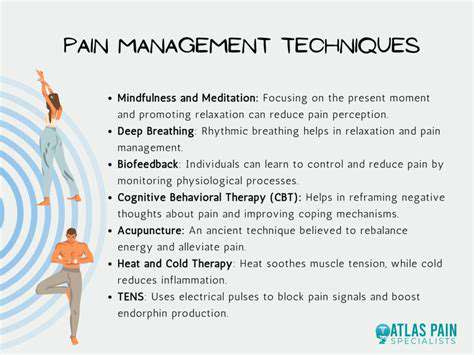
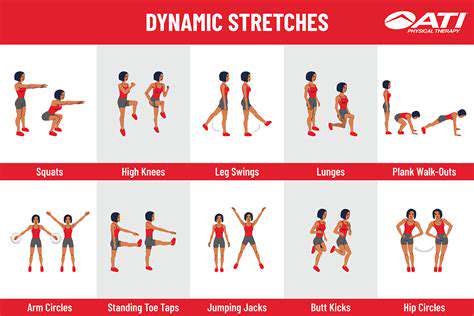
This website is dedicated to all aspects of hand and arm health. We cover the latest surgical trends, such as revolutionary techniques in hand surgery and advancements in robotic arm prosthetics. There are detailed guides on injury prevention, like how to avoid wrist injuries and repetitive strain injuries. We also offer a plethora of exercises for different groups - from athletes looking to optimize hand strength for sports to seniors aiming to improve hand mobility. Our content includes in - depth looks at hand and arm anatomy, the role of nutrition in hand health, and how to manage common conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome and hand arthritis. Whether you're seeking information for personal health or professional knowledge, our blog is a reliable source for hand and arm health insights.
Exploring the Connection Between Diet and Joint Health
Jul 08, 2025
How to Improve Your Hand Speed for Musical Performance
Jul 08, 2025
Advanced Care Protocols for Hand Fracture Recovery
Jul 07, 2025
How to Develop Fine Motor Skills Through Art
Jul 07, 2025
Next Level Workouts for Robust Hand Function
Jul 07, 2025
Dynamic Workouts for Robust Arm Muscle Recovery
Jul 06, 2025
Innovative Approaches to Treating Hand Nerve Damage
Jul 06, 2025
Finger Artistry: Exercises to Enhance Dexterity
Jul 06, 2025
Next Level Insights into Wrist Joint Mechanics
Jul 05, 2025
Techniques for Reducing Chronic Hand Inflammation
Jul 05, 2025
Cutting Edge Techniques in Tendon Repair Surgery
Jul 05, 2025
The Latest Trends in Hand Care and Beauty Products
Jul 05, 2025
The Role of Physical Therapy in Hand Mobility Restoration
Jul 04, 2025
How to Recover from a Hand Tendon Injury Effectively
Jul 04, 2025
How to Develop a Comprehensive Hand Exercise Routine
Jul 04, 2025
Exploring the Art of Hand Lettering and Calligraphy
Jul 04, 2025
Strategies for Preventing Hand and Wrist Injuries in Sports
Jul 04, 2025
Cutting Edge Workouts for Enhanced Wrist Mobility
Jul 03, 2025
Mastering Hand Strength: Essential Workouts for Grip Power
Jul 03, 2025