How to Manage Hand Pain in the Digital Age
Repetitive strain injuries (RSIs) are a significant health concern affecting a growing number of individuals across various industries. These injuries, often caused by prolonged and repetitive motions, can lead to debilitating pain and functional limitations, impacting work productivity and overall well-being. Understanding the causes and preventative measures is crucial for mitigating the risk of these injuries.
The prevalence of RSIs is increasing due to the rise of technology-driven work environments and the increasing demands placed on individuals to perform repetitive tasks efficiently. The nature of modern workplaces, often requiring extended periods of computer use and data entry, contributes significantly to the development of these injuries.
Understanding the Mechanics of RSI
RSIs develop gradually, often starting with mild discomfort that's easily dismissed. However, if left unaddressed, these conditions can escalate to chronic pain, inflammation, and nerve damage. The repetitive nature of the movements places excessive stress on tendons, muscles, and nerves, leading to micro-tears and inflammation.
Common Types of Repetitive Strain Injuries
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common type of RSI, characterized by numbness, tingling, and pain in the hand and wrist. It typically results from the compression of the median nerve in the carpal tunnel. Other common types include tendonitis (inflammation of tendons), epicondylitis (inflammation of the tendons around the elbow), and trigger finger.
These injuries can manifest in various parts of the body, affecting the wrists, hands, elbows, shoulders, and neck. The specific location and symptoms depend on the repetitive motions involved.
Risk Factors and Prevention Strategies
Several factors contribute to the risk of developing RSIs, including improper posture, inadequate workstation setup, and insufficient breaks during work. Ergonomic considerations play a vital role in preventing these injuries, highlighting the importance of a well-designed workspace.
Regular breaks, stretching exercises, and proper posture are essential for minimizing strain and preventing the development of RSIs. Maintaining good posture and taking regular breaks can significantly reduce the risk of developing these injuries.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Early diagnosis of RSIs is crucial for effective treatment. Physicians use a combination of physical examinations, medical history reviews, and diagnostic tests to identify the specific cause and extent of the injury.
Treatment options vary depending on the severity and type of RSI. They may include physiotherapy, occupational therapy, pain medication, and in some cases, surgery. Proper management and adherence to treatment plans are essential for successful recovery.
Long-Term Impact and Recovery
The long-term impact of RSIs can be significant, affecting an individual's ability to perform daily activities and participate in work or social life. Prolonged pain and discomfort can lead to reduced productivity and emotional distress.
Recovering from an RSI requires patience, dedication, and adherence to a prescribed treatment plan. Complete recovery time can vary significantly, depending on the severity of the injury and the individual's response to treatment.
Ergonomic Adjustments: Optimizing Your Workspace for Comfort
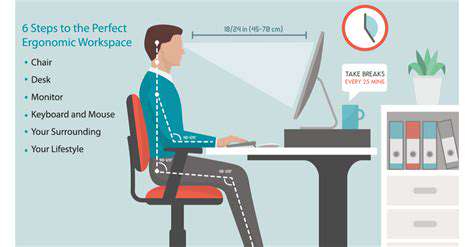
Adjusting Your Workstation
A properly adjusted workstation is crucial for preventing musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs). Ensure your chair provides adequate lumbar support, promoting a healthy spinal alignment. This support is vital for maintaining a neutral spine throughout the workday. Incorrect posture can lead to chronic pain and discomfort, impacting both your physical and mental well-being. Properly positioned monitors, keyboards, and mouses are also essential for ergonomic comfort.
Consider using a monitor stand to elevate your screen to eye level. This reduces strain on your neck and eyes. A good keyboard and mouse should be positioned so your wrists remain straight and aligned with your forearms. Poorly positioned peripherals can lead to repetitive strain injuries.
Keyboard and Mouse Placement
Your keyboard should be positioned directly in front of you, with your forearms resting comfortably alongside your body. Avoid awkward angles or reaching, as this can lead to muscle fatigue and strain. Ensure the keyboard is at a height that allows your wrists to remain straight when typing. A proper wrist rest can also help to alleviate pressure and strain on the wrists.
Your mouse should be within easy reach, allowing for smooth and natural movements. Positioning the mouse too far away can lead to unnecessary wrist and arm movements, increasing the risk of injury. A comfortable and ergonomic mouse can significantly improve your work experience.
Monitor Placement and Viewing Angle
Proper monitor placement is essential for eye and neck health. Place your monitor at arm's length, ensuring that the top of the screen is at or slightly below eye level. This reduces the need for excessive head tilting, and promotes a more relaxed posture. The distance should be sufficient to avoid eye strain and headaches caused by close-up work.
Make sure the monitor is positioned at an optimal viewing angle. An ideal angle for visual comfort is approximately 15-20 degrees below eye level. Avoid glare and reflections from windows or other light sources that can cause eye strain.
