Understanding the Impact of Stress on Hand Function
The Unseen Link Between Stress and Hand Function

The Impact of Chronic Stress
Chronic stress, the constant feeling of being overwhelmed and unable to cope, has a profound and often overlooked impact on our physical and mental well-being. It's not just a fleeting feeling of anxiety; it's a sustained state of physiological arousal that can lead to a cascade of negative consequences. This prolonged activation of the stress response system can significantly impair our ability to function effectively in all aspects of life, from work performance to personal relationships.
The body's natural stress response, while designed to protect us in the short term, can become detrimental when it persists. This sustained activation can lead to elevated levels of cortisol, a hormone associated with a range of issues, including weakened immune function, digestive problems, and cardiovascular complications. Understanding this connection between stress and these physical manifestations is crucial for preventive health strategies.
The Subtle Signs of Stress
Often, the signs of stress are subtle and easily dismissed as everyday occurrences. A nagging headache, persistent fatigue, or difficulty sleeping might seem like minor inconveniences, but they can be early warning signs of a more significant underlying issue. Regularly experiencing these symptoms can indicate a need for intervention and a shift in lifestyle to mitigate their impact.
Identifying these early signs is vital for managing stress effectively. Often, people are unaware of the subtle signals their bodies are sending until the symptoms become more pronounced. Early intervention is key to preventing the development of more serious health problems.
The Role of Lifestyle Choices in Stress Management
Stress isn't an inevitable part of life; it's often a result of our lifestyle choices and how we manage our daily responsibilities. A balanced diet, regular exercise, sufficient sleep, and mindfulness practices can significantly contribute to stress reduction. Integrating these healthy habits into your routine can create a buffer against the daily stressors that inevitably arise.
Prioritizing self-care and adopting healthy habits can be powerful tools in managing stress levels. This approach can not only reduce the immediate impact of stress but also build resilience to future challenges. Incorporating relaxation techniques, like deep breathing exercises or meditation, into your daily routine can effectively reduce stress and promote overall well-being.
The Importance of Seeking Professional Help
While lifestyle changes can be highly effective in managing stress, there are situations where professional help is necessary. If stress is significantly impacting your daily life, causing emotional distress, or interfering with your ability to function, seeking professional guidance is a sign of strength and a proactive approach to well-being. Therapists and counselors can provide support, tools, and strategies tailored to your specific needs.
When stress becomes overwhelming and significantly impacts your life, seeking professional help is crucial. A mental health professional can offer valuable insight, coping mechanisms, and strategies to manage stress in a healthy and sustainable way. Don't hesitate to reach out if you feel overwhelmed or if your stress levels are impacting your overall well-being.
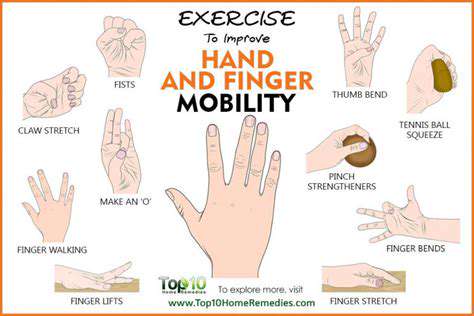
Physiological Responses to Stress Affecting Hand Movement
Physiological Mechanisms Underlying Stress-Induced Motor Impairment
Stress, a ubiquitous aspect of modern life, exerts profound effects on the human body, impacting not only mental well-being but also physical performance. This influence extends to fine motor skills, affecting the precision and dexterity required for tasks involving the hands. Understanding the physiological mechanisms behind this stress-induced motor impairment is crucial for developing effective coping strategies and interventions. Neurochemical changes, including alterations in the levels of cortisol and adrenaline, are key players in this process. These hormones, while crucial for short-term responses to threats, can disrupt the delicate balance of the nervous system when chronically elevated, leading to impaired motor control.
The autonomic nervous system plays a vital role in mediating the body's response to stress. When faced with stressors, the sympathetic nervous system activates, triggering a cascade of physiological changes, including increased heart rate and blood pressure. These changes, while necessary for immediate action, can significantly impact the precision required for hand movements. The parasympathetic nervous system, responsible for the body's rest-and-digest response, is often suppressed during stressful situations, further exacerbating the motor impairment by reducing the body's capacity for fine motor control. This disruption in the balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems contributes to the diminished dexterity and increased tremor observed during periods of high stress.
