Steps to Reduce Arm Fatigue Effectively
Understanding Arm Fatigue
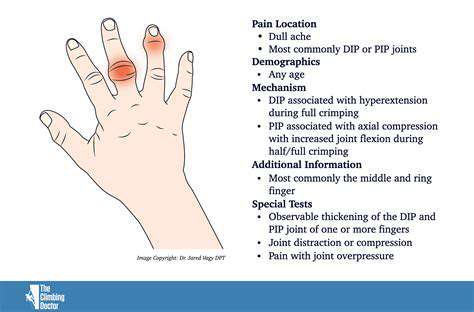
Arm fatigue, a common ailment in today's digital age, often results from extended periods of inactivity and repeated motions. Symptoms may include discomfort, pain, or tingling sensations in the arms, hands, and shoulders. Identifying the underlying causes is essential for developing practical solutions to minimize these problems. Incorrect posture and poorly arranged work areas are major factors, emphasizing the need for thoughtful workspace design to maintain arm health.
Multiple elements, such as job requirements, equipment choices, and individual physical characteristics, can affect the onset of arm fatigue. Recognizing these personal differences helps in customizing ergonomic approaches to address specific situations and avoid worsening conditions.
Proper Posture and Workstation Setup
Achieving and maintaining a neutral posture is vital for reducing arm strain. Ensure your shoulders remain relaxed, your spine aligned, and your wrists in a natural position, free from unnecessary bending. The right workstation configuration plays a key role. Your chair should offer proper lower back support, your screen positioned at eye level, and input devices placed within easy reach to lessen stress on your arms and hands.
The Impact of Repetitive Tasks
Repeated actions, like typing or operating machinery, can lead to significant arm fatigue. Continuous motion places excessive demand on muscles and tendons, resulting in discomfort and potential harm. Awareness of how these tasks influence body mechanics is crucial for implementing effective adjustments. Specialized equipment, such as ergonomically designed keyboards or supportive pads, can help mitigate the effects of these repetitive activities.
Choosing the Right Tools and Equipment
Selecting suitable tools can dramatically decrease arm fatigue. Devices designed with ergonomics in mind encourage natural hand positions, reducing unnecessary pressure. Chairs and monitors with adjustable features allow for personalized configurations to meet individual requirements. Additional aids, like adaptable workstations and specialized handles, can further minimize arm strain.
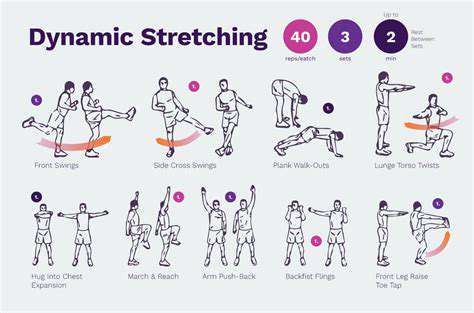
Taking Breaks and Stretching
Frequent pauses are necessary to prevent arm fatigue. Even brief intervals to stand, stretch, or walk can relieve muscle tension significantly. Simple stretches targeting the arms, hands, and shoulders enhance flexibility and prevent stiffness. Integrating these short breaks into daily routines improves comfort and lowers the risk of persistent discomfort.

Lifestyle Adjustments for Long-Term Arm Fatigue Relief

Prioritizing Physical Activity
Regular exercise is fundamental for sustained well-being. Participating in enjoyable activities, like walking, swimming, or cycling, enhances both physical and mental health. Strive for at least 150 minutes of moderate or 75 minutes of intense aerobic activity weekly, supplemented by strength training twice a week. Simple changes, such as choosing stairs over elevators or walking short distances, foster long-term consistency. This steady approach is crucial for lasting health benefits.
Maintaining regular physical activity is essential for enduring health improvements. Minor adjustments, like brief walks during breaks, accumulate substantial benefits over time. Gradual integration into daily life promotes lasting adherence. Focus on activities you find enjoyable rather than those perceived as obligations, as this sustains motivation and habit formation.
Mindfulness and Stress Management
Effective stress management is key to long-term health. Persistent stress affects both physical and mental well-being. Techniques like meditation or controlled breathing can help manage stress and induce relaxation. These methods build resilience and improve stress response capabilities.
Developing healthy stress-relief habits is crucial for sustained well-being. Stress impacts health in multiple ways, making relaxation practices like yoga or progressive muscle relaxation valuable tools. Regular use of these techniques enhances stress management skills.
Stress relief methods vary by individual. Explore different approaches to find what suits you best. Whether through outdoor activities, music, or hobbies, identify what brings relaxation. Consistent practice strengthens coping mechanisms for long-term stress management.
Dietary Adjustments for Lasting Well-being
A nutritious, balanced diet underpins long-term health. Emphasize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while reducing processed foods, sugary beverages, and unhealthy fats. Whole foods provide essential nutrients and stable energy levels.
Incremental dietary changes are more sustainable than radical shifts. Swapping sugary drinks for water, choosing whole grains, and increasing vegetable intake are simple yet effective steps. These adjustments yield significant health benefits over time.
Prioritizing nutrient-rich foods and minimizing processed items is fundamental to long-term health. Nutrition supports bodily functions and energy maintenance. A focus on whole foods enhances overall function, leading to improved vitality and well-being. This commitment fosters a higher quality of life.