Protocols for Maintaining Wrist Function
Secondary factors like poor posture and inadequate breaks compound these risks, potentially leading to chronic musculoskeletal problems if unaddressed.
Selecting Appropriate Wrist Supports
The market offers diverse support options from basic straps to rigid splints. Choice depends on activity type and duration - occasional typists might prefer lightweight options while industrial workers may require more substantial support. Proper fit proves equally important as the support type itself; ill-fitting devices can restrict natural movement and worsen existing issues.
Material breathability and adjustability features should guide selection, ensuring comfort during extended use without compromising effectiveness.
Optimal Keyboard and Mouse Positioning
Ideal workstation setup maintains neutral wrist alignment. Keyboards should sit directly before the user with elbows forming 90-degree angles. Forearms should parallel the floor, distributing weight evenly. Mice require close placement to prevent excessive reaching that strains tendons.
These adjustments, while simple, dramatically reduce cumulative stress that leads to conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome over time.
Incorporating Rest Periods and Stretches
Hourly five-minute breaks significantly reduce repetitive strain risks. During these pauses, gentle wrist exercises maintain circulation and flexibility:
- Flexion and extension movements
- Controlled rotation exercises
- Finger-to-palm stretches
Consistency with these routines prevents stiffness and maintains long-term wrist functionality.
Maintaining Proper Posture During Work
Whole-body alignment directly impacts wrist health. An upright spine position with shoulders relaxed prevents compensatory strain patterns. Work surfaces should accommodate natural arm positions without requiring awkward angles.
Seeking Professional Guidance
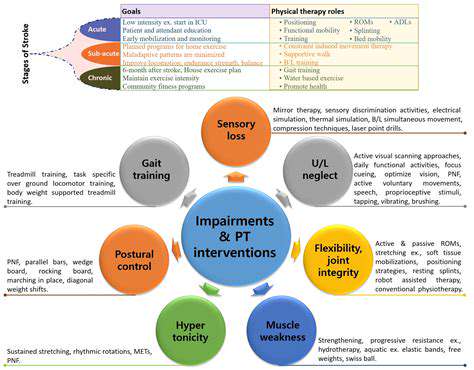
Persistent discomfort warrants medical consultation. Occupational therapists can assess workstation setups while physical therapists address underlying musculoskeletal issues. Early intervention prevents minor issues from becoming chronic conditions requiring extensive treatment.
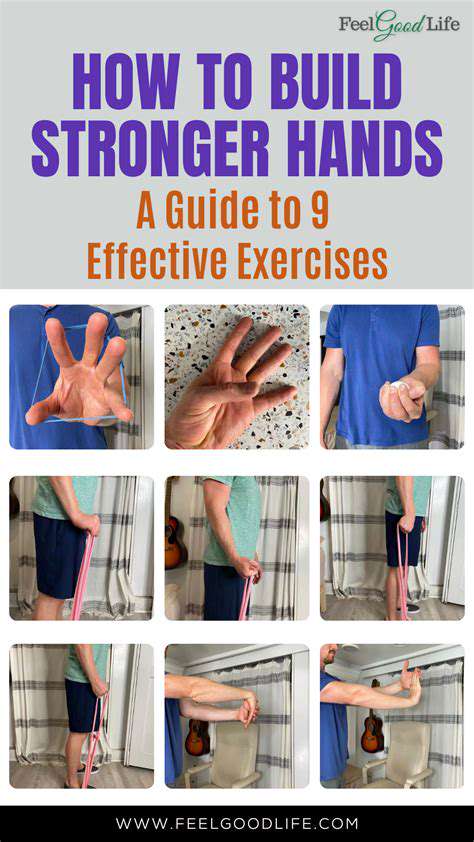
Effective Wrist Strengthening Exercises
Wrist Extensor Training
Extensor muscle development enhances pushing and gripping capabilities. Form supersedes intensity during these exercises - controlled motions with light weights yield better results than heavy, jerky movements. Resistance bands offer adjustable tension for progressive training.
Flexor Muscle Development
These muscles govern writing and grasping motions. Strengthening them improves stability for precision tasks. Three weekly sessions with proper recovery periods optimize results without overtraining risks.
Rotational Mobility Exercises
Forearm pronation and supination maintain full wrist mobility. Simple rotations with light implements preserve range of motion essential for tool use and sports activities.
Lateral Movement Training
Radial and ulnar deviation exercises strengthen side-to-side motion control. These often-neglected movements prove vital for tool manipulation and injury prevention.
Resistance Band Applications
Versatile bands accommodate various strength levels. Their portable nature enables office or travel workouts. Color-coded tension levels help users track progress systematically.
Light Weight Training
Dumbbells between 1-5 pounds allow focused muscle engagement. Slow, controlled lifts maximize effectiveness while minimizing joint stress.
Preparation and Recovery
Dynamic warm-ups increase blood flow before workouts. Post-session static stretches held for 30 seconds maintain flexibility and reduce soreness.
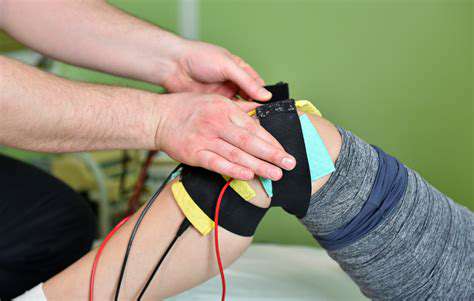
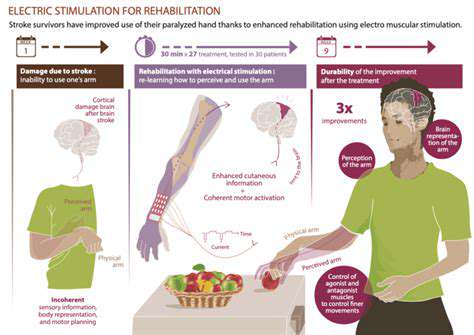
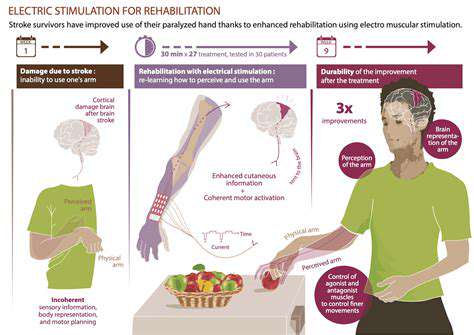
Managing Pain and Inflammation with Targeted Therapies
Inflammation Mechanisms
Chronic inflammation involves complex immune responses that perpetuate pain cycles. Different pain types (neuropathic vs. musculoskeletal) require distinct therapeutic approaches.
Modern Treatment Options
Current therapies target specific inflammatory mediators rather than broadly suppressing immune function. This precision reduces side effects while maintaining infection-fighting capacity.
Complementary Approaches
Anti-inflammatory diets rich in omega-3s complement medical treatments. Mindfulness practices and acupuncture modulate pain perception through neurological pathways.
Personalized Care Plans
Effective management considers individual pain thresholds, activity requirements, and treatment responses. Regular reassessment ensures continued appropriateness of therapeutic interventions.