Impact of Stress Hormones on Neuromuscular Coordination
The interplay between stress hormones and the neuromuscular system is complex and multifaceted. Elevated cortisol levels, a hallmark of chronic stress, can negatively impact the function of neurons responsible for motor control. This disruption in neural signaling can lead to reduced coordination between the brain and the muscles of the hand, making it more difficult to perform precise movements. Furthermore, the increased levels of adrenaline, a crucial hormone in the fight-or-flight response, can lead to muscle tension and stiffness, further hindering the ability to execute smooth and controlled hand movements. These physiological changes, when sustained over time, can contribute to the development of chronic hand tremors and difficulties with fine motor tasks.
The physiological effects of stress extend beyond the immediate hormonal response. Chronic stress can lead to changes in brain structure and function, impacting the areas of the brain responsible for motor planning and execution. This long-term impact can lead to a reduced capacity for complex hand movements, even when the immediate stressor has subsided. Individuals experiencing chronic stress may exhibit difficulties with tasks requiring hand-eye coordination, dexterity, and fine motor skills, highlighting the long-lasting repercussions of chronic stress on neuromuscular performance.
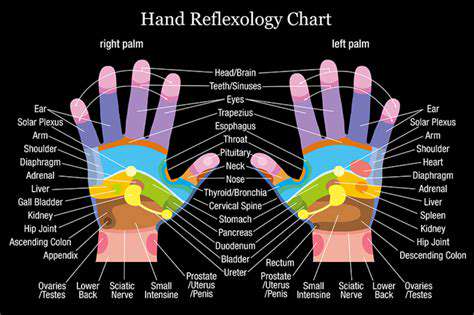
Stress-Related Conditions Affecting Hand Function

Stress and Cardiovascular Health
Chronic stress can significantly impact cardiovascular health, leading to a heightened risk of various heart-related conditions. Prolonged exposure to stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline can cause the heart to work harder and increase blood pressure, potentially contributing to the development of hypertension and atherosclerosis. This elevated strain on the cardiovascular system can ultimately result in heart attacks, strokes, and other serious complications.
The constant physiological response to stress can also lead to unhealthy lifestyle choices, such as poor diet and lack of exercise. These behaviors further exacerbate the risk of cardiovascular problems, creating a vicious cycle that is difficult to break without intervention. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle alongside stress management techniques is crucial for mitigating the negative impact of stress on cardiovascular health.
Stress and the Immune System
Stress can negatively affect the immune system's ability to function effectively, making individuals more susceptible to illnesses. This occurs because stress hormones suppress the activity of immune cells, reducing the body's defenses against pathogens. Consequently, individuals experiencing chronic stress often find themselves more prone to infections and take longer to recover from illnesses.
Furthermore, the compromised immune response associated with stress can also impair the body's ability to fight off cancer cells. This connection underscores the importance of managing stress to bolster the immune system and promote overall health.
Stress and Mental Health
A significant link exists between stress and various mental health conditions, including anxiety and depression. Prolonged exposure to stressful situations can disrupt the delicate balance of neurochemicals in the brain, leading to feelings of overwhelming anxiety and persistent sadness. These conditions can manifest as persistent worry, difficulty concentrating, sleep disturbances, and a loss of interest in previously enjoyed activities.
Chronic stress can contribute to the development and exacerbation of existing mental health conditions, highlighting the importance of stress management strategies for maintaining psychological well-being. Addressing stress effectively can be a crucial element in preventing and treating mental health disorders.
Stress and Digestive Issues
Stress can manifest in various ways, and one common consequence is a disruption of the digestive system. Chronic stress can lead to symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits. This is because stress affects the gut-brain axis, which is a complex communication network between the brain and the digestive tract. Stress hormones can alter the motility of the intestines and the production of digestive enzymes, leading to discomfort and potential digestive problems.
Stress-related digestive issues can range from mild discomfort to more severe conditions, emphasizing the importance of recognizing the connection between stress and the gut. Effective stress management techniques can often alleviate these symptoms and promote a healthier digestive system.