Understanding the Role of the Hand in Fine Motor Skill Development

Developing Dexterity
Fine motor skills, encompassing the precise movements of small muscles in the hands and fingers, are crucial for various daily tasks. Developing these skills early in life is essential for a child's overall development and future success. From grasping objects to writing letters, these skills form the bedrock of independent functioning. These abilities allow children to perform tasks like buttoning shirts, tying shoelaces, and using utensils with ease. Early intervention and practice are key to fostering their growth.
Fine motor skill development is a gradual process, building upon simpler movements. Initially, a child might struggle with tasks requiring precise coordination, but consistent practice enhances their dexterity and accuracy. These skills are heavily intertwined with cognitive development, as they often require problem-solving and strategic planning. It is important to recognize and encourage every milestone, big or small, in a child's development. Providing appropriate tools and resources can significantly support this process.
The Role of Sensory Input
Sensory input plays a significant role in fine motor skill development. The ability to perceive and process tactile information, such as the texture of different materials, is vital for manipulating objects effectively. Exposure to various textures, shapes, and sizes enhances a child's understanding of their surroundings and helps refine their motor control. A stimulating environment that offers diverse sensory experiences can greatly aid in this process.
Experiences like playing with playdough, building blocks, and manipulating puzzles provide essential sensory input and opportunities for practicing fine motor skills. These activities not only improve hand-eye coordination but also stimulate cognitive development. Furthermore, these experiences often involve problem-solving, fostering crucial cognitive skills that go hand-in-hand with fine motor development. It's important to create a supportive environment where children feel safe to explore and experiment.
Practice and Enrichment Activities
Consistent practice and engaging activities are essential for building and maintaining fine motor skills. Regular opportunities for activities that require precise hand movements, such as drawing, painting, and using small tools, are crucial for developing dexterity. These activities not only improve fine motor skills but also enhance creativity and cognitive development. The act of drawing, for example, requires a child to plan, execute, and refine their movements, strengthening their motor control and problem-solving abilities.
Engaging in activities like puzzles, lacing, and beading helps children refine their hand-eye coordination and strengthen their grasp. These activities are not only fun but also provide crucial practice for developing fine motor skills. Encouraging a child to participate in these activities can foster a love for learning and exploration. The more opportunities a child has to engage in these activities, the more they will develop their fine motor skills.
Providing a variety of age-appropriate materials and tools further encourages exploration and mastery of fine motor skills. The availability of diverse materials and the encouragement of experimentation are key to a child’s development in this area. This allows children to explore different textures, shapes, and sizes, ultimately refining their motor control and problem-solving skills. It is important to provide opportunities for them to express their creativity.
The Impact of Early Experiences on Hand Development
Prenatal Influences on Hand Formation
The development of a child's hands begins in the womb, influenced by a complex interplay of genetic factors and the prenatal environment. Maternal health, including nutrition, exposure to toxins, and overall well-being, significantly impacts the formation of the hand's bones, tendons, and muscles. For example, inadequate intake of essential nutrients during pregnancy can lead to developmental delays, potentially affecting the precision and dexterity of the developing hand.
Furthermore, exposure to certain environmental factors, like specific medications or infections, during gestation can disrupt the normal processes of hand development. Understanding these prenatal influences is crucial for recognizing potential risks and implementing preventative measures to support optimal hand development.
The Role of Sensory Input
Early experiences, particularly sensory input, play a vital role in shaping the fine motor skills and dexterity of a child's hands. Exposure to tactile stimulation, such as touching various textures, grasping objects of different sizes and shapes, and exploring different temperatures, helps stimulate nerve pathways and promote the development of hand-eye coordination. This early exposure to sensory experiences is critical for building a foundation for later motor skills.
Impact of Movement and Manipulation
The act of moving and manipulating objects with hands is fundamental to their growth and development. Early opportunities for exploring and manipulating objects, from grasping toys to playing with sand, facilitate the development of hand strength, dexterity, and fine motor skills. These experiences provide crucial practice for the muscles and nerves in the hands, enabling them to perform more complex movements as the child grows.