Chair Selection and Adjustments
Choosing the right chair is paramount for preventing back pain and discomfort. Look for chairs with adjustable lumbar support, seat height, and armrests. Ensure the chair provides adequate support for your lower back and promotes good posture throughout the day. A supportive chair can significantly reduce the risk of developing back problems.
Adjust the seat height so that your feet are flat on the floor and your knees are bent at a 90-degree angle. Proper seat height is vital for maintaining a neutral spine position. Adjust the backrest to support your lower back and ensure it's firm enough to maintain proper spinal alignment.
Taking Regular Breaks and Movement
Taking short, regular breaks is crucial for maintaining focus and preventing fatigue. Every 30-60 minutes, take a 5-10 minute break to stand up, stretch, and move around. This helps to improve blood circulation, reduce muscle tension, and prevent stiffness. These breaks can drastically improve your overall well-being.
Regular movement during your workday will significantly reduce the risk of developing MSDs. In addition to short breaks, incorporate more movement into your daily routine. Consider standing up while making phone calls or taking breaks. Walking to a colleague's desk instead of emailing is another great option.
Ergonomic Accessories
Invest in ergonomic accessories to further enhance your workspace. These can include wrist rests, keyboard trays, and ergonomic mice. These accessories can significantly improve comfort and reduce strain on your body. Consider a standing desk or a sit-stand desk to allow for a more dynamic posture.
Using appropriate accessories can make a huge difference in your work experience. They can help to avoid pain and discomfort and prevent injuries. These accessories can contribute to a healthier and more productive work environment.
Seeking Professional Help: When to Consult a Doctor
Recognizing the Signs of a Problem
Experiencing persistent hand pain can significantly impact daily life, affecting everything from simple tasks like gripping objects to more complex activities. Understanding the specific nature of your hand pain is crucial in determining the appropriate course of action. Is the pain sharp, dull, throbbing, or aching? Does it come and go, or is it constant? Where exactly is the pain located in your hand – the palm, fingers, wrist, or elsewhere? These details can provide valuable clues to the potential cause and help you communicate effectively with a healthcare professional.
Paying attention to the triggers of your pain is also important. Do certain activities or movements exacerbate the discomfort? Have you recently injured your hand, or is the pain a gradual onset? Identifying these patterns can help you pinpoint the source of the issue, whether it's a simple strain, a more serious condition, or even a symptom of an underlying health problem. Detailed descriptions of the pain, along with any relevant medical history, will be essential for your doctor to make an accurate diagnosis.
Determining the Severity and Potential Causes
While some hand pain resolves on its own with rest and home remedies, persistent or severe pain warrants professional medical attention. Symptoms like swelling, redness, or a noticeable change in the shape or function of your hand should never be ignored. These could indicate a more serious condition requiring prompt diagnosis and treatment. It's also important to consider any existing medical conditions you might have, as these could contribute to or exacerbate hand pain.
Potential causes of hand pain are diverse and range from simple injuries like sprains and strains to more complex conditions such as arthritis, carpal tunnel syndrome, or nerve damage. Underlying medical issues like diabetes or rheumatoid arthritis can also manifest as hand pain. Don't hesitate to seek medical advice if you suspect a serious condition or if your pain is significantly affecting your ability to perform daily tasks. Early intervention can often lead to more effective and timely treatment.
Understanding the Doctor's Role and Expectations
A healthcare professional plays a crucial role in diagnosing and managing hand pain. They will likely conduct a thorough physical examination, asking about your medical history, symptoms, and any recent injuries or illnesses. This detailed assessment helps them rule out potential causes and arrive at a proper diagnosis. Be prepared to provide specific details about the pain, including its location, intensity, and duration, as well as any factors that seem to trigger or alleviate it.
Open communication is essential throughout the consultation process. Don't hesitate to ask questions, clarify any concerns, or express any anxieties you may have regarding your hand pain. Your doctor will guide you through the diagnostic process, and together, you can develop a treatment plan that addresses your specific needs and goals. Trusting the expertise of your healthcare professional is vital in ensuring you receive the most appropriate care.
Exploring Potential Treatments and Management Strategies
Treatment options for hand pain are varied and depend on the underlying cause. This may include conservative approaches such as rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), as well as over-the-counter pain relievers. In some cases, physical therapy or occupational therapy may be recommended to improve hand function and reduce pain. For more severe or persistent conditions, your doctor might suggest other interventions such as medication, injections, or even surgery.
Managing hand pain effectively often involves a combination of strategies. This could include lifestyle modifications, such as adapting work or household tasks to reduce strain on the affected hand, and incorporating regular exercises to maintain flexibility and strength. Following your doctor's recommendations carefully and diligently will significantly enhance your recovery process and help you regain optimal hand function. Remember, consistent effort and adherence to the prescribed treatment plan are key to successful pain management.