The Motor cortex, a crucial region in the brain, plays a pivotal role in initiating and controlling voluntary movements, including those intricate hand movements necessary for tasks like writing, playing musical instruments, or performing surgery. Understanding the specific pathways and neural activation patterns within the motor cortex is fundamental to comprehending how precise hand movements are enabled. This intricate network of neurons, organized in a somatotopic manner, maps different body parts to specific locations within the cortex, highlighting the dedicated neural resources allocated to fine motor control.
Sensory Feedback Loops
Precise hand movements aren't solely driven by commands from the brain; they also rely heavily on sensory feedback. As we move our hands, various sensory receptors in the skin, muscles, and joints provide constant information about the position, pressure, and velocity of our hand movements. This sensory information is relayed back to the brain, allowing for adjustments and corrections in real-time, ensuring accuracy and smoothness in our actions. This continuous feedback loop is essential for maintaining stability and control during complex hand movements.
Neural Pathways and Synaptic Transmission
The intricate dance of hand movements relies on complex neural pathways that transmit signals from the brain to the muscles in the hand. These pathways involve multiple brain regions, including the motor cortex, basal ganglia, and cerebellum. Precise hand movements require the efficient and coordinated activation of these pathways. Synaptic transmission, the process by which neurons communicate with each other, plays a critical role in the speed and accuracy of these signals. Disruptions in these pathways or in synaptic transmission can lead to impaired motor function.
Role of the Basal Ganglia
The basal ganglia, a group of subcortical nuclei, play a significant role in regulating the initiation, execution, and termination of movements, including those involving the hands. They fine-tune the motor commands from the cortex, smoothing out movements and preventing unwanted tremors or involuntary actions. This modulation is particularly crucial for the precision required in tasks requiring delicate hand movements. Damage to the basal ganglia can lead to a range of motor impairments, impacting hand function.
Cerebellum's Contribution to Coordination
The cerebellum, often referred to as the little brain, plays a critical role in coordinating and refining motor movements, including those of the hands. It receives sensory input from the body, comparing it to the intended movement. This comparison allows the cerebellum to make adjustments and corrections to ensure smoothness and precision in hand movements. The cerebellum's contributions to motor control extend beyond simple coordination, influencing aspects like timing, force, and the execution of complex sequences of hand movements. Damage to the cerebellum can significantly impair coordination and precision in hand movements.
Global cuisine offers a breathtaking array of flavors, aromas, and culinary traditions. From the vibrant street food stalls of Southeast Asia to the sophisticated haute cuisine of France, each region boasts unique ingredients and cooking methods that tell a story of its history and culture. Exploring these diverse culinary landscapes is a fantastic opportunity to broaden our perspectives and appreciate the richness of human experience beyond our immediate surroundings.
Clinical Significance and Median Nerve Disorders

Clinical Significance of Median N
Understanding the clinical significance of median N values is crucial in various medical fields, particularly in oncology and epidemiology. Median N represents the midpoint of a distribution of N values, providing a valuable measure of central tendency. This central tendency is helpful in assessing the typical or average number of affected lymph nodes in a patient population. Analyzing median N alongside other clinical parameters offers insights into disease severity, prognosis, and treatment response.
Furthermore, comparing median N across different patient groups, such as those treated with various therapies, can reveal significant differences in disease progression or treatment efficacy. This comparative analysis can be instrumental in developing and refining treatment protocols and strategies.
Median N and Prognostic Factors
Median N values can serve as a strong prognostic indicator, especially in cancer. A higher median N often correlates with a poorer prognosis, suggesting a more advanced stage of disease and a greater likelihood of recurrence or metastasis. However, it's important to remember that median N is just one factor among many that contribute to overall prognosis. Clinicians must consider other factors like tumor size, grade, and patient demographics.
The relationship between median N and other prognostic factors provides valuable information in risk stratification. This allows for more precise risk assessment and tailoring of treatment plans to individual patients. It enables clinicians to make more informed decisions regarding surveillance, targeted therapies, or adjuvant treatments.