Influence of Early Play and Activities
Engaging in age-appropriate play and activities, like building blocks, painting, or playing with clay, provides rich opportunities for hand development. These activities encourage the exploration of different textures, shapes, and sizes, fostering the development of fine motor skills and hand-eye coordination. The repetitive movements and precision required in these activities directly contribute to the refinement of hand function.
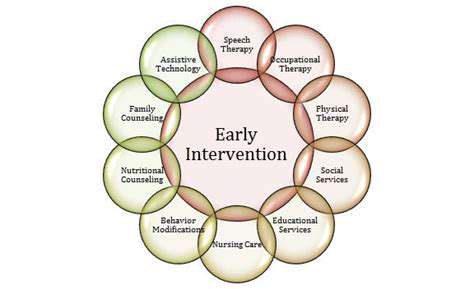
Early Intervention and Therapy
In cases where early experiences may have negatively impacted hand development, early intervention and therapy can be crucial for fostering the child's potential. Occupational therapists, for example, use targeted interventions to enhance hand function, improve dexterity, and promote independence in daily tasks. These therapies often include exercises and activities designed to strengthen hand muscles, improve coordination, and enhance sensory processing skills.
Long-Term Implications on Hand Function
The impact of early experiences extends far beyond the immediate period of development. Early experiences that support hand development lay the foundation for future learning and skill acquisition, impacting everything from writing and drawing to playing musical instruments and performing complex tasks. These early experiences can have a lasting impact on a child's independence, self-esteem, and overall well-being.
Cultural and Environmental Factors
Cultural contexts and environmental factors can significantly influence the opportunities for hand development. For instance, cultures that emphasize certain types of manual labor or crafts may provide more opportunities for developing fine motor skills than others. Similarly, the availability of resources and educational experiences within the child's environment can impact access to activities and tools that promote hand development. Understanding these factors is critical for creating supportive environments that promote optimal hand development for all children.
Promoting Hand Development: Practical Strategies and Activities

Enhancing Fine Motor Skills
Developing strong hand muscles and dexterity is crucial for various everyday tasks, from writing and drawing to buttoning shirts and using utensils. Early intervention and consistent practice are key to fostering these essential fine motor skills. Activities that involve manipulating small objects, like building blocks, threading beads, or playing with playdough, can significantly contribute to hand development and overall dexterity.
These activities engage multiple sensory pathways, encouraging the brain to connect with the hands and enhance coordination. By providing opportunities for children to explore and experiment with different textures and tools, we can help them build a strong foundation for future learning and development.
Beneficial Activities for Hand Development
Engaging in a variety of hands-on activities is paramount to promoting proper hand development. Activities like drawing, painting, sculpting, and playing musical instruments are excellent examples of how to stimulate hand-eye coordination. These activities encourage children to manipulate tools, explore different textures, and develop a sense of control over their movements.
Furthermore, activities like puzzles, lacing cards, and bead stringing are beneficial in developing fine motor skills and hand dexterity. These activities require precision and concentration, which are essential for cognitive development and overall well-being.
Importance of Sensory Exploration
Sensory exploration plays a vital role in stimulating hand development. Allowing children to explore different textures, weights, and shapes through play can significantly enhance their hand-eye coordination and fine motor skills. Experiencing various tactile sensations helps children understand the properties of objects and build a stronger connection between their hands and the world around them.
Providing a variety of sensory materials, such as different types of clay, textured fabrics, and items with varying weights, can foster exploration and creativity. This allows children to engage in hands-on learning experiences that stimulate their senses and promote a deeper understanding of the world around them.
The Role of Play in Hand Development
Play is an essential component in promoting hand development. Through play, children are naturally encouraged to explore and experiment with various objects and movements, leading to the development of their fine motor skills. Play-based learning activities are often more engaging and effective in helping children learn and develop. Structured play activities, such as building towers with blocks or creating art projects, provide a controlled environment for children to refine their hand movements.
Free play, however, is also vital. Unstructured play allows children to explore and discover their own interests and develop their creativity. This type of play often involves more complex hand movements and promotes problem-solving skills, which are crucial for overall development.