Elite Strategies for Enhancing Arm Joint Recovery
Pain Management Strategies
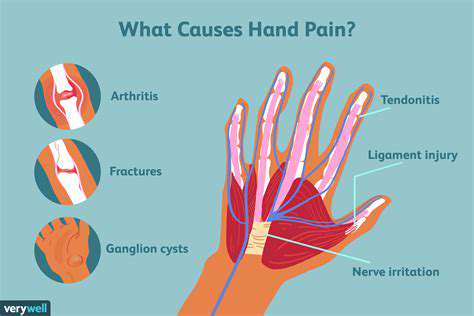
Effective pain management remains the cornerstone of post-surgical or injury recovery. Clinicians must balance pharmaceutical interventions with holistic approaches to achieve optimal results. While opioids serve a purpose for acute pain, their limitations and risks necessitate cautious prescribing. Many rehabilitation specialists now favor NSAIDs as first-line options, particularly when combined with innovative delivery systems like PCA pumps that empower patients in their own care journey.
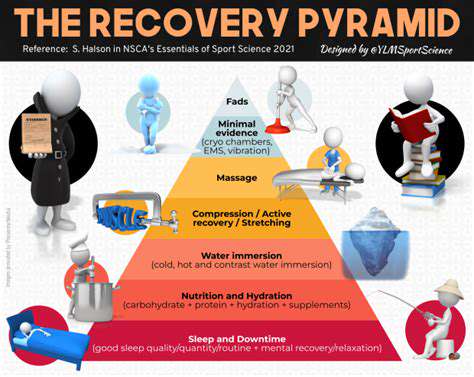
Beyond medication, therapeutic modalities show remarkable efficacy. The strategic application of thermal therapies - alternating between ice packs and heating pads - can dramatically reduce swelling while improving circulation. Manual therapies including myofascial release and trigger point work often yield better outcomes than medication alone, especially when initiated early in the recovery timeline.
Wound Care and Infection Prevention
Modern wound care protocols emphasize a dynamic approach rather than rigid routines. The concept of moist wound healing has revolutionized recovery times, with advanced hydrogel dressings and negative pressure therapy demonstrating particular effectiveness. Clinical teams must remain vigilant for subtle infection indicators - increased tenderness or changes in wound odor often precede visible symptoms.
Emerging technologies like smart dressings with pH sensors provide real-time infection monitoring, allowing for preemptive intervention. Proper wound care extends beyond physical treatment to patient education, ensuring individuals understand warning signs and proper hygiene practices during the vulnerable healing period.
Monitoring Vital Signs and Physiological Parameters
Contemporary monitoring extends beyond traditional vital signs to include sophisticated biomarkers. Capnography provides continuous respiratory monitoring, while advanced hemodynamic parameters offer deeper insights into circulatory status. The integration of wearable technology allows for 24/7 remote patient monitoring, enabling clinicians to detect concerning trends before they manifest as overt complications.
Fluid balance monitoring has evolved with the advent of non-invasive technologies like bioimpedance analysis. These innovations permit more precise management of hydration status, particularly crucial for patients with cardiovascular comorbidities or renal impairment.
Early Mobility and Physical Therapy
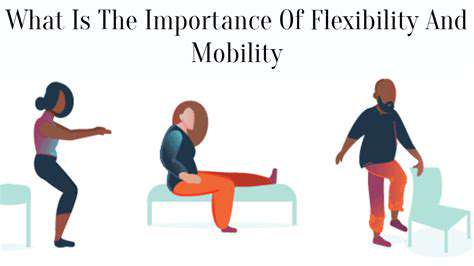
The paradigm has shifted from prolonged bed rest to immediate mobilization when medically appropriate. Early ambulation protocols now begin in some cases within hours post-procedure, utilizing specialized equipment like overhead track systems for safe patient movement. Rehabilitation specialists emphasize functional movement patterns over isolated exercises, accelerating return to daily activities.