Median N and Treatment Response
The median N value can also provide insights into treatment response. Comparing median N values before and after treatment can reveal the efficacy of a particular intervention. A significant decrease in median N after treatment suggests a positive response to therapy, while a lack of change or an increase suggests a less favorable response. This information is valuable in assessing the effectiveness of different treatment strategies and optimizing treatment protocols.
Median N and Patient Outcomes
Median N values are directly related to patient outcomes, and a strong correlation exists between median N and overall survival rates. A lower median N generally corresponds to a better patient outcome, whereas a higher median N often signifies a worse outcome. This relationship underscores the importance of identifying and treating patients with early-stage disease to improve long-term survival. Careful monitoring and appropriate interventions based on median N values are pivotal to achieving favorable outcomes.
Median N and Research Applications
Median N values are essential in research studies investigating cancer and other diseases. These values help researchers identify potential risk factors, assess treatment efficacy, and evaluate disease progression. By analyzing median N across different populations and treatment regimens, researchers can gain valuable insights into the complex interplay of factors influencing disease development and outcomes. This research can lead to the development of new diagnostic tools, treatment strategies, and preventative measures.
Maintaining Healthy Median Nerve Function: Practical Tips
Understanding Median Nerve Anatomy
The median nerve, a crucial component of the peripheral nervous system, plays a vital role in hand function. It originates in the brachial plexus and travels through the arm and forearm, eventually innervating various muscles and sensory receptors in the hand. Understanding its intricate pathways and connections is essential for comprehending how to maintain its health and function.
Its precise course through the arm and forearm is complex, with branches that supply specific regions of the hand. Damage or compression at any point along this path can lead to a range of symptoms, highlighting the importance of protecting this vital nerve.
Recognizing Median Nerve Compression Symptoms
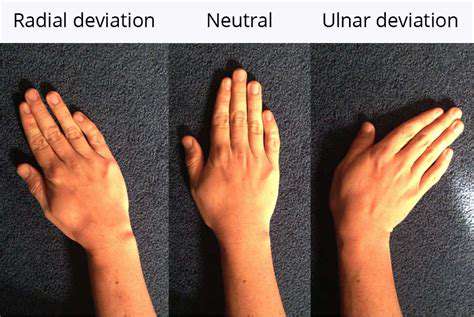
Symptoms of median nerve compression, often referred to as carpal tunnel syndrome, can vary in severity and presentation. Common symptoms include numbness and tingling in the thumb, index, middle, and part of the ring finger. These sensations are frequently worse at night and may be accompanied by pain in the wrist and hand.
Other possible symptoms include weakness in the hand, making tasks like gripping or pinching difficult. Early detection and appropriate intervention are crucial to mitigating potential long-term effects on hand function.
Lifestyle Modifications for Prevention
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle significantly impacts the well-being of the median nerve. Regular exercise, particularly activities that promote good circulation and flexibility in the wrist and hand, can help prevent compression. Avoiding repetitive motions or prolonged postures that put strain on the wrist is also crucial.
Ergonomic Practices at Work and Home
Ergonomic principles are essential for safeguarding the median nerve, both at work and at home. Proper workstation setup, including a supportive chair, a correctly positioned monitor, and a keyboard and mouse that facilitate a neutral wrist position, can significantly reduce the risk of compression.
At home, similar considerations apply when performing tasks that involve repetitive hand movements. Taking regular breaks and adjusting posture during activities like cooking or crafting can also help prevent strain and injury to the median nerve.
Dietary Considerations for Nerve Health
A balanced diet rich in nutrients essential for nerve health can contribute to maintaining the proper function of the median nerve. Consuming foods rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly B vitamins and vitamin E, can support nerve health and repair.
Including plenty of fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins in your diet provides the necessary building blocks for healthy nerve function, and overall good health.
Seeking Professional Medical Advice
If you experience persistent or worsening symptoms of median nerve compression, seeking professional medical advice is crucial. A healthcare professional can accurately diagnose the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment strategies. Ignoring symptoms can lead to further complications and potentially permanent nerve damage.
Don't hesitate to schedule an appointment with a neurologist or hand specialist if you have concerns about your median nerve health. Early intervention is key to effective management and preserving hand function.