Workouts for Superior Hand Performance
Introduction to Hand-Specific Training
Understanding the Importance of Hand-Specific Training
Training focused on the hands is essential for achieving optimal performance, going beyond general strength development. This method zeroes in on the small muscle groups and delicate movements that standard exercises often overlook. By targeting these frequently ignored muscles, people can dramatically enhance their grip, object manipulation, and fine motor abilities. The wrists, forearms, and hands become better equipped for tasks requiring precision, stamina, or brute force.
Benefits of Incorporating Hand Training into Your Routine
Adding hand-focused exercises to your fitness routine provides numerous advantages. Enhanced grip strength leads to better performance in sports, daily activities, and professional tasks. This specialized training also sharpens dexterity, allowing for more accurate and controlled motion. Additionally, it fortifies the supportive tissues in the hands, wrists, and forearms, lowering the likelihood of injuries like strains. Ultimately, consistent hand training results in a more durable and versatile musculoskeletal framework.
Common Hand Problems and How Training Can Help
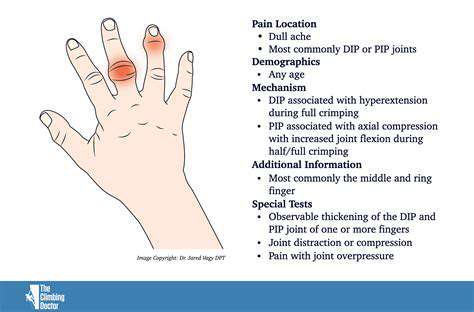
Various ailments, including carpal tunnel syndrome, tendinitis, and arthritis, can impair hand functionality. Hand-specific exercises serve as an effective management tool for these conditions. Strengthening the adjacent muscles through targeted workouts can relieve pressure on nerves and tendons, potentially reducing pain. Moreover, maintaining robust and flexible hand structures proactively prevents such issues from developing. Prioritizing hand health early builds resistance against future complications.
Key Exercises for Developing Grip Strength
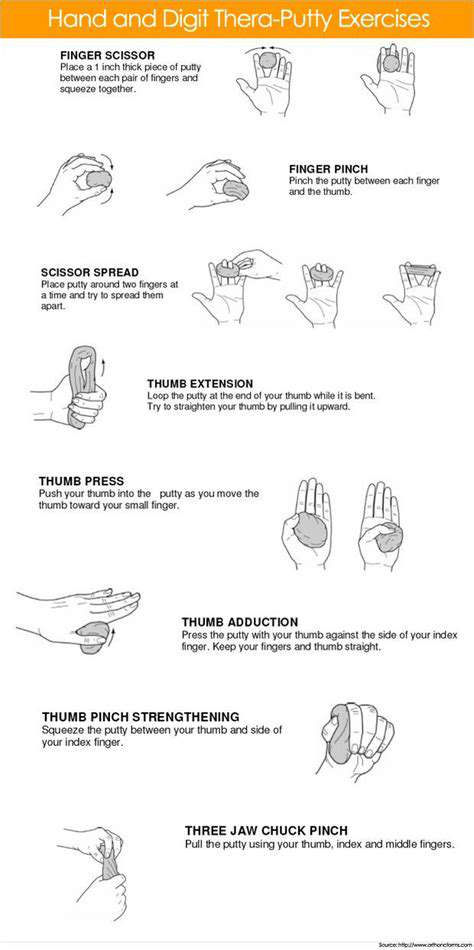
A powerful grip forms the foundation of hand performance. Effective exercises include resistance band wrist curls, finger extensions, and weighted handgrip squeezes. Progressively increasing resistance while incorporating these movements builds both strength and endurance. The aim isn't just to handle heavier weights but also to refine the speed and accuracy of hand motions.
Improving Dexterity and Fine Motor Skills
Hand training isn't solely about strength—it significantly enhances dexterity and fine motor control. Activities like playing instruments, crafting, or handling small tools demand precise coordination. Exercises that emphasize finger independence, such as manipulating small objects or practicing detailed writing, refine these skills. Regular practice hones control, enabling more nuanced and efficient hand movements.
Warm-up and Cool-down Procedures for Hand Workouts
Like any workout, proper warm-up and cool-down routines are critical for hand training. Warming up prepares muscles and tendons for exertion, minimizing injury risk. Gentle wrist rotations, finger stretches, and light squeezes are ideal. Cool-down exercises facilitate recovery by enhancing blood circulation and preventing stiffness. These should be performed slowly, focusing on maintaining flexibility and range of motion. Proper warm-up and cool-down practices are indispensable for optimal results and injury prevention.
Endurance Training for Sustained Hand Performance

Understanding the Benefits of Endurance Training
Endurance activities like running, swimming, and cycling enhance cardiovascular health and overall fitness. These exercises strengthen the heart, improving its efficiency in pumping blood. Regular endurance workouts can lower blood pressure and cholesterol, promoting a healthier cardiovascular system. They also boost oxygen utilization, increasing stamina during prolonged activity.
Beyond heart health, endurance training aids weight management by burning calories and revving up metabolism. Maintaining a consistent routine helps prevent obesity-related illnesses. Additionally, endurance exercise significantly benefits mental health, alleviating stress, anxiety, and depressive symptoms. This stems from endorphin release during physical activity, which elevates mood.
Key Considerations for Effective Endurance Training
To reap maximum benefits, tailor your endurance program to individual needs and objectives. Account for current fitness levels, health conditions, and desired outcomes. Proper warm-ups and cool-downs are non-negotiable for injury prevention and peak performance.
Progressive overload is fundamental in endurance training. Gradually increasing workout intensity, duration, or frequency allows the body to adapt and enhance endurance. This measured progression prevents overtraining, which can cause injuries and stall progress. Paying attention to bodily signals helps avoid strain and ensures safe, effective training.
Selecting enjoyable endurance activities sustains motivation and adherence. Mixing activities like running, swimming, and cycling combats monotony and offers comprehensive training.
Nutrition and hydration are pivotal for endurance training success. A balanced diet with fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and complex carbs fuels performance. Hydration during extended workouts maintains electrolyte balance and prevents dehydration.