Nutritional Support and Hydration
Post-traumatic metabolic demands require careful nutritional planning. Current protocols emphasize targeted amino acid supplementation, particularly leucine, to counteract muscle catabolism. Micronutrient optimization - especially vitamins C, D, and zinc - significantly impacts collagen synthesis and immune function. Hydration strategies now incorporate electrolyte-balanced formulas rather than plain water to better support cellular recovery.
Managing Post-Surgical/Injury Pain and Discomfort
Multimodal analgesia represents the gold standard, combining pharmacological agents with advanced interventional techniques. Peripheral nerve blocks and continuous catheter infusions provide superior pain control while minimizing systemic side effects. Cognitive-behavioral approaches teach patients pain coping mechanisms, reducing reliance on medication and improving long-term outcomes.
Psychological Support and Emotional Well-being
The biopsychosocial model recognizes emotional health as integral to physical recovery. Mindfulness-based stress reduction programs demonstrate particular efficacy in managing post-procedural anxiety. Peer support networks provide validation and practical coping strategies, while structured goal-setting helps maintain motivation during challenging rehabilitation phases.
Phase 2: Gradual Restoration of Strength and Function

Phase 2: Initial Assessment and Planning
This transitional phase begins with comprehensive functional testing beyond standard range-of-motion measurements. Computerized motion analysis provides objective data to guide personalized rehabilitation plans. The assessment process now incorporates patient-specific goals, whether returning to athletic competition or regaining independence with activities of daily living.
Progressive loading strategies form the foundation of modern rehabilitation protocols. Clinicians utilize isokinetic testing to establish precise baselines, allowing for measurable progress tracking. The integration of virtual reality systems enhances patient engagement during repetitive therapeutic exercises, improving compliance and outcomes.
Phase 2: Temporary Repairs and Stabilization
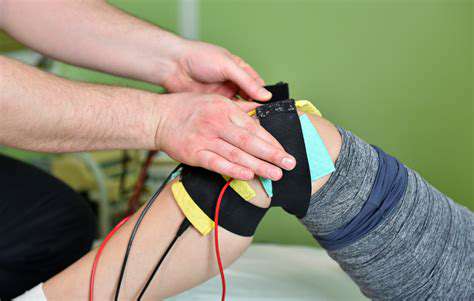
Contemporary bracing technology offers dynamic support that adapts to healing tissues. Smart braces with embedded sensors provide real-time feedback on joint loading and movement patterns. Biological scaffolding techniques accelerate tissue regeneration, particularly for tendon and ligament injuries where traditional healing proves slow.
The concept of relative rest has replaced complete immobilization in most rehabilitation scenarios. Controlled motion stimulates collagen alignment while preventing the deleterious effects of prolonged disuse. This approach requires careful monitoring to ensure tissues aren't overloaded during the vulnerable healing phase.
Phase 2: Detailed Restoration and Reconstruction
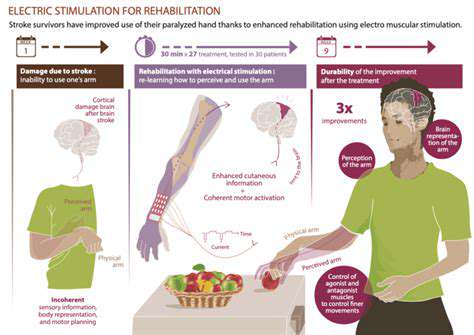
Advanced rehabilitation now incorporates neuromuscular re-education as a core component. Proprioceptive training using unstable surfaces rebuilds the neural connections disrupted by injury. Eccentric loading protocols demonstrate particular effectiveness for tendinopathies, remodeling tissue architecture to withstand future demands.
The final rehabilitation stage focuses on sport- or activity-specific drills. Plyometric progression protocols rebuild explosive power while ensuring proper movement mechanics to prevent reinjury. Return-to-play decisions now incorporate objective metrics rather than subjective assessments, reducing the risk of premature activity resumption.